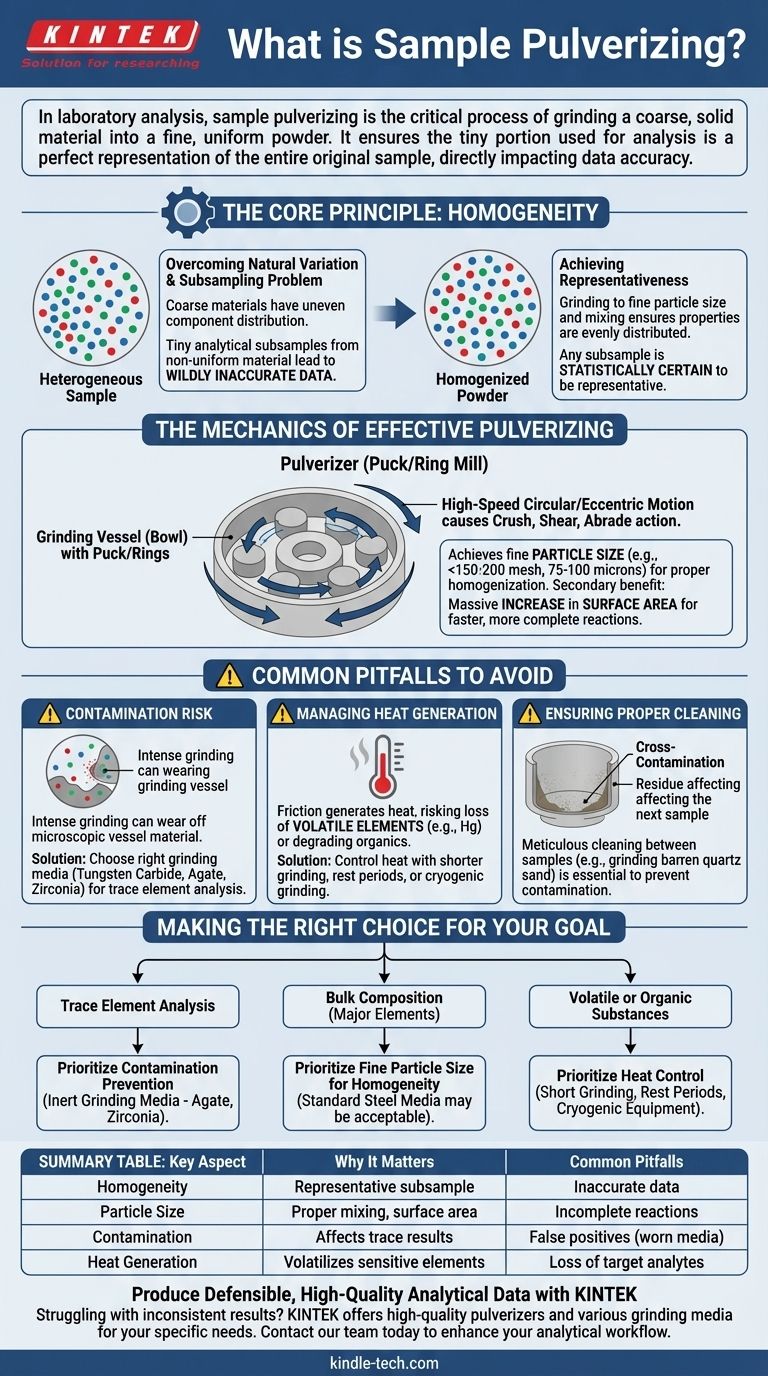
In laboratory analysis, sample pulverizing is the critical process of grinding or milling a coarse, solid material into a fine, uniform powder. This is a foundational step in sample preparation, designed to ensure that the tiny portion of material ultimately used for chemical or physical analysis is a perfect representation of the entire original sample. The quality of this single step directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of all subsequent experimental results.
The fundamental goal of pulverizing isn't just to make a sample smaller. It is to eliminate sampling error by creating a perfectly homogeneous material, ensuring that the microscopic portion you analyze accurately reflects the composition of the whole.
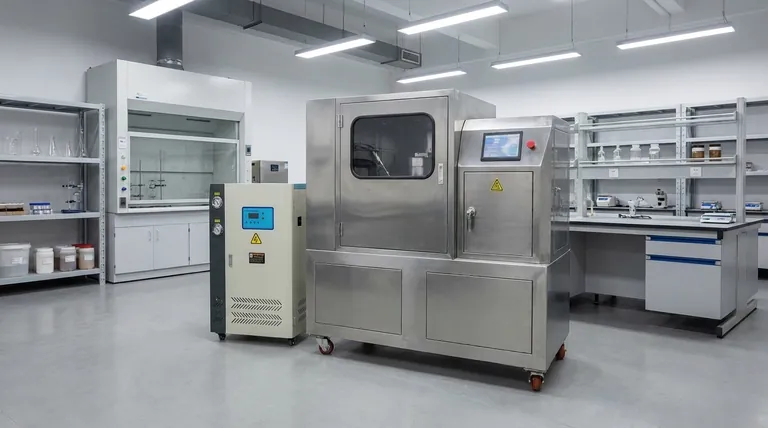

The Core Principle: Why Homogeneity is Non-Negotiable
The entire purpose of pulverizing hinges on one concept: homogeneity. Without it, analytical data is often meaningless.
Overcoming Natural Variation
Most raw samples, such as rock, soil, ore, or industrial materials, are inherently heterogeneous. This means their constituent components are unevenly distributed. A chunk from one side may have a higher concentration of a target element than a chunk from the other.
The Problem of Subsampling
Modern analytical instruments typically use a very small amount of material for each measurement—often just a few milligrams or less. If you take this tiny subsample from a coarse, non-uniform material, your results will be determined entirely by random chance. You might grab a particle rich in your target analyte, or one with none at all, leading to wildly inaccurate data.
Achieving Representativeness
Pulverizing solves this by grinding the entire sample down to a fine, consistent particle size and then mixing it thoroughly. This process ensures that the chemical and physical properties are evenly distributed throughout the powder. Consequently, any small subsample taken from this homogenized powder is statistically certain to be representative of the original bulk sample.
The Mechanics of Effective Pulverizing
While the concept is simple, the execution requires precision. The mechanics of the process are designed to achieve both fine particle size and uniformity without compromising the sample's integrity.
How a Pulverizer Works
Laboratory pulverizers, often called "puck mills" or "ring mills," use a grinding vessel (a bowl) containing a puck and/or rings. The vessel is subjected to high-speed circular or eccentric motion, causing the internal components to crush, shear, and abrade the sample material with immense force until it is reduced to a fine powder.
The Importance of Particle Size
The goal is typically to reduce the sample so it can pass through a specific mesh screen, such as a 150 or 200-mesh sieve (approximately 100 or 75 microns, respectively). Achieving a consistent, fine particle size is the primary mechanism for ensuring the sample can be properly homogenized.
Increasing Surface Area
A secondary benefit of pulverizing is a massive increase in the sample's surface area. This is crucial for analytical techniques like acid digestion or leaching, where a chemical reaction must occur on the particle surfaces. More surface area allows for faster, more complete, and more repeatable reactions.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Pulverizing is a powerful tool, but it also presents significant risks. An unmanaged process can introduce more error than it removes.
Contamination Risk
This is the most significant pitfall. The intense grinding action can cause microscopic amounts of the grinding vessel itself to wear off and mix into the sample. This is known as contamination. For example, analyzing for iron (Fe) in a sample ground in a standard hardened steel vessel will produce falsely high results.
Choosing the right grinding media is critical. Tungsten carbide, agate, or zirconia vessels are used when analyzing for elements present in steel or to minimize contamination in high-purity applications.
Managing Heat Generation
The friction involved in pulverizing generates significant heat. This can be a problem for samples containing volatile elements (like mercury) or heat-sensitive organic compounds, which can be driven off and lost before analysis.
Ensuring Proper Cleaning
Poor cleaning protocols lead to cross-contamination, where residue from a previous sample affects the next one. Pulverizer components must be meticulously cleaned between each sample, often by grinding a barren material like quartz sand to scrub the surfaces clean before introducing the next unknown sample.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal approach to pulverizing depends entirely on your final analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is trace element analysis: Prioritize preventing contamination by selecting inert grinding media (e.g., agate or zirconia) and implementing rigorous cleaning protocols between every sample.
- If your primary focus is bulk composition (major elements): Achieving a consistent, fine particle size is paramount for homogeneity; contamination from standard steel media may be acceptable if you are not analyzing for its constituent elements.
- If your primary focus is analyzing volatile or organic substances: You must control heat generation by using shorter grinding times, resting periods, or specialized cryogenic grinding equipment that uses liquid nitrogen.
Mastering sample pulverizing is the first and most important step toward producing defensible, high-quality analytical data.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters | Common Pitfalls |
|---|---|---|
| Homogeneity | Ensures subsample is representative of the whole bulk material. | Inaccurate data from non-uniform samples. |
| Particle Size | Crucial for proper mixing and increased surface area for reactions. | Incomplete digestion or leaching in analysis. |
| Contamination | Choice of grinding media (e.g., tungsten carbide, agate) affects trace element results. | False positives from worn grinding vessel material. |
| Heat Generation | Can volatilize sensitive elements or degrade organic compounds. | Loss of target analytes before measurement. |
Produce Defensible, High-Quality Analytical Data with KINTEK
Are you struggling with inconsistent results or contamination in your sample preparation? The foundation of reliable analysis starts with perfect pulverizing. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a range of pulverizers with various grinding media (like tungsten carbide, agate, and zirconia) to meet your specific analytical needs—whether for trace element analysis, bulk composition, or heat-sensitive substances.
Let our experts help you choose the right equipment to eliminate sampling error and ensure your data is accurate. Contact our team today to discuss your lab's pulverizing requirements and enhance your analytical workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Low-Temperature Water-Cooled Touchscreen Vibratory Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- Why are zirconia grinding balls preferred for BCZYYb electrolyte precursors? Achieving Pure Proton Conductivity
- What are the disadvantages of a colloidal mill? Key Limitations in Heat, Wear, and Particle Size Reduction
- What is comminution in sampling? The Key to Accurate & Representative Lab Results
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a sag mill? A Guide to Primary vs. Secondary Grinding
- Why is a hammer mill essential for processing raw materials in garden waste pelletization? Optimize Feedstock Sizing.
- What are the factors affecting the efficiency of milling operations? Optimize Your Grinding Process for Maximum Output
- What is the significance of advanced stirring and mixing systems? Maximize Carbon Capture and Reaction Efficiency
- Why use alternating cycles for carbide powder grinding? Key Benefits of Thermal Control in Milling



















