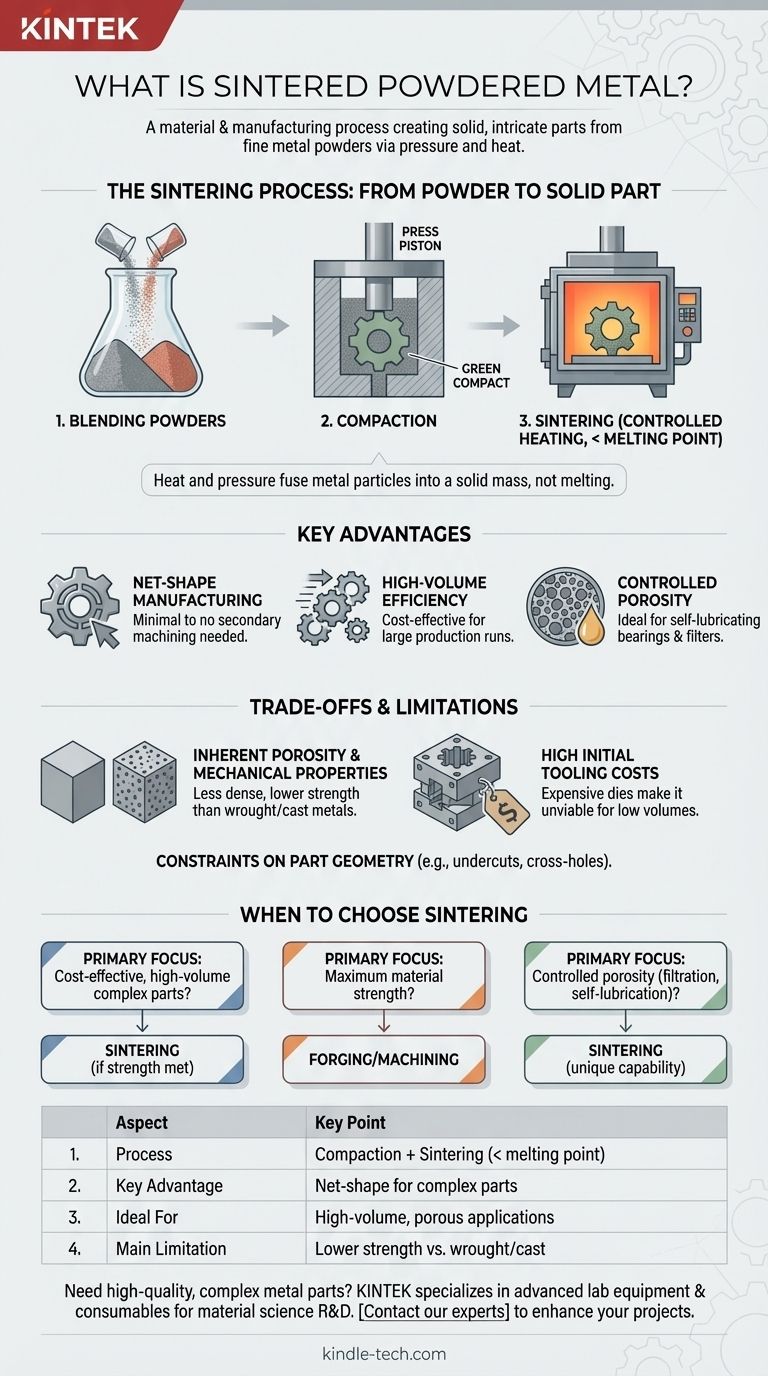
Sintered powdered metal is a material and a manufacturing process used to create solid, often intricate metal parts from fine metal powders. The core of the process involves two main steps: first, compressing the powder into a desired shape, and second, heating it to a high temperature below its melting point, which causes the individual particles to bond together and form a solid piece.
At its core, powdered metallurgy is not about melting metal, but about using heat and pressure to fuse metal particles into a solid mass. This approach unlocks unique advantages for producing complex parts in high volumes, but it comes with distinct trade-offs in material strength and tooling investment.
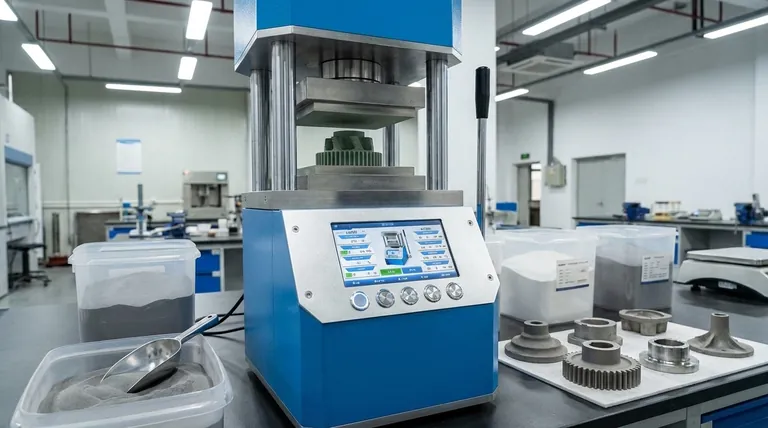

The Sintering Process: From Powder to Solid Part
Understanding the final material requires understanding the journey it takes. The process transforms loose powder into a dense, functional component through a precise, multi-step method.
Step 1: Blending the Powders
The process begins not with a solid block of metal, but with fine, engineered metal powders. These powders can be a single element like iron or copper, or they can be pre-alloyed.
Critically, different powders and lubricants can be precisely blended at this stage. This allows for the creation of unique composite materials that would be difficult or impossible to form through traditional melting and casting.
Step 2: Compaction into a "Green Compact"
The blended powder is fed into a rigid die cavity, which is the negative of the final part shape. A powerful press then compacts the powder under extreme pressure.
This step forms a fragile, precisely shaped component known as a green compact. It has the dimensions of the final part but possesses very low mechanical strength, similar to a tightly packed sandcastle.
Step 3: Sintering (Controlled Heating)
The green compact is then moved into a high-temperature furnace for the sintering stage. The part is heated to a temperature below its melting point, often above 1800°F (980°C).
At this elevated temperature, a process called atomic diffusion occurs. The atoms on the surfaces of the individual powder particles migrate across the boundaries, fusing the particles together and turning the fragile compact into a solid, metallic part. This process is conducted in a controlled atmosphere (such as an inert or reducing gas) to prevent the metal from oxidizing.
Key Advantages of Sintered Powdered Metal
Engineers choose this process for several distinct and powerful reasons that set it apart from traditional machining or casting.
Net-Shape Manufacturing
Sintering creates parts that are net-shape or near-net-shape, meaning they come out of the furnace already in their final or very close to final form. This drastically reduces or eliminates the need for costly and wasteful secondary machining operations.
High-Volume Production Efficiency
Once the initial tooling (the die) is made, the process is extremely fast and repeatable. This makes sintering highly cost-effective for producing thousands or millions of identical parts, such as gears, bushings, and automotive components.
Controlled Porosity
Unlike fully dense materials made by melting, sintered parts can be designed with a specific level of inherent porosity. This characteristic is a key advantage for certain applications, such as self-lubricating bearings that are impregnated with oil or filters that require a porous structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, powdered metallurgy is not the solution for every problem. Its benefits come with important trade-offs that must be considered.
Inherent Porosity and Mechanical Properties
Unless secondary densification steps are taken, sintered parts are typically less dense than their wrought or cast counterparts. This residual porosity can make them less strong and more brittle, limiting their use in applications requiring maximum tensile strength or fatigue resistance.
High Initial Tooling Costs
The hardened steel or carbide dies required for compaction are complex and expensive to produce. This high upfront investment makes the process economically unviable for low-volume production or prototyping.
Constraints on Part Geometry
The need to press powder in a die and eject the green compact places limitations on part design. Features like undercuts, cross-holes, or threads are generally not possible without secondary machining operations. Part size is also limited by the capacity of available presses.
When to Choose Sintering for Your Project
Use these guidelines to determine if powdered metallurgy aligns with your engineering and business goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production of complex parts: Sintering is an excellent choice, provided the mechanical strength requirements are met by the material.
- If your primary focus is maximum material strength and impact resistance: Forging or machining from a solid billet is likely a better, though more expensive, alternative.
- If your primary focus is creating parts with controlled porosity for filtration or self-lubrication: Sintering provides unique capabilities that are unattainable with most other metalworking processes.
Understanding these core principles empowers you to select the right manufacturing method for your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Point |
|---|---|
| Process | Compaction + heating below melting point (sintering) |
| Key Advantage | Net-shape manufacturing for complex parts |
| Ideal For | High-volume production, self-lubricating bearings, filters |
| Main Limitation | Lower strength/ductility vs. wrought/cast metals |
Need high-quality, complex metal parts produced efficiently?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for material science and manufacturing R&D. Our expertise supports the development and optimization of sintering processes, helping you achieve precise, cost-effective results for your laboratory or production needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK solutions can enhance your powdered metallurgy projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
People Also Ask
- What technical conditions does a heated hydraulic press provide for PEO batteries? Optimize Solid-State Interfaces
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- What does a hydraulic heat press do? Achieve Industrial-Scale, Consistent Pressure for High-Volume Production
- Why do you need to follow the safety procedure in using hydraulic tools? Prevent Catastrophic Failure and Injury
- How does a vacuum furnace environment influence sintered Ruthenium powder? Achieve High Purity and Theoretical Density



















