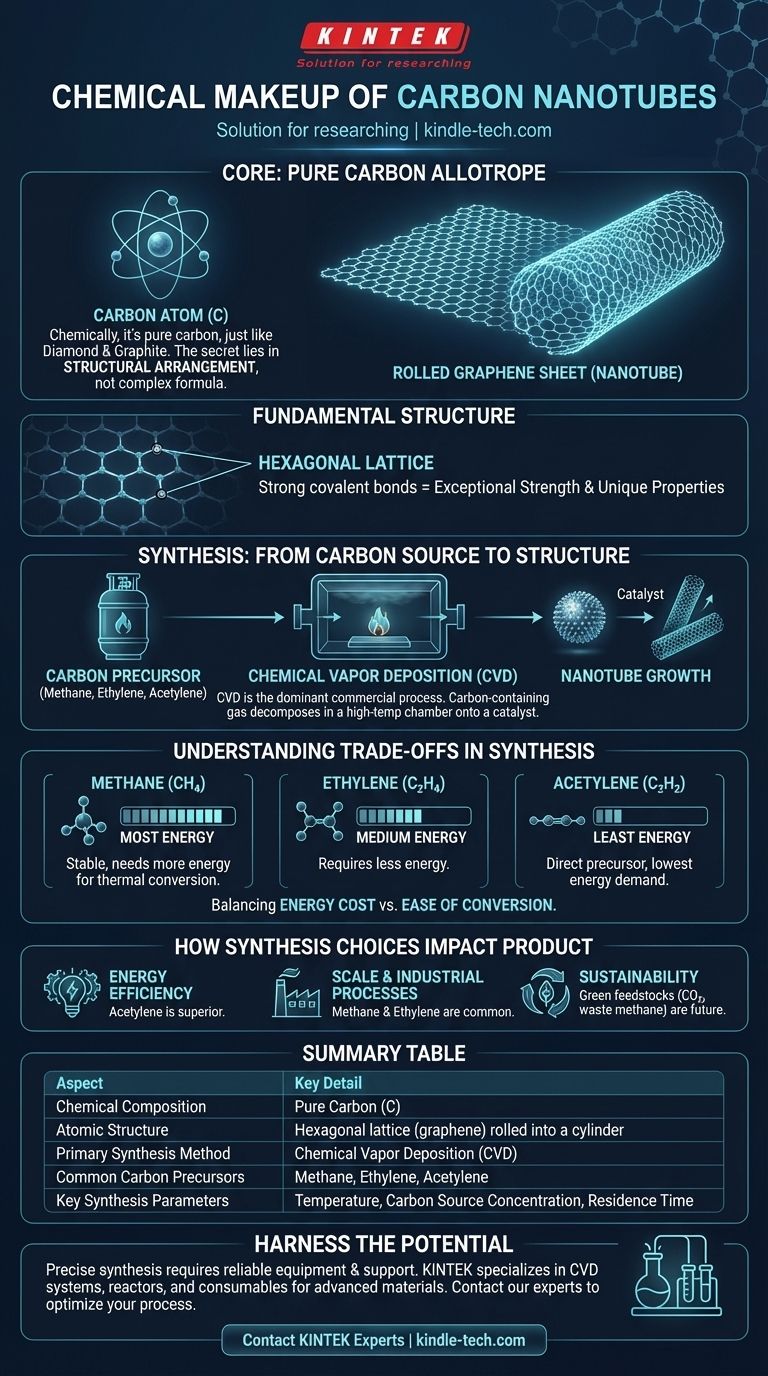
At its core, a carbon nanotube is an allotrope of carbon. This means its chemical makeup consists purely of carbon atoms, just like diamond and graphite. The extraordinary properties of a nanotube do not come from a complex chemical formula but from the unique structural arrangement of these carbon atoms into a hollow, cylindrical tube.
While their chemical makeup is simply pure carbon, the remarkable properties of carbon nanotubes arise not from what they are made of, but from how those carbon atoms are structurally arranged—a result dictated entirely by the manufacturing process.

The Fundamental Structure: A Rolled Sheet of Graphene
Allotropes of Carbon
Carbon is unique in its ability to form different structures, known as allotropes, with vastly different properties. The rigid, transparent structure of a diamond is pure carbon. The soft, opaque layers of graphite are also pure carbon.
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are another member of this family. They can be visualized as a single sheet of graphite (called graphene) rolled into a seamless cylinder.
The Hexagonal Lattice
The defining feature of this structure is the hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms, forming a honeycomb-like pattern. This strong covalent bonding is the source of the nanotubes' exceptional mechanical strength and unique electrical properties.
From Carbon Source to Nanotube Structure
Because CNTs are pure carbon, their synthesis involves liberating carbon atoms from a source material and encouraging them to assemble in the correct cylindrical structure.
The Dominance of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
While early methods like laser ablation existed, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the dominant commercial process used today. In CVD, a carbon-containing gas is introduced into a high-temperature chamber, where it decomposes and the carbon atoms deposit onto a substrate in the presence of a metal catalyst.
The Role of Carbon Precursors
The carbon-containing gas is known as the precursor. Common precursors include hydrocarbon gases like methane, ethylene, and acetylene. The choice of precursor is a critical decision that impacts the entire process.
Controlling Synthesis Parameters
The final quality and yield of the nanotubes are highly sensitive to the operating conditions. The most critical parameters are temperature, carbon source concentration, and the residence time the gas spends in the reaction chamber.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Synthesis
The selection of a carbon source is not arbitrary; it involves a direct trade-off between energy consumption and the ease of chemical conversion.
The Energy Cost of Different Precursors
Different precursors require different amounts of energy to break down and release their carbon atoms. This is because some molecules are more stable than others.
Methane requires the most energy for this thermal conversion. Ethylene requires less, and acetylene can act as a direct precursor, requiring the least amount of additional energy to form the nanotube structure.
Balancing Productivity and Purity
The goal of any synthesis process is to maximize productivity and efficiency. Adjusting parameters like temperature and concentration can increase the growth rate but may also introduce defects or impurities if not carefully controlled. The process must be fine-tuned to balance the speed of production with the structural integrity of the final product.
How Synthesis Choices Impact the Final Product
Choosing a synthesis strategy depends directly on the desired outcome, whether it's maximizing energy efficiency, scale, or sustainability.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Acetylene is a superior precursor, as it requires the least energy to convert into the carbon building blocks for nanotubes.
- If your primary focus is leveraging established industrial processes: Methane and ethylene are common feedstocks, and their synthesis via CVD is well-understood for large-scale production.
- If your primary focus is sustainability: Emerging methods using green feedstocks, such as captured carbon dioxide or waste methane, represent the future of CNT production.
Ultimately, understanding the link between the carbon source and the final atomic arrangement is the key to unlocking the full potential of these remarkable materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Carbon (C) |
| Atomic Structure | Hexagonal lattice (graphene) rolled into a cylinder |
| Primary Synthesis Method | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
| Common Carbon Precursors | Methane, Ethylene, Acetylene |
| Key Synthesis Parameters | Temperature, Carbon Source Concentration, Residence Time |
Ready to harness the potential of carbon nanotubes in your research or production?
The precise synthesis of high-quality CNTs requires reliable lab equipment and expert support. KINTEK specializes in providing the CVD systems, reactors, and consumables essential for advanced materials development. Our team can help you select the right precursors and optimize your process parameters for maximum efficiency, yield, and purity.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your carbon nanotube innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit



















