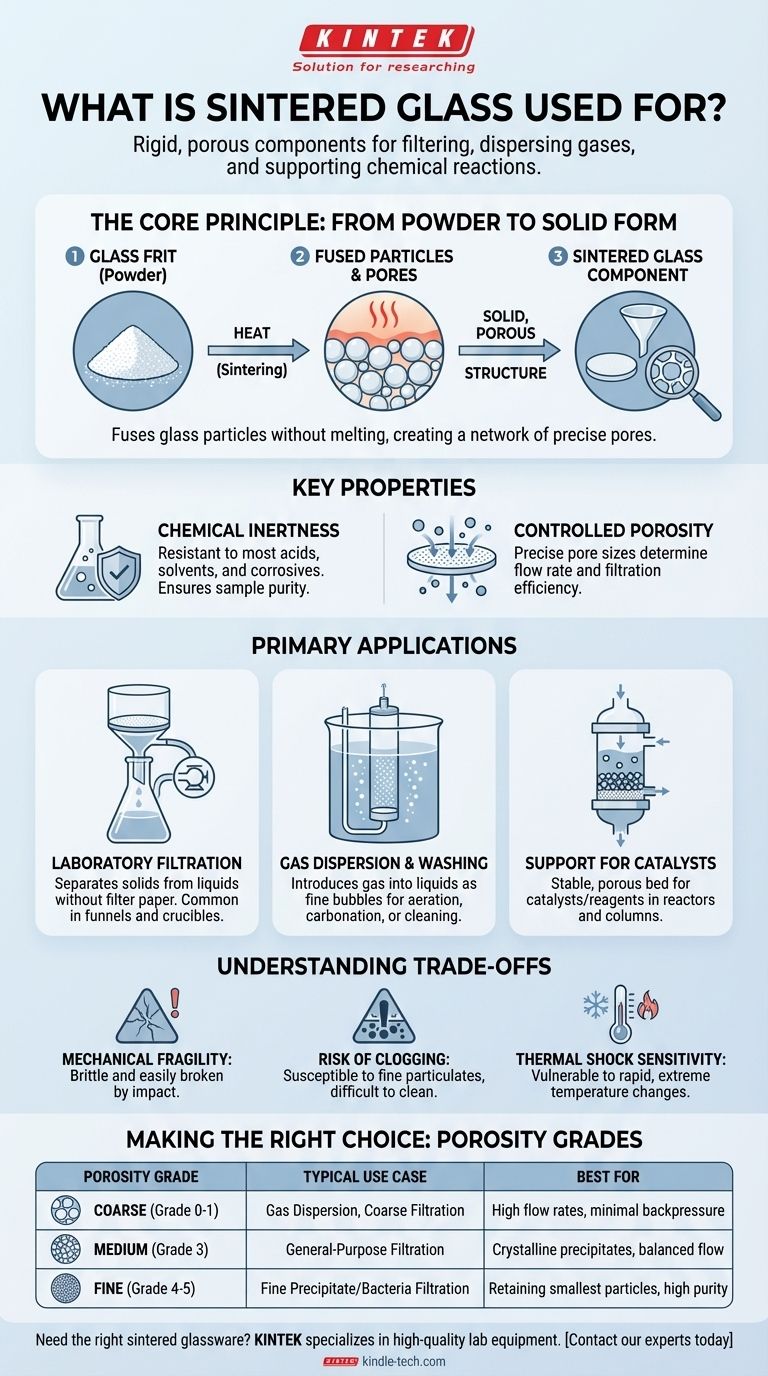
In essence, sintered glass is used to create rigid, porous components for filtering liquids, dispersing gases, and supporting chemical reactions. Often called "fritted glass," its primary applications are found in laboratory and industrial settings where its controlled porosity and chemical inertness are critical for separating materials or facilitating interactions between different phases.
The core principle of sintered glass is transforming fine glass powder into a solid, sponge-like structure. This process creates a network of precisely-sized pores, making it an invaluable tool for applications that demand fine filtration or controlled gas diffusion without the risk of chemical contamination.

How Sintering Creates Porous Glass
Sintering is a thermal process that fuses small particles together using heat, but without melting the material into a liquid. This principle is key to understanding the unique properties of sintered glass.
From Powder to a Solid Form
The process begins with finely ground glass powder, often called glass frit. This powder is placed into a mold of the desired shape, such as a disc or crucible. It is then heated in a furnace to a temperature where the glass softens but does not fully melt. At this temperature, the surfaces of the individual glass particles stick together, or sinter, forming a solid, cohesive mass.
The Key Property: A Network of Pores
Because the glass particles only fuse at their points of contact, the spaces between them remain open. This creates a continuous network of interconnected microscopic channels running through the material. The size of these pores is determined by the size of the glass particles used in the initial powder, allowing manufacturers to produce sintered glass with different, standardized porosity grades.
Why Use Glass? Chemical Inertness
The primary advantage of using glass is its exceptional chemical resistance. Sintered glass components do not react with most acids, solvents, or other corrosive chemicals. This makes them ideal for scientific experiments and chemical processes where sample purity is paramount, preventing contamination that might occur with metal or plastic filters.
Primary Applications of Sintered Glass
The unique combination of controlled porosity and chemical inertness makes sintered glass essential for several key applications.
Laboratory Filtration
The most common use for sintered glass is in filtration funnels (like Büchner or Hirsch funnels) and crucibles. These devices have a built-in disc of sintered glass that acts as the filter medium. They are used to separate solid precipitates from a liquid, often with the aid of a vacuum to speed up the process. This eliminates the need for filter paper, which can react with chemicals or shed fibers into the filtrate.
Gas Dispersion and Washing
Sintered glass discs or cylinders, known as spargers or gas diffusers, are used to introduce a gas into a liquid. When gas is forced through the porous frit, it breaks up into thousands of tiny bubbles. This dramatically increases the surface area of the gas in contact with the liquid, significantly improving the efficiency of processes like aeration, carbonation, or "gas washing" to remove impurities.
Support for Catalysts and Reagents
In chemical reactors or chromatography columns, a sintered glass disc can serve as a stable, porous bed to support a catalyst, resin, or other solid-phase material. It allows liquids or gases to flow through evenly while holding the solid material securely in place, ensuring uniform reaction conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, sintered glass has limitations that users must be aware of to use it effectively and safely.
Mechanical Fragility
Like all glassware, sintered glass is brittle and can be easily broken if dropped or subjected to mechanical stress. The porous structure can be even more delicate than solid glass.
Risk of Clogging
The fine pores that make sintered glass so effective at filtration are also susceptible to clogging by fine particulates. Once clogged, it can be very difficult to clean. Aggressive cleaning or attempting to scrape the surface can damage the filter. Proper cleaning often involves back-flushing with a solvent or soaking in specialized cleaning acids.
Sensitivity to Thermal Shock
Rapid and extreme temperature changes can cause the glass to crack, a phenomenon known as thermal shock. While the borosilicate glass typically used is resistant to heat, the porous structure can have internal stresses that make it more vulnerable than solid glassware.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The effectiveness of sintered glass depends entirely on selecting the correct porosity grade for your specific application. Porosity is typically graded from coarse to very fine.
- If your primary focus is high flow rates for coarse filtration or gas dispersion: Choose a coarse or extra-coarse pore size (e.g., Grade 0 or 1) to minimize backpressure and maximize throughput.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose filtration of crystalline precipitates: A medium pore size (e.g., Grade 3) offers a good balance between retaining fine particles and maintaining a reasonable flow rate.
- If your primary focus is filtering very fine precipitates or bacteria: You must use a fine or very fine pore size (e.g., Grade 4 or 5) to ensure complete capture of the smallest particles.
By understanding how sintered glass is made, you can leverage its unique properties to achieve precise control and purity in your scientific or industrial processes.
Summary Table:
| Porosity Grade | Typical Use Case | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Coarse (Grade 0-1) | Gas Dispersion, Coarse Filtration | High flow rates, minimal backpressure |
| Medium (Grade 3) | General-Purpose Filtration | Crystalline precipitates, balanced flow |
| Fine (Grade 4-5) | Fine Precipitate/Bacteria Filtration | Retaining smallest particles, high purity |
Need the right sintered glassware for your application? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including sintered glass funnels, crucibles, and spargers with precise porosity grades. Our products ensure chemical inertness and reliable performance for your filtration and reaction needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- 400-700nm Wavelength Anti Reflective AR Coating Glass
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE tape applied to ceramic crevice formers when assembling Alloy 22? Precision Tips for Corrosion Testing
- Why is a PTFE beaker preferred for fluorosilicone rubber and POSS-V mixtures? Ensure Purity and Precision
- Why are PTFE or Teflon molds preferred for small-batch ceramic casting? Ensure Damage-Free Demolding & Purity
- What are the process advantages of using PTFE channels in electrode installation ports? Ensure Precise Data Integrity
- How do Teflon (PTFE) baskets facilitate glass thin-film leaching? Enhance Accuracy with Chemical Inertness















