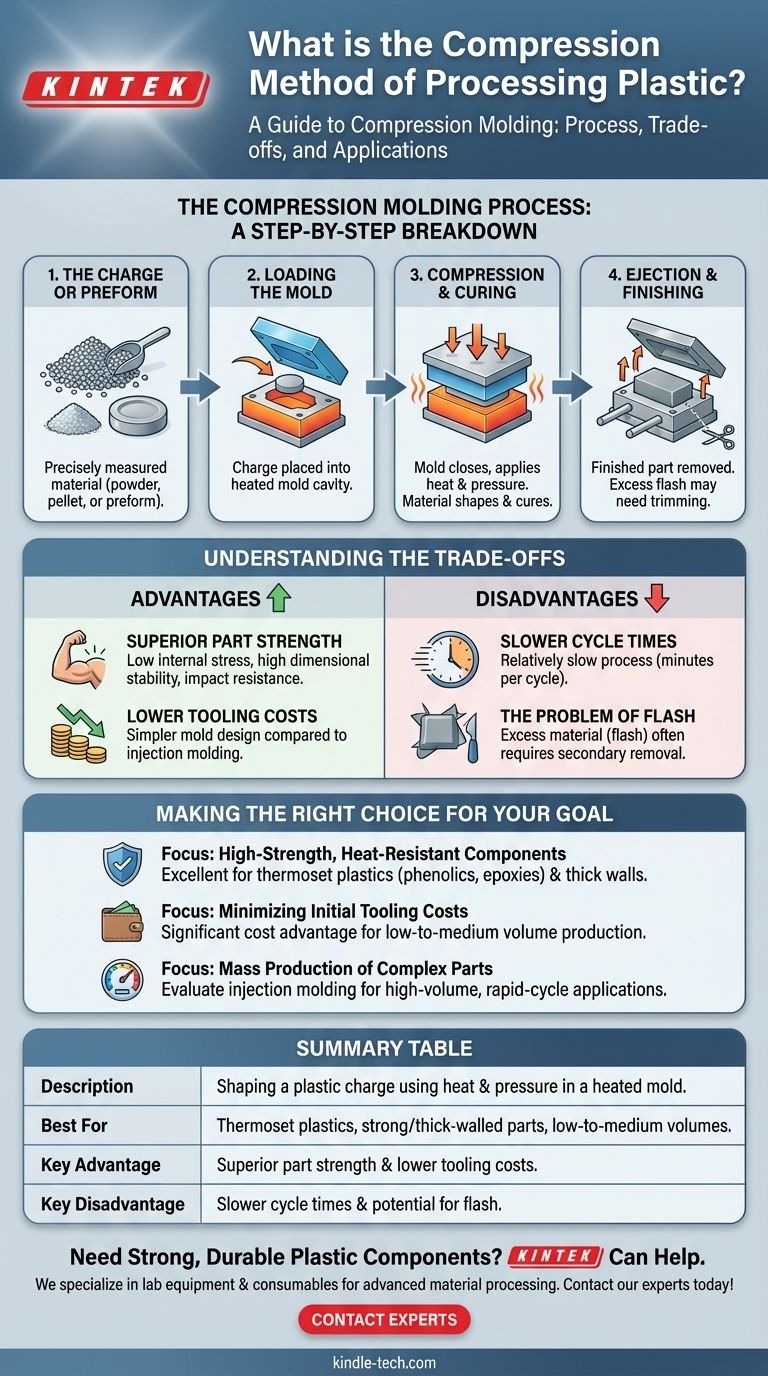
In essence, compression molding is a manufacturing process where a precise amount of plastic material is shaped using heat and pressure inside a heated mold. The material, often a pre-formed slug, is placed into the open mold cavity, the mold is closed, and pressure is applied, forcing the material to fill the cavity and conform to its shape as it cures.
The core principle of compression molding is its simplicity and effectiveness for creating strong, durable parts, particularly from thermoset plastics. While slower than other methods, it excels in producing components with excellent structural integrity and low internal stress.
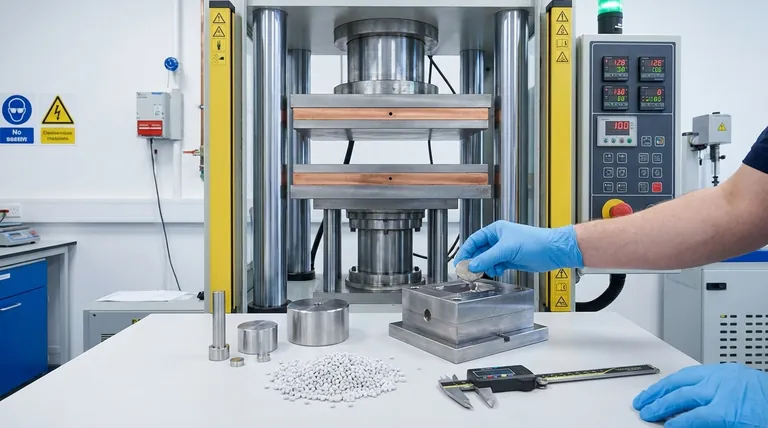

How Compression Molding Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Think of compression molding like making a waffle. You place the raw material (batter) onto a heated surface, close the lid to apply pressure, and allow heat to transform it into a finished product.
The Charge or Preform
The process begins with the "charge," which is a carefully measured quantity of the molding material. This can be in powder, pellet, or a pre-formed shape designed to roughly match the mold's contours.
Loading the Mold
The charge is placed directly into the bottom half of a heated, open mold. The mold halves are typically made of high-strength steel and are heated to a specific temperature required to soften the plastic and initiate the curing process.
Compression and Curing
The top half of the mold is then closed, applying significant hydraulic pressure. This pressure forces the softened material to flow and fill every part of the mold cavity. The combination of sustained heat and pressure not only shapes the part but also initiates a chemical reaction in thermoset plastics, causing them to harden permanently.
Ejection and Finishing
Once the curing cycle is complete, the mold is opened and the finished part is removed, often with the help of ejector pins. The part is now a solid, stable component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No manufacturing process is perfect for every application. Compression molding has a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages that make it ideal for some projects and unsuitable for others.
Advantage: Superior Part Strength
Because the material flows a shorter distance and is under consistent pressure, compression-molded parts have very low internal stress. This results in components with high dimensional stability, strength, and impact resistance, especially for parts with thick walls.
Advantage: Lower Tooling Costs
Compression molds are generally simpler in design compared to the complex runner and gate systems required for injection molding. This simplicity translates directly to lower initial tooling and setup costs.
Disadvantage: Slower Cycle Times
The need to heat the material and wait for it to cure within the mold makes compression molding a relatively slow process. Cycle times can range from one to several minutes, making it less suitable for extremely high-volume production compared to injection molding.
Disadvantage: The Problem of Flash
It is common for a small amount of excess material, known as "flash," to be squeezed out at the parting line where the mold halves meet. This flash must be removed in a secondary de-flashing or trimming operation, adding a step to the overall process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a manufacturing process depends entirely on the requirements of your part, including its material, complexity, and production volume.
- If your primary focus is high-strength, heat-resistant components with thick walls: Compression molding is an excellent choice, especially when using thermoset plastics like phenolics or epoxies.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial tooling costs for simpler, larger parts: Compression molding offers a significant cost advantage for low-to-medium volume production runs.
- If your primary focus is mass production of complex, thin-walled parts at high speed: You should evaluate injection molding, as it is far better suited for high-volume, rapid-cycle applications.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental trade-offs between strength, speed, and cost is the key to selecting the ideal manufacturing process for your product.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Shaping a plastic charge using heat and pressure in a heated mold. |
| Best For | Thermoset plastics, strong/thick-walled parts, low-to-medium volumes. |
| Key Advantage | Superior part strength and lower tooling costs. |
| Key Disadvantage | Slower cycle times and potential for flash (excess material). |
Need to produce strong, durable plastic components? The compression molding process might be the perfect solution for your laboratory or manufacturing needs. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables necessary for advanced material processing. Our expertise can help you select the right technology to achieve superior part strength and optimize your production costs. Contact our experts today via our contact form to discuss how we can support your project with reliable equipment and tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What are the specific functions of graphite molds in the vacuum hot-press sintering process? Expert Insights for Ceramics
- What role do high-temperature pressure molds play in SiCp/Al fabrication? Enhancing Densification and Thermal Uniformity
- Why is hot press molding preferred over traditional solution casting? Expert Comparison for Polymer Electrolytes
- What technical requirements must specialized pressure-bearing molds meet? Optimize Sulfide Electrolyte Densification
- What roles do graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing of Al-Sc alloys? Ensure Precision & Purity



















