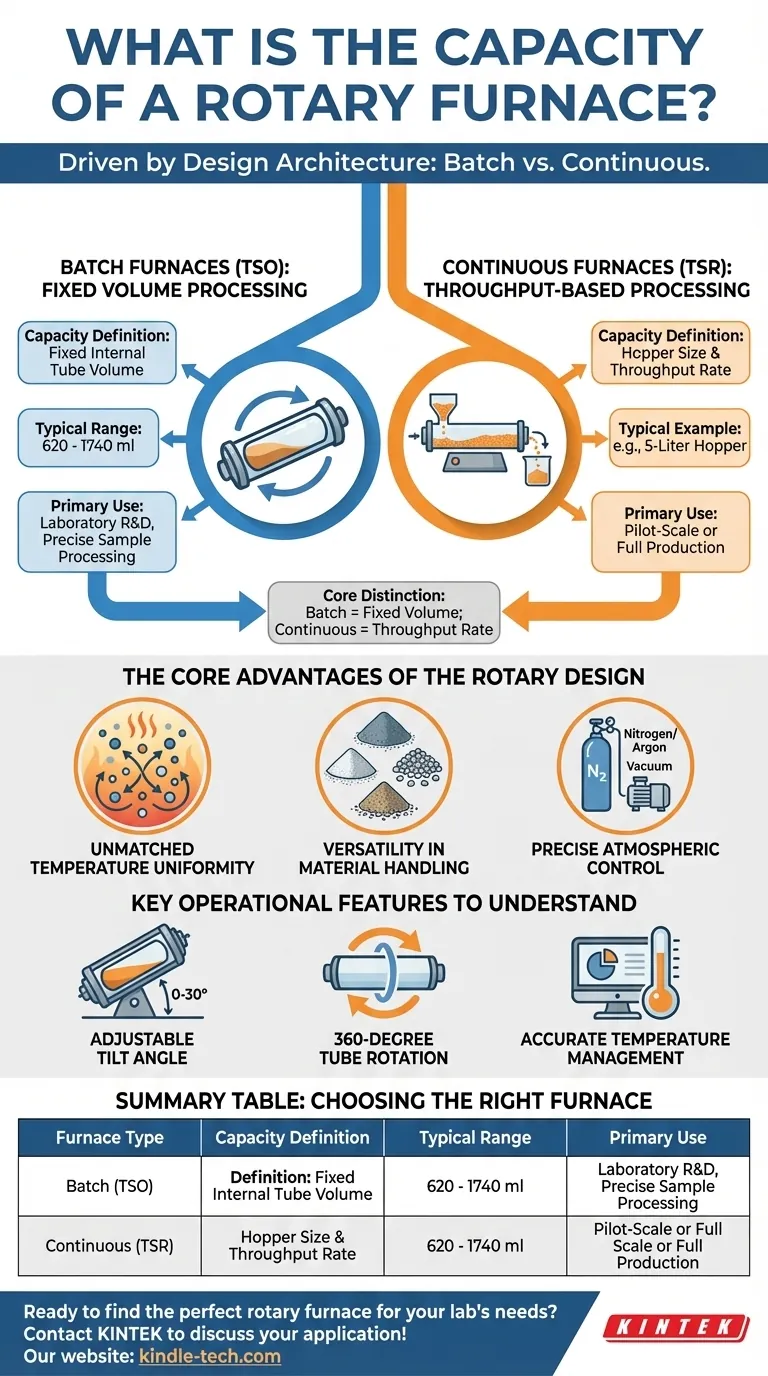
The capacity of a rotary furnace depends entirely on its design architecture. These furnaces are built in two distinct configurations: batch processing models with fixed, smaller capacities, or continuous processing models designed for high-throughput production where capacity is limited by external hoppers.
The core distinction is simple: batch furnaces are defined by a fixed processing volume, typically measured in milliliters for lab work, while continuous furnaces are defined by their throughput rate and the size of their feeding systems, often measured in liters.

The Two Architectures of Rotary Furnaces
The most critical factor determining a rotary furnace's capacity and application is whether it operates in batches or continuously. This is the fundamental design choice that dictates its use.
Batch Furnaces (TSO): Fixed Volume Processing
Batch-style rotary furnaces are designed to process a single, defined amount of material at one time.
Their capacity is measured by the internal volume of the processing tube. The typical range for these furnaces is between 620 and 1740 ml.
This architecture is ideal for laboratory research, material development, and any application requiring precise control over a specific, finite sample.
Continuous Furnaces (TSR): Throughput-Based Processing
Continuous rotary furnaces are built for an ongoing, uninterrupted flow of material.
Their "capacity" is not a measure of the tube's internal volume but rather the size of the feed and collection hoppers. For example, a system might use a 5-liter hopper to constantly feed material through the heating zone.
This design is suited for pilot-scale manufacturing or full production environments where consistent throughput is the primary goal.
The Core Advantages of the Rotary Design
Beyond capacity, the reason to choose a rotary furnace lies in its unique ability to manipulate materials during thermal processing.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The constant rotation of the furnace tube ensures that the material inside is thoroughly mixed. This action eliminates hot spots and temperature gradients, leading to exceptionally uniform heat treatment.
Versatility in Material Handling
Rotary furnaces excel at processing a wide variety of material types. They can effectively heat powders, granules, and other solids that would be difficult to heat evenly in a static furnace.
Precise Atmospheric Control
These systems are designed for high-purity applications. They can operate with specific atmospheres by introducing gases like nitrogen or argon, or they can be used under vacuum conditions with an external pump.
Key Operational Features to Understand
Several key features enable the precision and efficiency of a rotary furnace.
Adjustable Tilt Angle
The entire furnace body can typically be tilted, often between 0 and 30 degrees. This allows operators to control the residence time and flow rate of material through the heating tube.
360-Degree Tube Rotation
The full rotation of the tube is the central mechanism for mixing. This constant agitation is what guarantees that every particle is exposed to the same processing conditions.
Accurate Temperature Management
Modern rotary furnaces use sophisticated computer control systems to manage temperature. This allows for high accuracy and ensures the quality and repeatability of the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct rotary furnace requires a clear understanding of your primary processing objective.
- If your primary focus is laboratory-scale R&D: A batch (TSO) furnace is the correct choice, as its fixed volume (620-1740 ml) is designed for precise control over discrete samples.
- If your primary focus is continuous production: A continuous (TSR) furnace is necessary for its high-throughput capability, which is determined by the hopper size.
- If your primary focus is achieving perfect heat distribution: The rotary mechanism itself is the key feature, as its ability to mix and tumble material is superior to any static furnace design.
Ultimately, matching the furnace architecture—batch or continuous—to your specific material processing goal is the key to a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Capacity Definition | Typical Range | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch (TSO) | Fixed internal tube volume | 620 - 1740 ml | Laboratory R&D, precise sample processing |
| Continuous (TSR) | Hopper size & throughput rate | e.g., 5-liter hopper | Pilot-scale or full production |
Ready to find the perfect rotary furnace for your lab's needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including both batch and continuous rotary furnaces. Whether you require precise temperature control for R&D or high-throughput capabilities for production, our experts can help you select the ideal solution to achieve uniform heating, precise atmospheric control, and superior material processing.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process



















