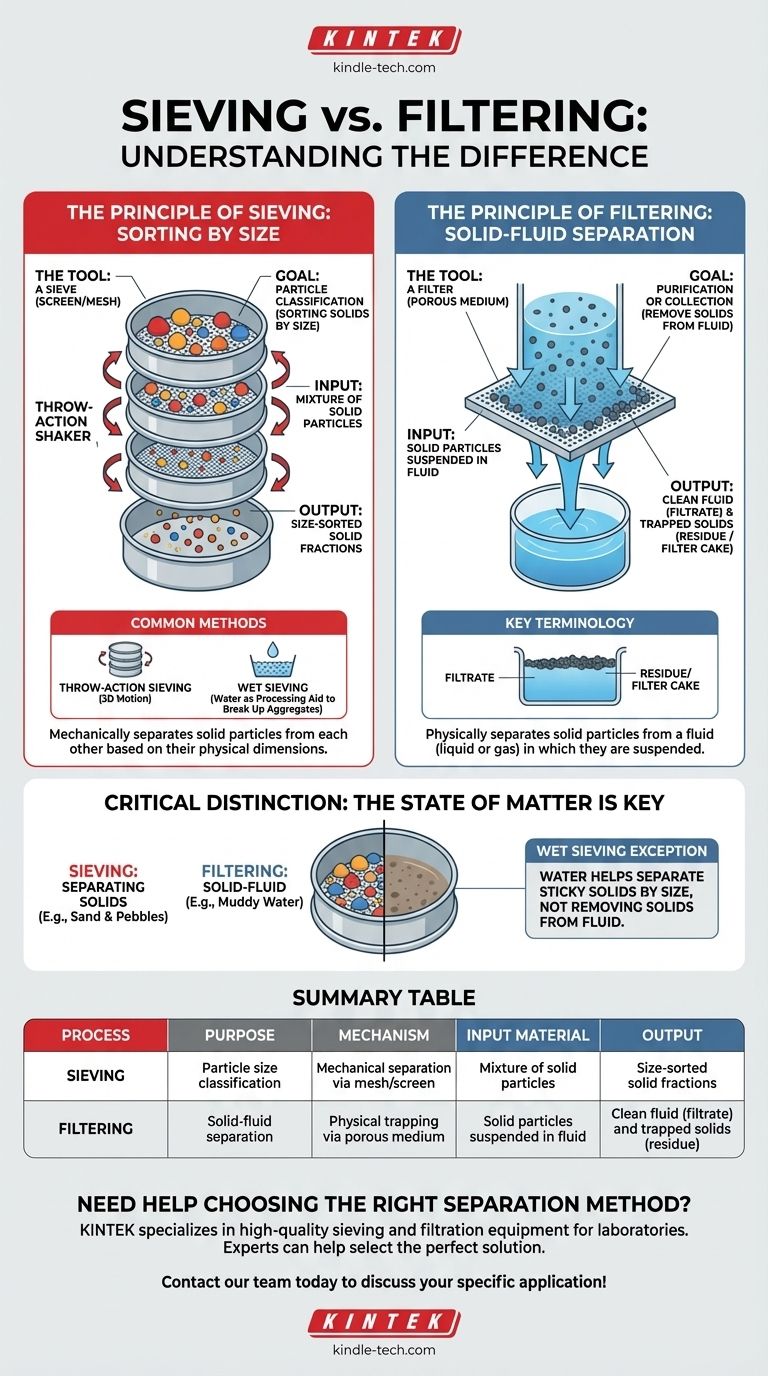
At its core, "sieving filtering" is not a single process. These are two distinct methods for separating materials. Sieving is a mechanical process that separates solid particles from each other based on their size, while filtering is a physical process that separates solid particles from a fluid (a liquid or a gas) in which they are suspended.
The fundamental difference lies in the materials you are trying to separate. Sieving sorts solids from other solids by size. Filtering removes solids from a surrounding fluid.
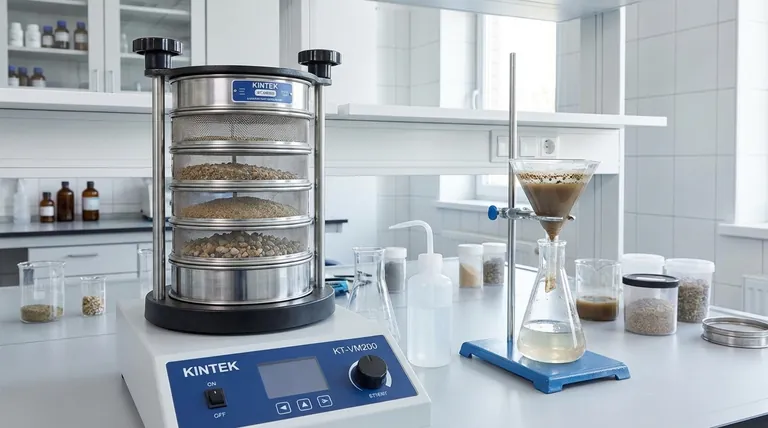

The Principle of Sieving: Sorting by Size
Sieving is a straightforward technique used almost exclusively for sorting solid particles into different size fractions.
The Tool: A Sieve
A sieve is simply a screen, mesh, or plate containing holes of a uniform size and shape.
The Goal: Particle Classification
The primary goal of sieving is to classify a mixture of solid particles. When a sample is placed on a sieve and agitated, particles smaller than the mesh openings fall through, while larger particles are retained on top.
Common Sieving Methods
Modern sieving often uses automated shakers for consistent results. Throw-action sieving, for example, uses an electromagnetic drive to create a three-dimensional motion, ensuring the entire sample is exposed to the sieve surface for efficient separation.
For particles that are clumped together or coated in fine dust, wet sieving is used. Water is added to the sample to help wash finer particles through the mesh and break up aggregates, ensuring an accurate size measurement.
The Principle of Filtering: Solid-Fluid Separation
Filtering is a more complex process designed to capture solid particulates from a fluid stream.
The Tool: A Filter
A filter is a porous medium that allows fluids to pass through but is fine enough to trap solid particles. This medium can be paper, cloth, a membrane, or a bed of granular material.
The Goal: Purification or Collection
The objective of filtering is to remove unwanted solids from a fluid (like purifying water) or to collect the solid product from a liquid (like harvesting crystals from a solution).
Key Filtering Terminology
The fluid that successfully passes through the filter is called the filtrate. The solid material that is trapped by the filter is known as the residue or filter cake.
Understanding the Critical Distinction
Confusing these two processes is common, but the distinction is essential for choosing the correct method.
The State of Matter is Key
Think of your starting material. If you have a dry pile of mixed gravel and sand, you need a sieve to separate them. If you have muddy water, you need a filter to trap the mud and let the clear water pass through.
Sieving is like a coin sorter separating dimes from quarters. Filtering is like a coffee maker holding back the solid grounds while allowing the liquid coffee to flow into the pot.
The Exception That Proves the Rule: Wet Sieving
Wet sieving can seem like a filter, but its purpose is different. You are not trying to separate the solid particles from the water; you are using the water as a processing aid.
The goal is still to sort particles by size. The water simply helps fine, sticky particles (like clay) wash through the sieve mesh instead of clumping to larger rocks. Once the process is done, the water is drained away, leaving behind size-sorted solids.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct process, you must first identify the components of your mixture and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is sorting a dry mixture of solids by size (e.g., sand and pebbles): Use sieving, which mechanically separates particles based on their physical dimensions.
- If your primary focus is removing solid particles from a liquid or gas (e.g., dust from air or sediment from water): Use filtering, which traps solids on a porous medium while allowing the fluid to pass through.
- If your primary focus is size-sorting fine particles that are clumped or coated (e.g., clay-covered aggregate): Use wet sieving, where a liquid aids the sieving process but the fundamental goal remains solid-from-solid size separation.
Understanding this core distinction between separating solids by size versus removing them from a fluid is the key to mastering material separation techniques.
Summary Table:
| Process | Purpose | Mechanism | Input Material | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sieving | Particle size classification | Mechanical separation via mesh/screen | Mixture of solid particles | Size-sorted solid fractions |
| Filtering | Solid-fluid separation | Physical trapping via porous medium | Solid particles suspended in fluid | Clean fluid (filtrate) and trapped solids (residue) |
Need help choosing the right separation method for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality sieving and filtration equipment for laboratories. Whether you're classifying particle sizes or purifying fluids, our experts can help you select the perfect solution to improve your process efficiency and accuracy. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy



















