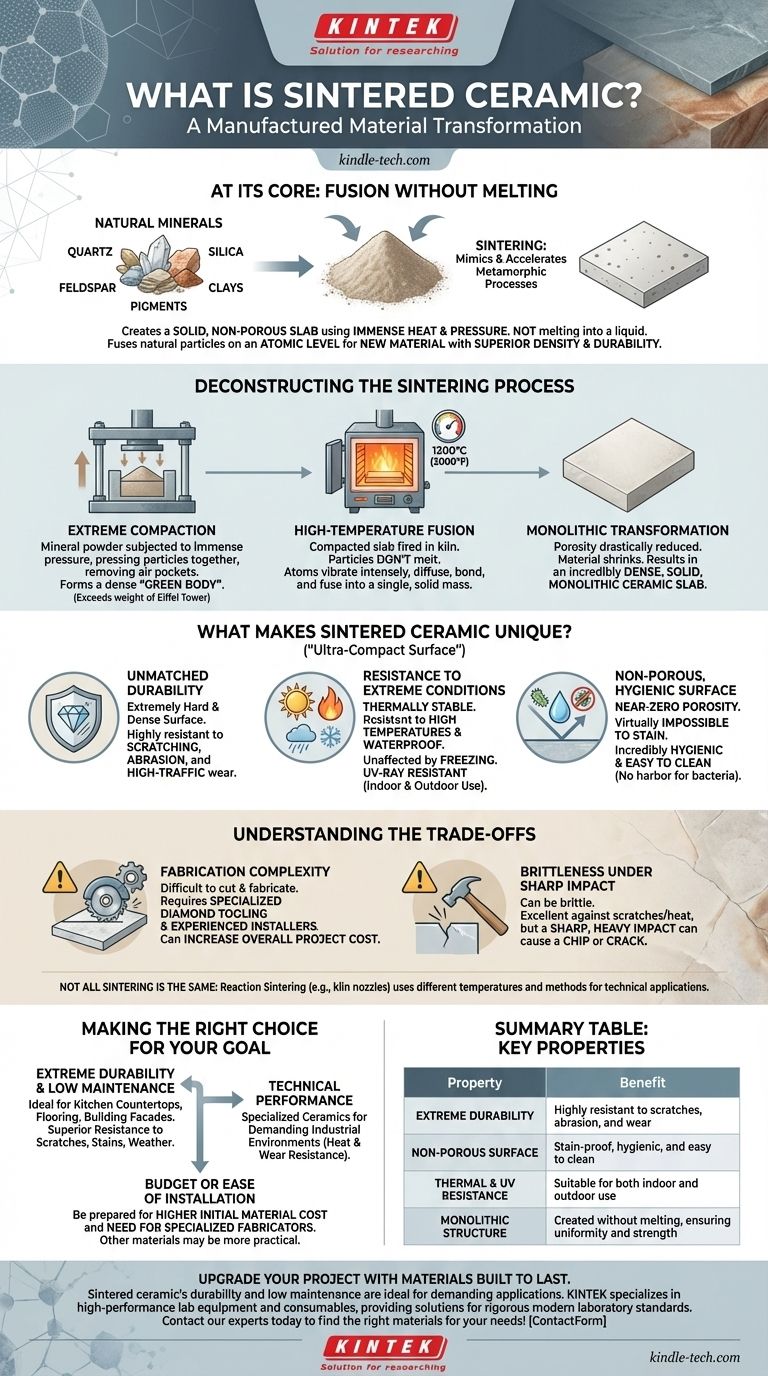
At its core, sintered ceramic is a manufactured material created by taking natural minerals, grinding them into a fine powder, and then fusing them into a solid, non-porous slab using immense heat and pressure. This process, known as sintering, mimics and accelerates the metamorphic processes that create natural stone, but does so without ever melting the material into a liquid.
The crucial concept to grasp is that sintering is not about melting, but about transformation. It's a high-tech process that compacts and fuses natural particles together on an atomic level, creating an entirely new material with a density and durability that often surpasses its natural counterparts.

Deconstructing the Sintering Process
To truly understand sintered ceramic, you must understand how it is made. The process is a precise sequence of engineered steps, each contributing to the final material's exceptional properties.
The Raw Ingredients: A Natural Foundation
The journey begins with a carefully selected blend of natural materials. These typically include minerals like quartz and feldspar for hardness, silica for structure, and various clays to provide elasticity and binding properties. Mineral pigments are added to achieve the desired color and pattern.
Step 1: Extreme Compaction
The mineral powder is subjected to extreme compaction. This pressure, sometimes described as exceeding the weight of the Eiffel Tower, presses the individual particles together, removing air pockets and forming a dense, coherent slab known as a "green body."
Step 2: High-Temperature Fusion
The compacted slab is then moved into a kiln where it is fired at temperatures around 1200°C (over 2000°F). At this heat, the particles don't melt. Instead, their atoms vibrate so intensely that they diffuse across the boundaries of neighboring particles, bonding and fusing them into a single, solid mass.
The Result: A Monolithic Transformation
This fusion process drastically reduces the material's porosity and causes it to shrink, resulting in an incredibly dense and solid slab. The final product is a monolithic piece of ceramic, fundamentally changed from its original powdered state.
What Makes Sintered Ceramic Unique?
The manufacturing process imbues sintered ceramic, also known as an "ultra-compact surface," with a unique combination of performance characteristics.
Unmatched Durability
Sintering creates an extremely hard and dense surface. This makes the material highly resistant to scratching, abrasion, and wear from high-traffic use.
Resistance to Extreme Conditions
Because it was forged in extreme heat, sintered ceramic is thermally stable and resistant to high temperatures. It is also waterproof, unaffected by freezing conditions, and its mineral-based colors are resistant to fading from UV rays, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
A Non-Porous, Hygienic Surface
Perhaps its most significant advantage is its near-zero porosity. With no pores for liquids to penetrate, the material is virtually impossible to stain. This also makes it incredibly hygienic and easy to clean, as bacteria have nowhere to harbor.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is without its considerations. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging the specific challenges and limitations of sintered ceramic.
Fabrication Complexity
The same hardness that makes sintered ceramic so durable also makes it difficult to cut and fabricate. It requires specialized diamond tooling and experienced installers, which can increase the overall cost of a project compared to softer materials.
Brittleness Under Sharp Impact
Like many extremely hard materials, sintered ceramic can be brittle. While it excels at resisting scratches and heat, a sharp, heavy impact (like dropping a cast-iron pan on an edge) can potentially cause a chip or crack.
Not All Sintering Is the Same
"Sintering" is a broad term. For instance, reaction sintering is a different method used for technical applications like kiln nozzles or heat exchangers. This process uses lower temperatures and results in different properties, showcasing that the specific method is always tailored to the desired outcome.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When deciding if sintered ceramic is right for you, align the material’s properties with your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and low maintenance: Sintered ceramic is an ideal choice for high-use surfaces like kitchen countertops, flooring, and building facades due to its superior resistance to scratches, stains, and weather.
- If your primary focus is technical performance: Specialized sintered ceramics are engineered for demanding industrial environments where resistance to heat and wear is critical.
- If your primary focus is budget or ease of installation: Be prepared for a higher initial material cost and the need for specialized fabricators, which may make other materials more practical for your project.
Understanding the sintering process empowers you to see beyond the surface and select a material based on its fundamental, engineered properties.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Extreme Durability | Highly resistant to scratches, abrasion, and wear |
| Non-Porous Surface | Stain-proof, hygienic, and easy to clean |
| Thermal & UV Resistance | Suitable for both indoor and outdoor use |
| Monolithic Structure | Created without melting, ensuring uniformity and strength |
Upgrade your project with materials built to last. Sintered ceramic's superior durability and low maintenance make it the ideal choice for demanding applications. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions that meet the rigorous standards of modern laboratories. Contact our experts today to find the right materials for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of spring-loaded alumina ceramic rods? Ensure Data Purity in Electrode Test Assemblies
- What is the maximum operating temperature of alumina? The Critical Role of Purity and Form
- What is the maximum temperature for alumina tube? Unlock Its Full Potential with High Purity
- What are the high temperature properties of alumina? Discover Its Stability, Strength, and Limits
- Which of the following is used in furnace to withstand high temperature? Key Materials for Extreme Heat



















