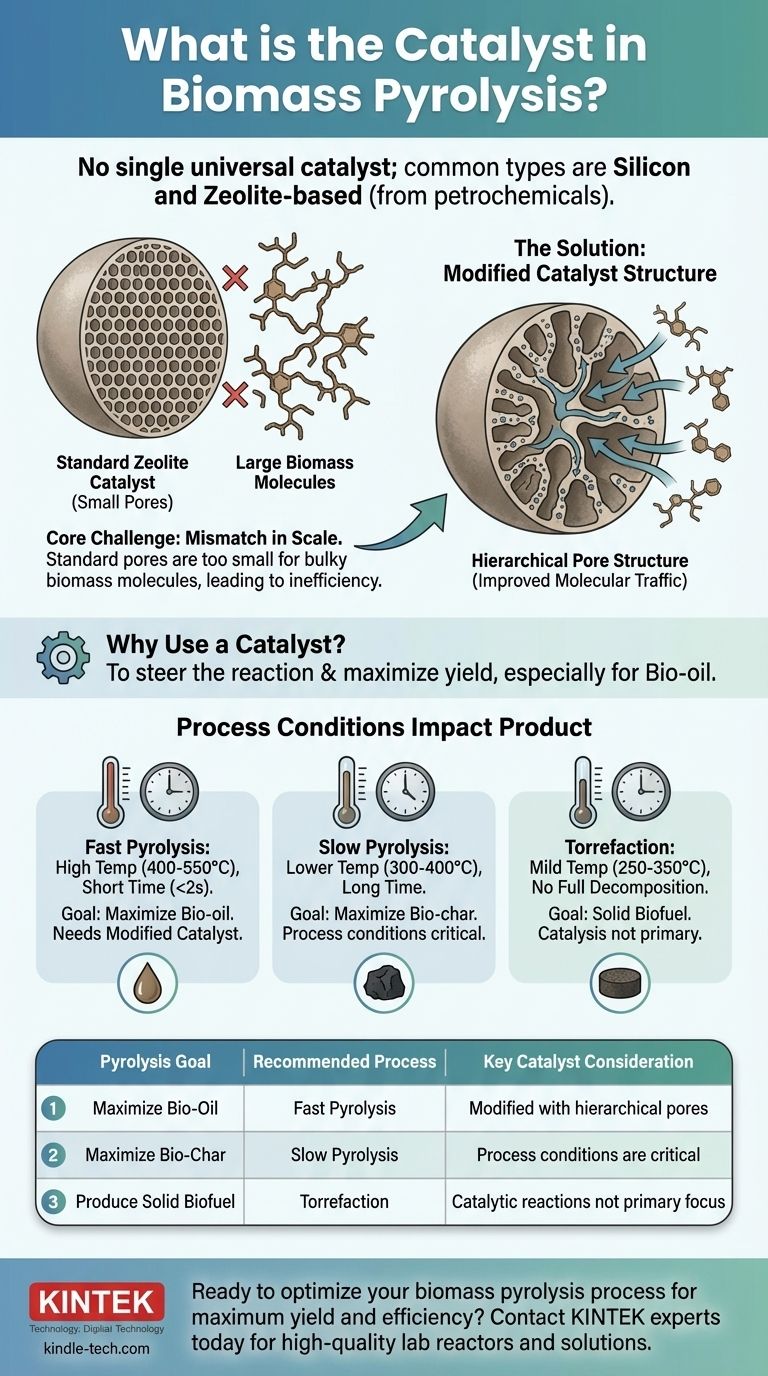
In biomass pyrolysis, there is no single universal catalyst. The most common types are silicon and zeolite-based catalysts, which are borrowed from the petrochemical industry. However, their effectiveness is limited because they were not designed to handle the large, complex polymer molecules found in biomass.
The core challenge in catalytic pyrolysis is a mismatch between the tool and the material. Standard commercial catalysts have pores too small for bulky biomass molecules, leading to inefficiency. True optimization requires either modifying the catalyst's structure or fundamentally altering the pyrolysis process itself to match the desired outcome.

The Role of a Catalyst in Pyrolysis
Catalysts are introduced into the pyrolysis process to gain control over the chemical reactions. Without them, the thermal breakdown of biomass is less predictable.
Why Use a Catalyst?
Biomass itself is highly variable in its chemical makeup. A catalyst provides a way to steer the reaction toward producing a higher yield of a specific, desirable compound. Most research focuses on maximizing the yield of bio-oil, a liquid fuel.
Common Catalyst Types
The most prevalent catalysts used are silicon-based and zeolite-based. These are well-understood, commercially available materials that have a long history of use in refining crude oil into gasoline and other products.
The Central Challenge: A Mismatch in Scale
The primary difficulty in using commercial catalysts for biomass pyrolysis stems from a fundamental difference in the size of the molecules being processed.
Designed for a Different Job
Zeolite catalysts have a very precise, crystalline structure with narrow pores. This design is perfect for cracking small, uniform hydrocarbon molecules found in petroleum.
However, the natural polymers in biomass, like cellulose and lignin, are significantly larger and more complex. They cannot easily enter the small pores of a standard zeolite catalyst to be converted.
The "Molecular Traffic" Problem
Because the large biomass molecules can't access the active sites within the catalyst's pores, the process becomes inefficient. This can lead to lower yields of the desired bio-oil and faster deactivation of the catalyst itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Solutions
Achieving an effective catalytic pyrolysis process involves balancing the limitations of the catalyst with the goals of the operation.
Catalyst Modification
The most promising solution is to re-engineer the catalyst itself. By creating a multidimensional pore structure, researchers can introduce larger channels (meso- and macropores) alongside the traditional micropores.
This hierarchical structure acts like a highway system, allowing bulky biomass molecules to enter the catalyst and break down into smaller intermediates, which can then be processed by the highly active micropores. This improves what is known as "molecular traffic control."
Process Condition Adjustment
Beyond the catalyst, the process conditions have a massive impact on the final product. The choice of catalyst is often secondary to the choice of pyrolysis method.
- Fast Pyrolysis: Involves very high temperatures (400-550°C) and short residence times (under 2 seconds). This process is specifically chosen to maximize the production of liquid bio-oil.
- Slow Pyrolysis: Uses lower temperatures (300-400°C) and much longer times. This method is designed to maximize the yield of solid biochar, a valuable soil amendment.
- Torrefaction: A milder heating process (250-350°C) that doesn't fully decompose the biomass, but instead creates a solid, densified biofuel with improved handling and combustion properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your strategy for pyrolysis must be dictated by your desired end-product. The catalyst and process are tools to achieve that specific goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-oil yield: Use fast pyrolysis and prioritize modified catalysts with hierarchical pore structures that can accommodate large biomass molecules.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality biochar: Use slow pyrolysis, where precise control over heating rate and temperature is more critical than the specific catalyst used.
- If your primary focus is creating a densified solid biofuel: Use torrefaction, which is a thermal treatment where complex catalytic reactions are not the main objective.
Ultimately, successful biomass conversion depends on harmonizing the feedstock, the catalyst, and the process conditions to achieve a specific chemical transformation.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Goal | Recommended Process | Key Catalyst Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Maximize Bio-Oil | Fast Pyrolysis | Modified catalysts with hierarchical pores |
| Maximize Bio-Char | Slow Pyrolysis | Process conditions are more critical than catalyst |
| Produce Solid Biofuel | Torrefaction | Catalytic reactions are not the primary focus |
Ready to optimize your biomass pyrolysis process for maximum yield and efficiency? The right lab equipment is crucial for testing catalysts and perfecting your method. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab reactors, furnaces, and consumables tailored for biomass conversion research. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve superior control over your pyrolysis outcomes and accelerate your biofuel development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Measuring Cylinder 10/50/100ml
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of an electrolytic cell in the pre-plating stage of multicomponent nickel-based boriding?
- What general precaution should be taken when handling the electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe and Accurate Lab Results
- What contaminants should be avoided during the operation of a proton exchange membrane? Protect Your PEM from Heavy Metals & Organics
- What are the proper storage procedures for the multifunctional electrolytic cell? Protect Your Investment and Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is an electrolysis cell also known as? Understanding Electrolytic vs. Galvanic Cells



















