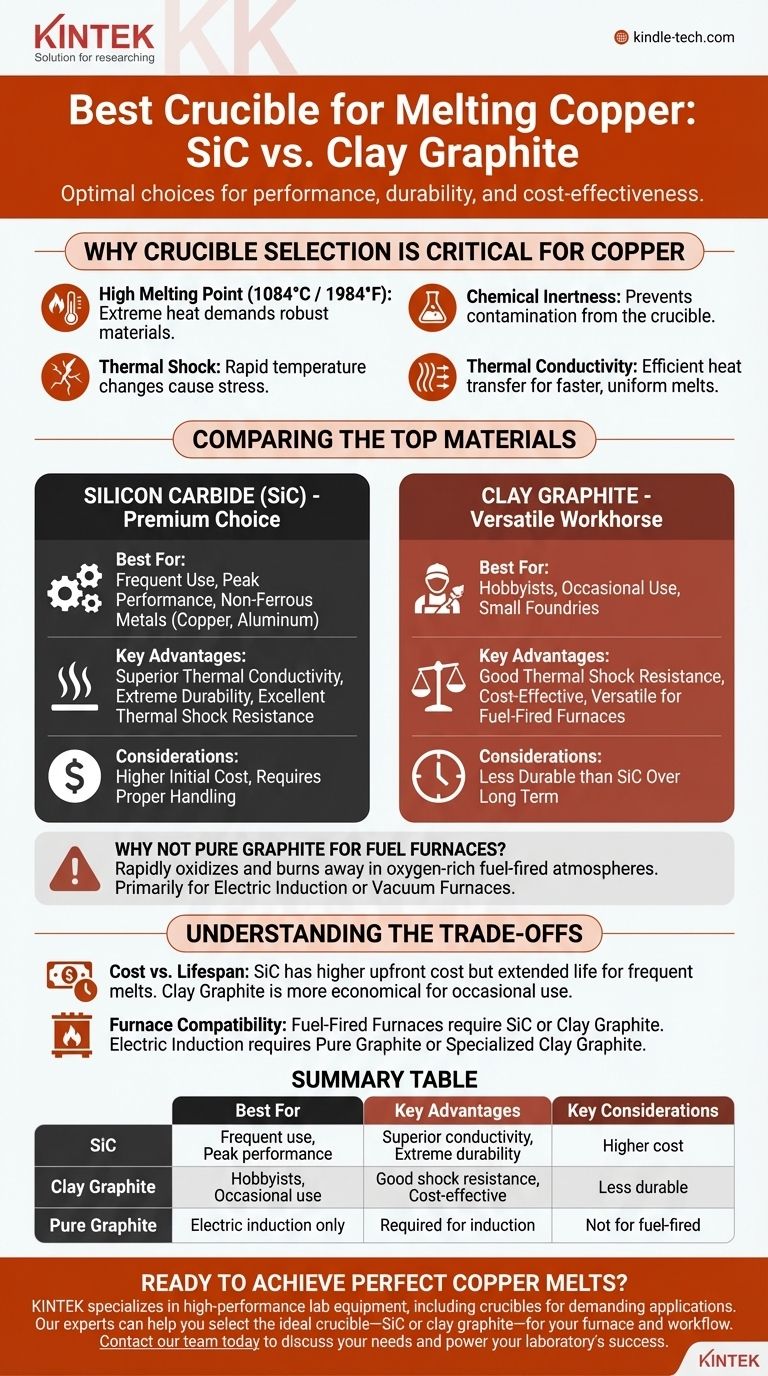
For melting copper, your best options are silicon carbide (SiC) or a high-quality clay graphite crucible. Silicon carbide is the superior choice for durability and performance, especially with frequent use, while clay graphite offers a reliable and more cost-effective alternative for hobbyists and occasional melting. The specific choice depends heavily on your furnace type and how often you plan to work.
The "best" crucible isn't just about the material; it's about matching the material's properties to your specific furnace and workflow. Understanding the fundamental differences between crucible types is the key to ensuring both safety and efficiency in your melts.

Why Crucible Selection is Critical for Copper
Copper melts at a relatively high temperature for a non-ferrous metal (1084°C or 1984°F). This heat, combined with the stress of repeated heating and cooling cycles, places extreme demands on your crucible. Choosing the wrong material can lead to a failed casting, a ruined crucible, or a dangerous furnace failure.
The Challenge of Thermal Shock
A crucible undergoes immense stress as it goes from room temperature to over 1000°C and back down. This rapid expansion and contraction is known as thermal shock.
Materials with excellent thermal shock resistance, like silicon carbide and clay graphite, are engineered to withstand these cycles without cracking.
The Need for Chemical Inertness
You need a crucible that will not react with or contaminate the molten copper.
Using a crucible made of a lower-melting-point metal, like steel, is a critical mistake. It will not only rapidly degrade but will also leach iron into your copper, ruining the purity of your final cast.
The Importance of Thermal Conductivity
Efficient heat transfer is key to a successful melt. A crucible with high thermal conductivity allows heat from your furnace to pass through to the metal quickly and evenly.
This results in shorter melt times, lower fuel or electricity consumption, and a more uniform temperature throughout the molten metal.
Comparing the Top Crucible Materials for Copper
Each common crucible material has a distinct profile of strengths and weaknesses. The ideal choice for you is a matter of balancing performance, cost, and equipment compatibility.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Crucibles
These are the premium choice for melting non-ferrous metals like copper and aluminum. They are typically black or dark gray and have a slightly rough texture.
SiC crucibles offer the best thermal conductivity, leading to very fast and efficient melts. They are also extremely durable and resistant to both thermal shock and physical damage, providing a very long service life when handled correctly.
Clay Graphite Crucibles
This is the most common and versatile type of crucible, often seen as the workhorse for hobbyists and small foundries. They are composed of a mix of graphite and ceramic clays.
Clay graphite provides a great balance of good thermal shock resistance and affordability. While not as durable or conductive as silicon carbide, it is a significant upgrade from pure clay and is perfectly suitable for melting copper.
Why Not Pure Graphite?
Pure graphite crucibles are primarily designed for use in electric induction furnaces or vacuum furnaces.
When used in a propane or gas-fired furnace, the direct flame and oxygen-rich atmosphere will cause the graphite to rapidly oxidize and burn away, severely shortening its life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a crucible isn't just about picking the most expensive option. It's about making an informed decision based on your specific setup and goals.
Cost vs. Lifespan
A silicon carbide crucible may cost significantly more upfront than a clay graphite one. However, its extended lifespan can make it more economical over time if you perform melts frequently.
For the occasional user, the lower initial cost of a clay graphite crucible makes it the more practical starting point.
Furnace Compatibility is Non-Negotiable
This is the most important factor. Using the wrong crucible in your furnace will lead to failure.
For fuel-fired furnaces (propane, natural gas, waste oil), you must use either a silicon carbide or clay graphite crucible that is rated for direct flame contact.
For electric induction furnaces, a pure graphite or a specialized clay graphite crucible is required for the furnace to function correctly and efficiently heat the metal.
Proper Care is Essential
No crucible will survive if mistreated. Always preheat a new crucible slowly on its first use to drive off any residual moisture absorbed during shipping or storage. Never introduce cold or wet metal into a pool of molten metal, as this can cause a steam explosion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your decision on your primary objective to ensure you get the best performance and value for your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is longevity and peak performance for frequent use: A silicon carbide crucible is the definitive professional choice and a worthwhile investment.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and versatility for a hobbyist setup: A high-quality clay graphite crucible is the ideal starting point and will serve you well.
- If you are using an electric induction furnace: A pure graphite crucible is specifically designed for your equipment and is the correct technical choice.
Choosing the right crucible is the foundation of a safe, efficient, and successful metal casting process.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Type | Best For | Key Advantages | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Frequent use, peak performance | Superior thermal conductivity, extreme durability, excellent thermal shock resistance | Higher initial cost, requires proper handling |
| Clay Graphite | Hobbyists, occasional use | Good thermal shock resistance, cost-effective, versatile for fuel-fired furnaces | Less durable than SiC over the long term |
| Pure Graphite | Electric induction furnaces only | Required for induction furnace operation | Not suitable for fuel-fired furnaces (will oxidize) |
Ready to Achieve Perfect Copper Melts?
Choosing the right crucible is the first step to a safe, efficient, and successful casting process. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of crucibles designed for demanding applications like melting copper.
Our experts can help you select the ideal crucible—whether durable silicon carbide or versatile clay graphite—to match your specific furnace type and workflow, ensuring you get the best performance and value.
Contact our team today to discuss your needs and let KINTEK provide the reliable equipment that powers your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of DC magnetron sputtering? Key Limitations for Your Lab
- What is deposition in environmental chemistry? Understanding How Air Pollution Harms Ecosystems
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is sputtering technology? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the fundamental of magnetron sputtering? Master High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















