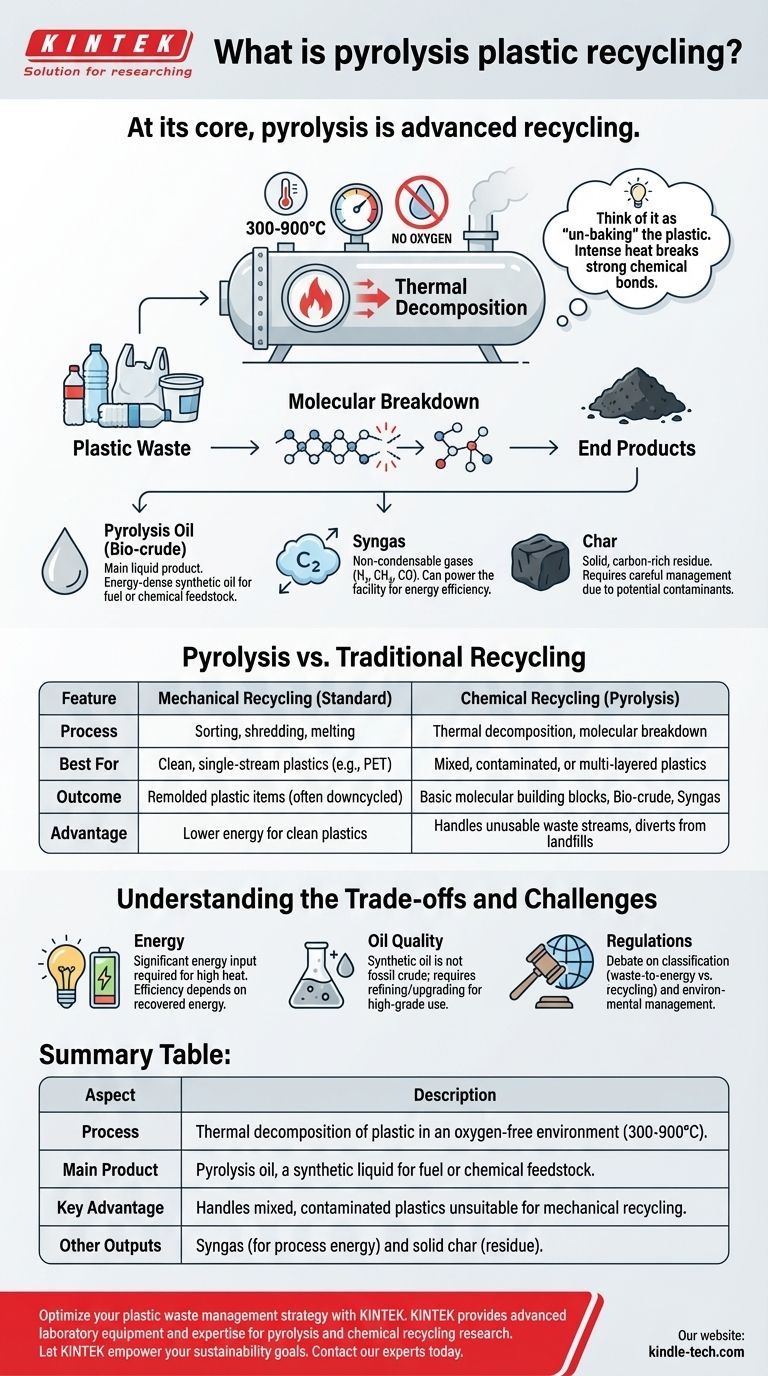
At its core, pyrolysis is a form of advanced recycling that uses high heat to break down plastic waste into more basic substances. The process works by subjecting plastics to extreme temperatures (typically 300-900°C) in an environment completely devoid of oxygen, which prevents them from burning and instead causes their long polymer chains to break apart into smaller molecules. The primary output is a synthetic liquid known as pyrolysis oil, which can be used as a fuel or a chemical feedstock.
While often called 'recycling,' it is more accurate to view pyrolysis as a chemical recovery process. It transforms complex plastic waste into simpler molecules for fuel or chemical production, representing a different pathway than traditional mechanical recycling which remolds plastic into new items.

How Pyrolysis Works: A Chemical Breakdown
Pyrolysis deconstructs plastic at a molecular level. Unlike melting plastic to reshape it, this process fundamentally alters its chemical structure.
The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition
Think of pyrolysis as "un-baking" the plastic. Intense heat provides the energy needed to snap the strong chemical bonds that hold long polymer chains together.
This decomposition breaks the complex, solid plastic down into a mixture of simpler, smaller molecules in liquid and gas forms.
The Importance of an Oxygen-Free Environment
The absence of oxygen is the critical factor that distinguishes pyrolysis from incineration (burning).
With oxygen, the plastic would simply combust, releasing its energy as heat and producing carbon dioxide, water, and ash. Without oxygen, the material breaks down into valuable chemical components instead of just being destroyed.
The End Products: Oil, Gas, and Char
The process doesn't just create one output. It yields a mix of three primary substances:
- Pyrolysis Oil (or Bio-crude): This is the main liquid product. It's an energy-dense synthetic oil that can be refined into fuel or used as a feedstock to create new chemicals and plastics.
- Syngas: A mixture of non-condensable gases (like hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide) that can be captured and used to power the pyrolysis facility itself, making the process more energy-efficient.
- Char: A solid, carbon-rich residue similar to charcoal. Its disposal or use must be carefully managed, as it can sometimes contain contaminants from the original plastic waste.
Pyrolysis vs. Traditional Recycling
Pyrolysis was developed to address the inherent limitations of conventional recycling methods.
Mechanical Recycling: The Standard Approach
Most recycling today is mechanical. This involves sorting, cleaning, shredding, and melting plastic to form pellets, which are then used to manufacture new products.
This method works well for clean, single-stream plastics like PET bottles. However, its effectiveness drops sharply with mixed, contaminated, or multi-layered plastics, often resulting in lower-quality "downcycled" materials.
Chemical Recycling: The Pyrolysis Advantage
Pyrolysis is a form of chemical recycling. Its major advantage is its ability to handle waste streams that are unsuitable for mechanical recycling.
Because it breaks plastics down to their basic molecular building blocks, it can process mixed plastic types, films, and even materials with some level of food or dirt contamination. This makes it a powerful tool for diverting a much wider range of plastic waste from landfills and incineration.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While promising, pyrolysis is not a perfect solution. It comes with a distinct set of technical and environmental considerations.
Energy Input vs. Energy Output
Reaching the high temperatures required for pyrolysis consumes a significant amount of energy. A facility's overall environmental benefit hinges on its efficiency and whether the energy recovered from the syngas and oil outweighs the energy required to run the process.
Quality and Use of Pyrolysis Oil
The synthetic oil produced is not equivalent to fossil crude oil. It is often acidic and can contain impurities that must be removed through a secondary upgrading or refining process before it can be used as a high-grade fuel or a feedstock for new plastics.
Regulatory and Environmental Debates
There is ongoing debate about how to classify pyrolysis. Some environmental groups argue that processes converting plastic to fuel should be considered waste-to-energy, not true recycling. The handling of hazardous byproducts and control of air emissions are also critical factors for ensuring the process is environmentally sound.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Pyrolysis is a specialized technology that excels in specific scenarios. Its value depends entirely on the problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is diverting hard-to-recycle plastics from landfills: Pyrolysis is one of the most promising technologies available, as it can handle mixed and contaminated waste that mechanical processes cannot.
- If your primary focus is creating a true closed-loop for new plastics: The pathway is more complex. The pyrolysis oil must undergo significant, energy-intensive upgrading to become a suitable feedstock for producing virgin-quality polymers again.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency with clean plastics: Mechanical recycling remains the superior choice for clean, sorted plastics like PET and HDPE, as it requires far less energy to re-melt than to deconstruct them chemically.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a powerful tool for managing complex plastic waste, but it complements, rather than replaces, traditional recycling methods.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Thermal decomposition of plastic in an oxygen-free environment (300-900°C). |
| Main Product | Pyrolysis oil, a synthetic liquid for fuel or chemical feedstock. |
| Key Advantage | Handles mixed, contaminated plastics unsuitable for mechanical recycling. |
| Other Outputs | Syngas (for process energy) and solid char (residue). |
Optimize your plastic waste management strategy with KINTEK.
As a specialist in advanced laboratory equipment, KINTEK provides the tools and expertise to support research and development in pyrolysis and chemical recycling processes. Whether you are exploring new feedstock formulations or optimizing reaction conditions, our reliable lab equipment is designed for precision and durability.
Let KINTEK empower your sustainability goals. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your recycling research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of quartz tubes in halide electrolyte synthesis? Ensure Purity & Precise Stoichiometry
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- Why are quartz tubes preferred for chromium powder combustion? Superior Heat Resistance & Optical Clarity



















