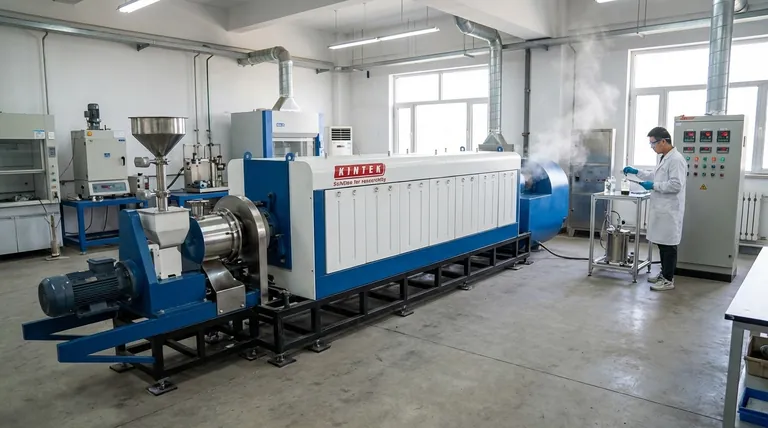
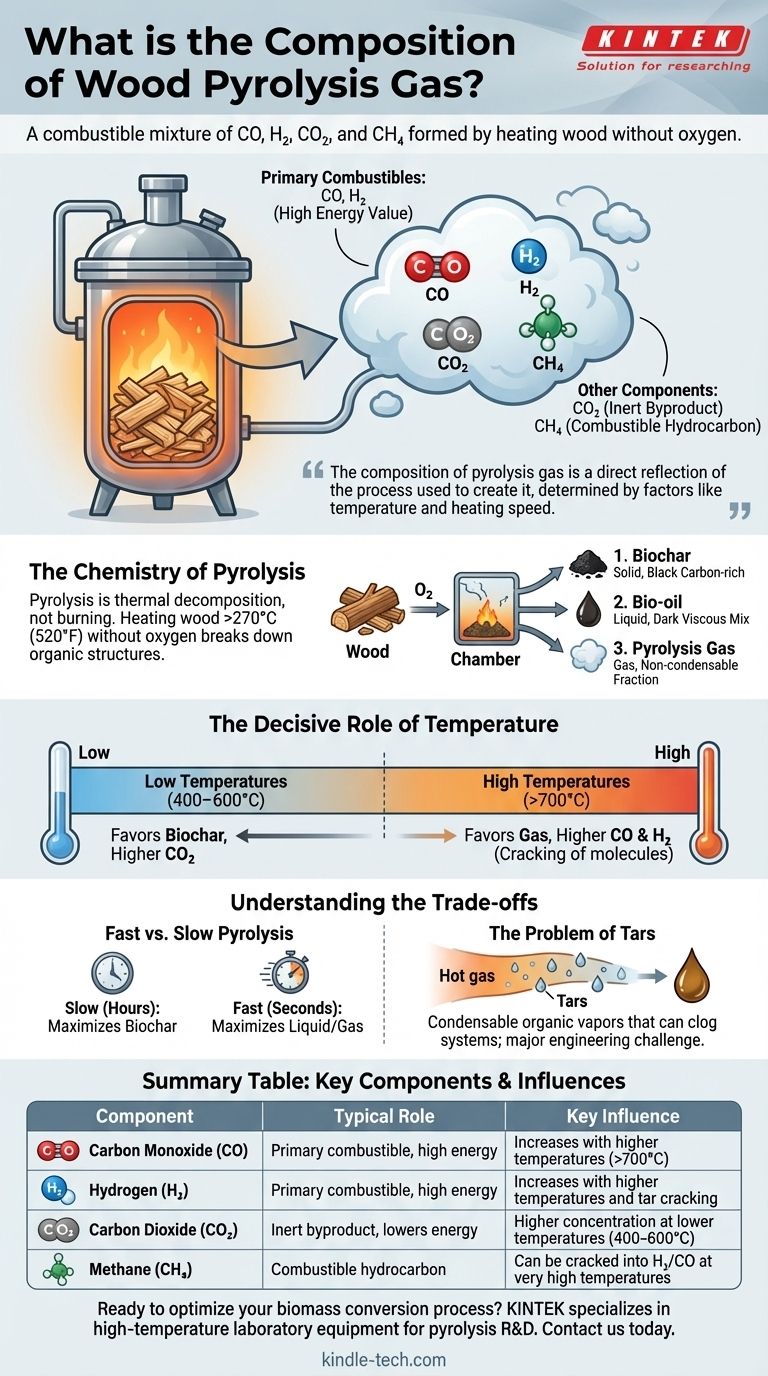
At its core, wood pyrolysis gas is a combustible mixture primarily composed of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H₂), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and methane (CH₄). This gas, often called syngas or wood gas, is one of three products created when wood is heated to high temperatures in an environment with little to no oxygen. The exact percentage of each gas is not fixed; it changes dramatically based on the process conditions, especially temperature.
The composition of pyrolysis gas is a direct reflection of the process used to create it. While always containing a mix of CO, H₂, CO₂, and CH₄, the ratio of these components—and thus the gas's energy value—is determined by factors like temperature and the speed of the heating process.

The Chemistry of Pyrolysis
What is Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is thermal decomposition, not burning. When you heat wood above 270°C (520°F) without oxygen, its complex organic structures (cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin) break down into simpler substances.
This is fundamentally different from combustion, which occurs when wood is heated with oxygen. Combustion releases energy as heat and light, leaving behind non-combustible ash. Pyrolysis rearranges the chemical energy of the wood into new, stable forms.
The Three Core Products
The decomposition of wood via pyrolysis results in three distinct products:
- Biochar (Solid): A black, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal. It is the solid residue left after the volatile components have been driven off.
- Bio-oil (Liquid): A dark, viscous liquid that condenses from the hot vapor. It is a complex mix of water and hundreds of organic compounds.
- Pyrolysis Gas (Gas): The non-condensable fraction that remains a gas after cooling. This is the focus of your question.
Unpacking the Gas Composition
The gas produced during pyrolysis is a mixture whose properties depend heavily on the process parameters.
The Primary Combustibles: CO and H₂
Carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H₂) are the most valuable components from an energy perspective. They are the defining ingredients of "syngas" and are produced when larger organic molecules "crack" or break apart at high temperatures.
The Other Key Components: CO₂ and CH₄
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) is an unavoidable byproduct, formed from the decomposition of carboxyl groups in the wood. Methane (CH₄) is the simplest hydrocarbon and is also formed as the wood structure breaks down. Lesser amounts of other light hydrocarbons like ethane and ethene may also be present.
The Decisive Role of Temperature
Temperature is the single most important variable controlling gas composition and yield.
- Low Temperatures (400–600°C): This range favors the production of biochar. The resulting gas has a lower energy content, with higher concentrations of CO₂.
- High Temperatures (>700°C): This range favors the production of gas. The intense heat causes secondary "cracking" of heavier molecules (like tars and even methane) into smaller, simpler gas molecules like H₂ and CO. This increases both the total gas yield and its overall energy value.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The ideal gas composition is not universal; it depends entirely on the intended application. Understanding the process trade-offs is key.
Fast vs. Slow Pyrolysis
The heating rate significantly changes the product distribution. Slow pyrolysis, where the temperature is increased over hours, maximizes the yield of biochar. Fast pyrolysis, which heats the wood to the target temperature in seconds, maximizes the liquid (bio-oil) and gas yields by minimizing the time for char-forming reactions to occur.
The Inevitable Problem of Tars
The hot gas stream coming directly out of the pyrolyzer is not "clean." It contains condensable organic vapors known as tars. If the gas is cooled, these tars condense into a sticky, thick liquid that can clog pipes, foul sensors, and damage engines. Managing and either removing or cracking these tars is a major engineering challenge in utilizing pyrolysis gas.
Feedstock Matters
While this guide focuses on wood, the type of wood, its moisture content, and its particle size all influence the process. Drier, smaller particles pyrolyze more efficiently and can lead to a cleaner, more consistent gas output.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal approach to pyrolysis depends on which of the three products you want to prioritize.
- If your primary focus is producing high-energy gas for fuel: You must use high temperatures (>700°C) and likely a secondary catalytic or thermal cracking step to convert unwanted tars into more H₂ and CO.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar for agriculture or carbon sequestration: You should use slow pyrolysis at lower temperatures (400-600°C), accepting that the co-produced gas will be of lower quality and volume.
- If your primary focus is producing bio-oil as a liquid fuel precursor: You should use fast pyrolysis at moderate temperatures (around 500°C), which creates a significant volume of gas as a valuable co-product.
Ultimately, wood pyrolysis is a flexible platform for converting biomass into a portfolio of valuable products, and the gas composition is a direct lever you can control to meet your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Component | Typical Role in Pyrolysis Gas | Key Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Primary combustible, high energy value | Increases with higher temperatures (>700°C) |
| Hydrogen (H₂) | Primary combustible, high energy value | Increases with higher temperatures and tar cracking |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | Inert byproduct, lowers energy value | Higher concentration at lower temperatures (400-600°C) |
| Methane (CH₄) | Combustible hydrocarbon | Can be cracked into H₂/CO at very high temperatures |
Ready to optimize your biomass conversion process?
The precise composition of your pyrolysis gas is critical to your project's success, whether your goal is maximizing energy output, producing biochar, or creating bio-oil. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature laboratory equipment and consumables essential for R&D and quality control in pyrolysis applications.
Our experts can help you select the right furnaces and reactors to achieve the exact gas composition you need. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and results.
Get in touch with our specialists
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Oscillating Orbital Shaker
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of regeneration? Optimize Your Desiccant System's Efficiency
- What is the temperature maintained in calcination zone of rotary kiln? It's All About Your Material
- What is the principle of a fluidized bed reactor? Achieve Superior Mixing and Heat Transfer
- What makes activated carbon activated? The Process That Creates a Molecular Sponge
- What is the source of heat in a rotary kiln? Unlocking the Secrets of Efficient Thermal Processing
- What is a fluidized bed chemical reaction? A Guide to Superior Heat Transfer & Continuous Processing
- What is the historical origin and evolution of the rotary kiln? From 1885 Patent to Modern Industrial Giant
- Does calcination produce CO2? Understanding the Role of Carbonates in Thermal Decomposition



















