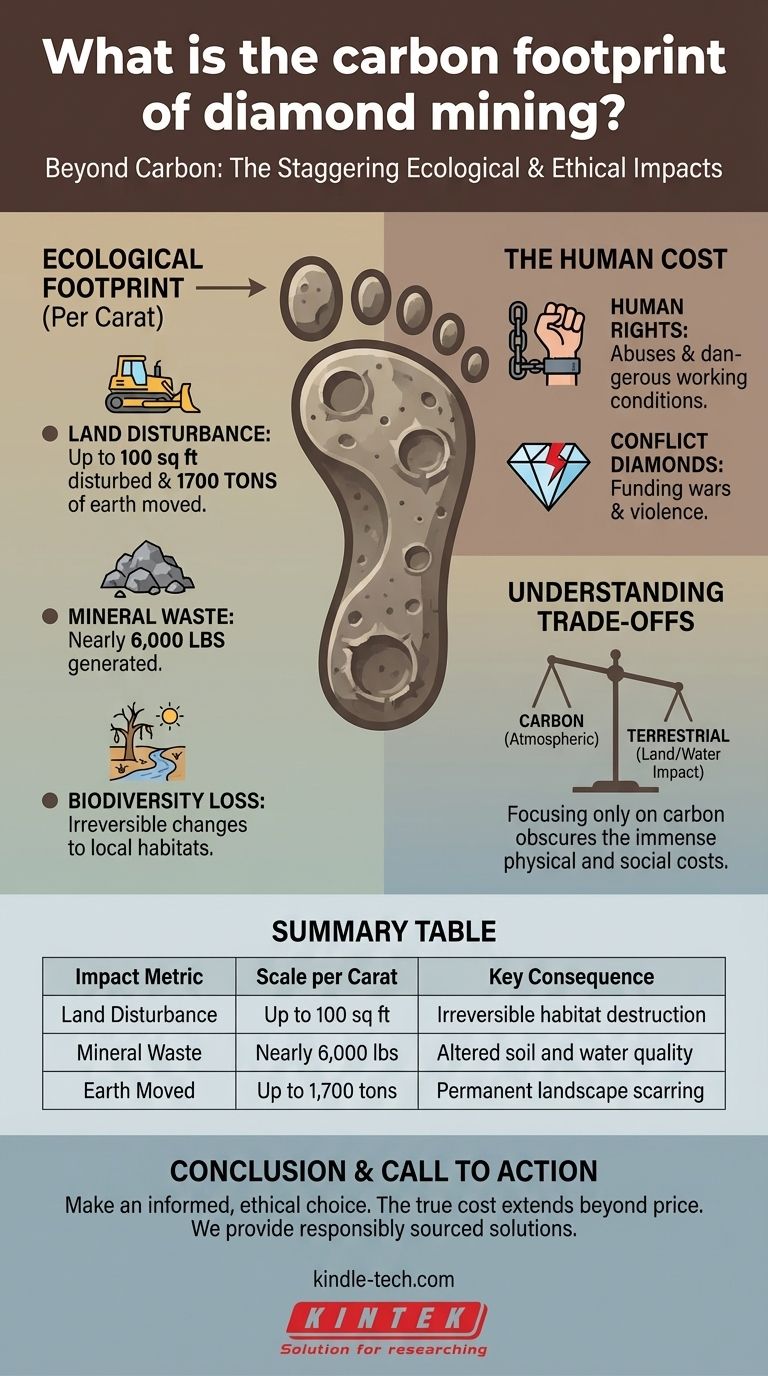
While a precise carbon footprint for diamond mining is difficult to pin down, the more immediate and well-documented consequences are its staggering ecological and ethical impacts. For every single carat extracted, mining operations disturb vast tracts of land, create thousands of pounds of waste, and have been historically linked to severe human rights issues.
The true "footprint" of a mined diamond extends far beyond its carbon emissions. It is more accurately measured by its irreversible impact on landscapes, ecosystems, and human lives.

Beyond Carbon: The Full Ecological Footprint
While the fuel used for heavy machinery in mining certainly generates carbon emissions, this specific metric is often overshadowed by the direct, physical destruction of the environment.
Massive Land Disturbance
Extracting diamonds is an incredibly earth-intensive process. It requires excavating and moving enormous quantities of soil and rock to find the small, precious crystals.
For every carat of diamond unearthed, miners can disturb nearly 100 square feet of land and move up to 1700 tons of earth.
Significant Mineral Waste
The material removed from the earth doesn't simply disappear. It becomes mineral waste, which can have lasting consequences for the surrounding area.
The extraction process for a single carat generates almost 6,000 pounds of mineral waste. This byproduct can alter local landscapes and impact soil and water quality.
Irreversible Biodiversity Loss
This level of excavation permanently changes the environment. It can lead to the removal of waterways and the complete destruction of local habitats.
These actions result in what experts call irreversible changes to biodiversity, meaning the local ecosystem cannot recover to its original state.
The Human Cost of Diamond Mining
The environmental toll is only one part of the story. For decades, the diamond industry has been plagued by serious ethical concerns.
Human Rights and Worker Safety
The history of diamond mining is unfortunately tied to human rights abuses and dangerous working conditions in various parts of the world, particularly in Africa.
The Shadow of 'Conflict Diamonds'
Illegally traded diamonds, often called "conflict diamonds" or "blood diamonds," have been used to fund wars and armed rebellions, perpetuating violence and instability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Focusing exclusively on a single metric like carbon can obscure the broader and more severe impacts associated with natural diamonds.
Why Carbon Isn't the Whole Story
The most significant consequences of diamond mining are not atmospheric but terrestrial. The permanent scarring of land, destruction of ecosystems, and potential for human exploitation are the primary costs.
While modern mining companies are working to improve practices, the fundamental nature of digging massive open pits in the earth remains incredibly disruptive.
The Challenge of a Single Number
The exact carbon footprint can vary dramatically from one mine to another. A mine in Canada running on hydropower will have a vastly different emissions profile than one in Africa powered by diesel generators.
This variability makes a single, universal "carbon footprint per carat" figure misleading and ultimately less useful than understanding the consistent impacts of land and water use.
Making an Informed Decision
To assess the true impact of a mined diamond, you must look beyond any single number and consider the complete picture.
- If your primary focus is land and water impact: Recognize that the physical footprint of mined diamonds is immense, permanent, and well-documented.
- If your primary focus is ethical sourcing: Demand a transparent and verifiable chain of custody to ensure your diamond is not connected to conflict or human rights violations.
- If your primary focus is strictly carbon emissions: Acknowledge that this metric alone fails to capture the most significant environmental and social consequences of diamond mining.
Ultimately, an informed choice requires weighing the full spectrum of environmental, social, and ethical factors involved in bringing a diamond from the earth to the market.
Summary Table:
| Impact Metric | Scale per Carat | Key Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Land Disturbance | Up to 100 sq ft | Irreversible habitat destruction |
| Mineral Waste | Nearly 6,000 lbs | Altered soil and water quality |
| Earth Moved | Up to 1,700 tons | Permanent landscape scarring |
Make an informed, ethical choice for your laboratory. The true cost of materials extends beyond price to their environmental and social impact. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality, responsibly sourced lab equipment and consumables that help you achieve your research goals without compromising your values. Contact our experts today to discover sustainable solutions for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function? Expert Guide to Diamond Film Fabrication











