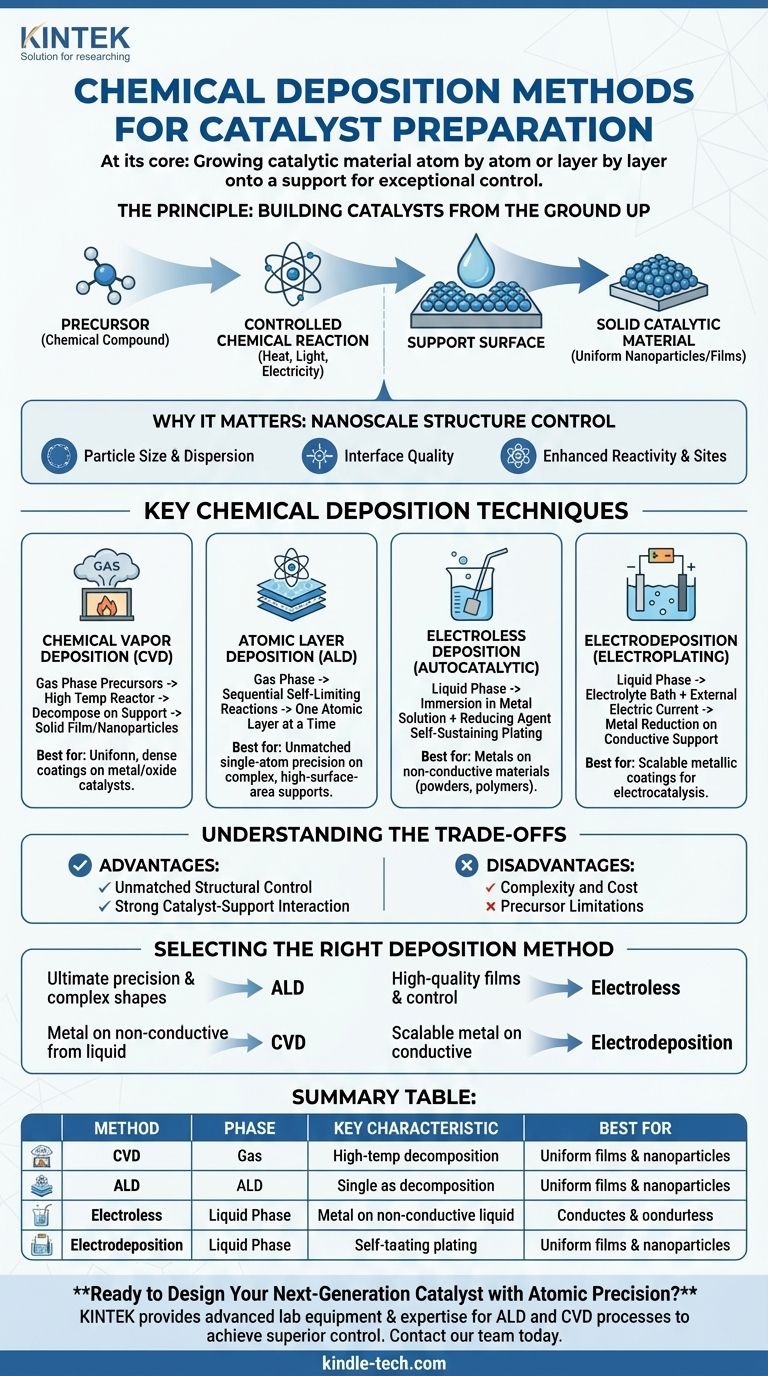
At its core, chemical deposition is a family of catalyst preparation techniques where the active catalytic material is grown directly onto a support surface from chemical precursors. Unlike traditional methods that load pre-formed particles onto a support, deposition builds the catalyst from the bottom up, atom by atom or layer by layer, offering exceptional control over its final structure, size, and location.
While more complex and costly than bulk methods like impregnation, chemical deposition provides unparalleled precision. It is the method of choice when the exact atomic-level architecture of the catalyst is critical for achieving superior activity, selectivity, and long-term stability.

The Principle: Building Catalysts from the Ground Up
Chemical deposition fundamentally changes the catalyst creation process from one of assembly to one of direct synthesis on the final support material. This provides a level of control that is difficult to achieve otherwise.
The Core Concept: Precursor to Solid
All chemical deposition methods share a common principle: a chemical compound containing the desired catalytic element, known as a precursor, is introduced to a support material.
Through a controlled chemical reaction triggered by heat, light, or electricity, this precursor decomposes or reacts at the support's surface, leaving behind the desired solid catalytic material while volatile byproducts are removed.
Why This Control Matters
The performance of a catalyst is dictated by its structure at the nanoscale. Key factors include the size of the active particles, their dispersion across the support, and the interface between the particle and the support.
Deposition methods allow for precise tuning of these factors, enabling the creation of highly uniform nanoparticles, single-atom catalysts, or ultra-thin films that maximize the number of active sites and enhance chemical reactivity.
Key Chemical Deposition Techniques
Several distinct techniques fall under the chemical deposition umbrella, each with unique mechanisms and applications. They can be broadly categorized by whether the precursor is in a gas or liquid phase.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
In CVD, volatile gaseous precursors are introduced into a high-temperature reactor containing the catalyst support. The high temperature causes the precursors to react and decompose on the support, forming a solid film or nanoparticles.
This method is highly effective for creating uniform, dense coatings and is a workhorse for producing supported metal and metal oxide catalysts.
Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD)
ALD is a more precise variant of CVD that builds the catalyst one atomic layer at a time. It uses a sequence of self-limiting surface reactions, where each step only proceeds until the entire surface is covered by a single layer of molecules.
This technique offers unmatched control over thickness and composition down to the single-atom level. It is ideal for coating complex, high-surface-area supports and for creating catalysts with precisely engineered active sites.
Electroless Deposition (Autocatalytic Plating)
This is a liquid-phase technique where a support is immersed in a solution containing metal ions and a chemical reducing agent. The deposition reaction is initiated on the surface and becomes self-sustaining (autocatalytic), plating a metallic film without any external electrical power.
Electroless deposition is extremely versatile for depositing metals like nickel, copper, and palladium onto a wide variety of materials, including non-conductive powders and polymers.
Electrodeposition (Electroplating)
Similar to electroless deposition, this method uses a liquid solution (an electrolyte bath). However, it requires an external electric current to drive the reduction of metal ions onto the support, which must be electrically conductive and acts as the cathode.
Electrodeposition is an efficient and scalable method for applying metallic catalyst coatings to conductive supports, common in applications like electrocatalysis for fuel cells and water splitting.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition method requires a clear understanding of its advantages and the practical challenges involved.
Advantage: Unmatched Structural Control
The primary benefit is precision. The ability to control particle size, film thickness, and composition at the atomic scale allows for the rational design of catalysts with optimized performance for specific reactions.
Advantage: Strong Catalyst-Support Interaction
Deposition methods often create a strong chemical bond between the active material and the support. This enhances the catalyst's stability, preventing the active particles from detaching or clumping together (sintering) at high operating temperatures.
Disadvantage: Complexity and Cost
The precision of deposition comes at a price. These methods typically require specialized equipment, such as vacuum systems for CVD/ALD or controlled electrochemical cells. The processes can also be slower and more expensive than simple bulk synthesis.
Disadvantage: Precursor Limitations
The success of any deposition technique hinges on the availability of a suitable precursor. An ideal precursor must be sufficiently volatile (for gas-phase methods), stable during delivery, and react cleanly on the support without leaving behind harmful impurities. Finding the right precursor can be a significant research challenge.
Selecting the Right Deposition Method
Your choice of method should be guided by your specific performance targets, the nature of your support material, and practical constraints.
- If your primary focus is ultimate precision and uniform coating on complex shapes: Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) is the superior choice for creating highly defined single-atom or nanoparticle catalysts.
- If your primary focus is creating high-quality thin films or supported nanoparticles with good control: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) offers a practical balance between precision and deposition rate.
- If your primary focus is depositing a metal catalyst onto a non-conductive support from a liquid phase: Electroless deposition provides a versatile solution without the need for an external electrical circuit.
- If your primary focus is coating a conductive support with a metallic catalyst in a scalable manner: Electrodeposition is an efficient and widely used industrial method for electrocatalytic applications.
Ultimately, choosing a chemical deposition method is a strategic decision that balances the pursuit of atomic-level perfection against the practical constraints of cost and scalability.
Summary Table:
| Method | Phase | Key Characteristic | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Gas | High-temperature decomposition of gaseous precursors | Uniform thin films & nanoparticles |
| Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) | Gas | Atomic-level precision via self-limiting reactions | Single-atom catalysts, complex supports |
| Electroless Deposition | Liquid | Autocatalytic plating without external power | Metal deposition on non-conductive supports |
| Electrodeposition | Liquid | Uses external electric current | Scalable metal coatings on conductive supports |
Ready to Design Your Next-Generation Catalyst with Atomic Precision?
The right preparation method is critical to your catalyst's performance. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert support needed for sophisticated chemical deposition processes like ALD and CVD. Whether you are developing catalysts for energy storage, chemical synthesis, or environmental applications, our solutions help you achieve superior control over particle size, dispersion, and stability.
Let's discuss how our expertise can accelerate your R&D. Contact our team today to find the perfect deposition solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings



















