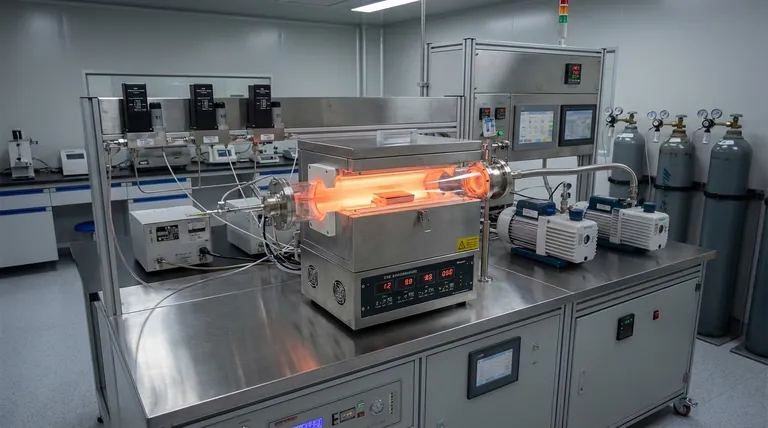
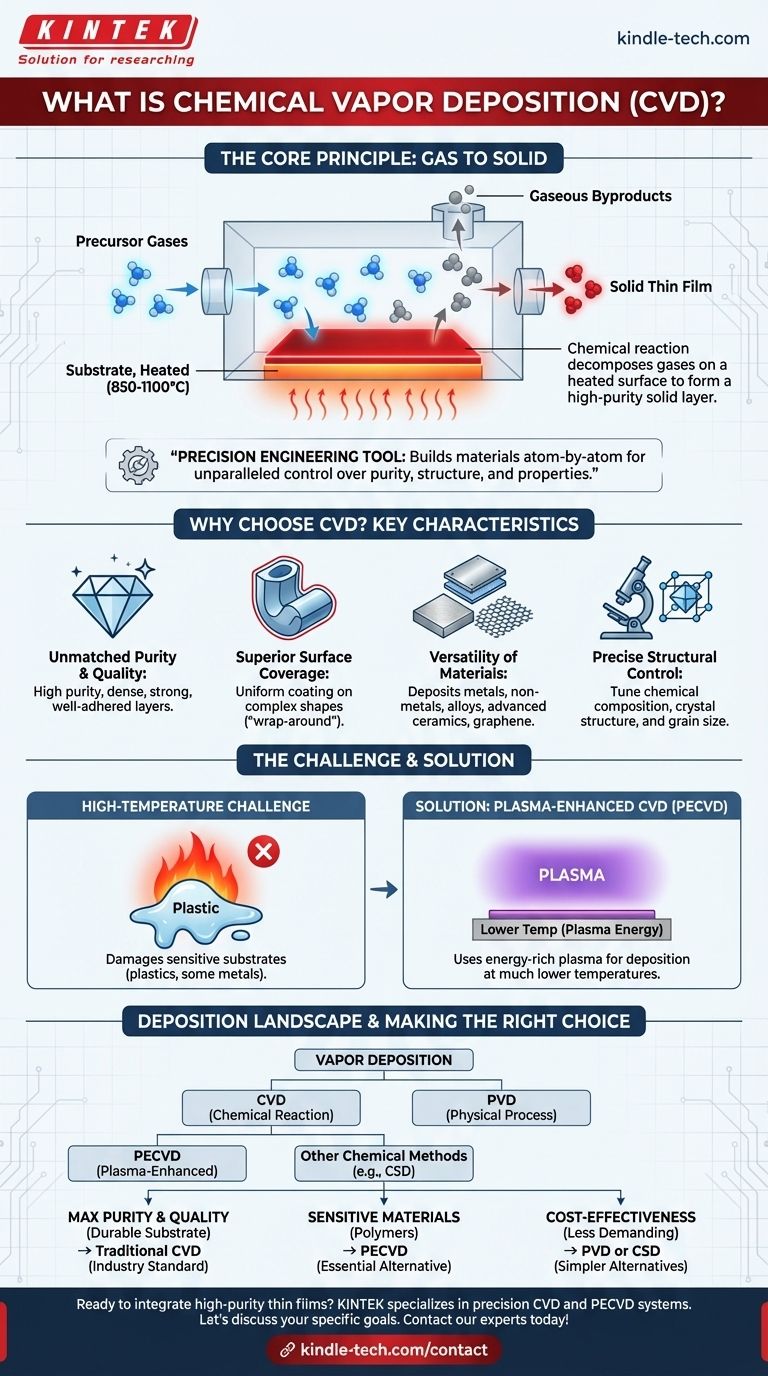
In essence, the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) method is a manufacturing process used to create high-purity, high-performance solid thin films. It works by flowing precursor gases into a reaction chamber where they chemically react and decompose on a heated surface, known as a substrate, to form a solid deposit. This technique is fundamental to modern industries like microelectronics and material science.
Chemical Vapor Deposition is not just a coating method; it is a precision engineering tool. Its primary value lies in its ability to build materials atom-by-atom from gaseous chemicals, offering unparalleled control over the final film's purity, structure, and properties.

How Does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Work?
The CVD process transforms gas-phase chemicals into a solid-state material, creating a thin, functional layer on a base object.
The Core Principle: Gas to Solid
The foundation of CVD is a controlled chemical reaction. Precursor gases, which contain the elements you want to deposit, are introduced into a vacuum chamber containing the object to be coated, called the substrate.
When these gases come into contact with the heated substrate, they react or decompose, leaving behind a solid material that bonds to the surface. The remaining gaseous byproducts are then exhausted from the chamber.
The Role of Energy
Traditionally, heat is the energy source that drives the chemical reaction. The substrate is typically heated to high temperatures, often between 850°C and 1100°C.
This high thermal energy is what breaks the chemical bonds in the precursor gases, allowing the deposition to occur. The specific temperature is a critical parameter for controlling the film's quality.
Why Choose CVD? Key Characteristics
CVD is selected over other methods when the quality and specific properties of the final film are paramount.
Unmatched Purity and Quality
Films produced by CVD are known for their high purity and density. The process creates a strong, well-adhered layer that is exceptionally hard and resistant to damage.
Superior Surface Coverage
A key advantage of CVD is its ability to create a uniform coating, even on objects with complex shapes. This is known as having good "wrap-around" properties, ensuring a consistent film thickness across the entire surface.
Versatility of Materials
The CVD process is incredibly versatile. It can be used to deposit a wide range of materials, including metal films, non-metal films (like silicon dioxide), multi-component alloys, and advanced ceramics. It is also a key method for producing graphene.
Precise Structural Control
By carefully adjusting process parameters like temperature, pressure, and gas composition, engineers can precisely control the final film's chemical composition, crystal structure, and grain size.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, CVD is not without its challenges. The primary drawbacks are its high operating temperature and equipment complexity.
The High-Temperature Challenge
The most significant limitation of traditional CVD is its high reaction temperature. Many potential substrate materials, such as plastics or certain metals, cannot withstand the intense heat without melting or deforming.
Equipment and Facility Costs
Implementing CVD requires sophisticated equipment and cleanroom facilities. This makes the initial investment and operating costs significantly higher than some alternative coating methods.
Mitigating the Temperature Problem: Plasma
To overcome the temperature limitation, variations like Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) have been developed. This method uses an energy-rich plasma, rather than just heat, to facilitate the chemical reaction.
Using plasma allows the deposition to occur at much lower temperatures, making it possible to coat temperature-sensitive substrates that would be damaged by traditional CVD.
Where CVD Fits in the Deposition Landscape
CVD is one of several techniques used for creating thin films, each with its own specific use case.
CVD vs. PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition)
Vapor deposition is broadly divided into two families: CVD and PVD. While CVD uses a chemical reaction to form the film, PVD uses a physical process (like evaporation or sputtering) to transfer material from a solid source to the substrate.
Other Chemical Deposition Methods
CVD is the most prominent member of a family of chemical deposition techniques that also includes Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD) and electroplating. These methods all rely on chemical processes to form a solid material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition method depends entirely on the material requirements, substrate limitations, and project budget.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and film quality on a durable substrate: Traditional, high-temperature CVD is the industry standard for achieving superior performance.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material like a polymer: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the essential alternative that enables high-quality films at lower temperatures.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a less demanding application: You should investigate simpler alternatives like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) or Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD).
Ultimately, understanding the trade-offs between chemical and physical processes empowers you to select the precise tool for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Precursor gases react on a heated substrate to form a solid thin film. |
| Key Advantage | Unmatched film purity, density, and uniform coverage on complex shapes. |
| Primary Limitation | High operating temperatures (850-1100°C) can damage sensitive substrates. |
| Common Variant | Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) enables lower-temperature deposition. |
| Typical Applications | Microelectronics, advanced ceramics, protective coatings, graphene synthesis. |
Ready to integrate high-purity thin films into your research or production?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including systems for Chemical Vapor Deposition. Whether you need the high-temperature performance of traditional CVD or the versatility of Plasma-Enhanced CVD for temperature-sensitive materials, our solutions are designed to deliver the superior film quality and control your work demands.
Let's discuss your specific substrate and material goals. Contact our experts today to find the ideal deposition system for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















