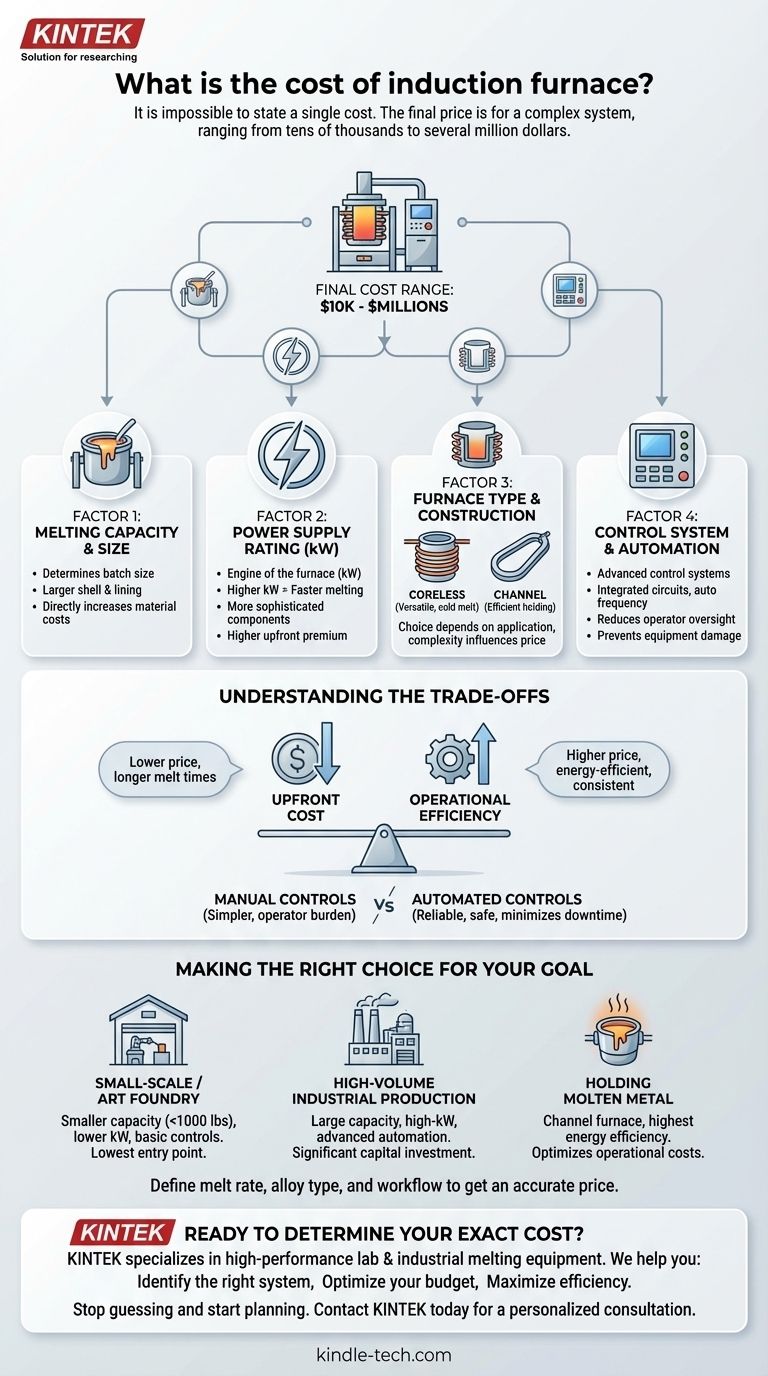
It is impossible to state a single cost for an induction furnace. The final price is not for a single product but for a complex system, with costs ranging from tens ofthousands to several million dollars. The price is determined by your specific operational requirements, including melting capacity, power rating, and the level of system automation.
The cost of an induction furnace is fundamentally tied to three core factors: its size (capacity), its power supply (kW rating), and its type (e.g., coreless vs. channel). Understanding how these elements align with your production goals is the only way to determine a realistic budget.
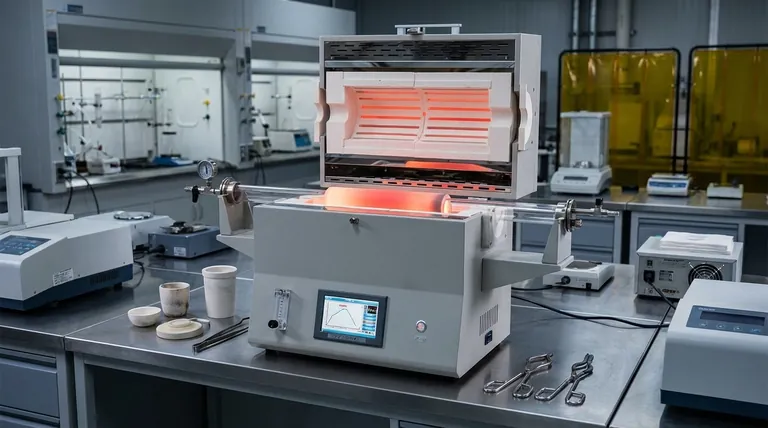

The Primary Factors Driving Induction Furnace Cost
An induction furnace is not an off-the-shelf item. It's a configured system where each major component directly influences the final investment.
Factor 1: Melting Capacity and Furnace Size
The most significant cost driver is the physical size of the furnace, which dictates how much metal you can process at once.
A larger furnace requires a heavier, more robust steel shell and a significantly greater amount of refractory lining to contain the molten metal. This directly increases material and manufacturing costs.
Factor 2: Power Supply Rating (kW)
The power supply is the engine of the furnace. Its rating, measured in kilowatts (kW), determines your melting speed.
A higher kW rating requires more sophisticated and expensive components, such as larger silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs) and inverter boards. As noted in technical specifications, these units need constant power circuit control systems that automatically adjust voltage and current, adding to their complexity and cost.
A higher-power unit melts metal faster, increasing throughput, but comes at a significant upfront premium.
Factor 3: Furnace Type and Construction
Induction furnaces are not all built the same. The two primary designs serve different purposes and have different cost structures.
A coreless furnace uses a simple, water-cooled copper coil to induce current directly into the metal charge. It is versatile and excellent for melting a wide variety of metals from a cold state.
A channel furnace, as described in the references, functions more like a transformer where a loop of molten metal acts as the secondary coil. These are extremely efficient for holding large amounts of metal at temperature or for melting low-temperature alloys, but they are less flexible.
The choice between these designs depends entirely on your application, with construction complexity influencing the price.
Factor 4: Control System and Automation
Modern furnaces rely on advanced control systems for efficiency and safety.
A basic system offers manual controls, while advanced systems feature large-scale integrated circuits for stable performance, automatic frequency scanning, and comprehensive protection systems for over-voltage or over-current conditions.
More sophisticated automation, while increasing the initial cost, reduces the need for constant operator oversight and can prevent costly equipment damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace requires balancing upfront investment against long-term operational value. A lower initial price can easily lead to higher costs down the line.
Upfront Cost vs. Operational Efficiency
A smaller power supply will reduce the initial purchase price but will result in longer melt times, lowering your plant's overall productivity.
Similarly, a well-engineered furnace with a high-integrated circuit design may cost more initially but will be more energy-efficient, reducing electricity costs over the life of the equipment. It is praised for being a "clean" technology precisely because of this efficiency.
Manual vs. Automated Controls
Opting for a simpler, manual control system can lower the initial quote. However, this places a greater burden on the operator to manage the melting process.
A system with comprehensive protection systems and a high-sensitive trigger circuit offers superior reliability and safety. This automation protects the expensive power supply components and ensures consistent, successful startups, minimizing downtime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine your likely cost, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is a small-scale or art foundry: A smaller capacity (under 1000 lbs) coreless furnace with a lower-rated power supply and basic controls offers the lowest point of entry.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production: A large-capacity furnace with a high-kW power supply and advanced automation is necessary to meet throughput demands, representing a significant capital investment.
- If your primary focus is holding molten metal at temperature: A channel furnace provides the highest energy efficiency for this specific task, optimizing operational costs over upfront flexibility.
Ultimately, defining your required melt rate, alloy type, and operational workflow is the critical first step to getting an accurate price for your system.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Cost | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Capacity | Higher capacity = Higher cost | Determines batch size and furnace shell size. |
| Power Supply (kW) | Higher kW rating = Higher cost | Drives melting speed and throughput. |
| Furnace Type | Coreless vs. Channel furnace | Coreless is versatile; Channel is efficient for holding. |
| Automation Level | Advanced controls = Higher cost | Improves safety, efficiency, and reduces operator burden. |
Ready to Determine Your Exact Induction Furnace Cost?
Navigating the complex variables of capacity, power, and automation is the key to an accurate budget. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab and industrial melting equipment, providing tailored solutions that balance upfront investment with long-term operational value.
We help you:
- Identify the right system for your production volume and metal type.
- Optimize your budget by matching specifications to your actual needs.
- Maximize efficiency with reliable equipment designed for precision and durability.
Stop guessing and start planning. Let our experts provide a detailed quote based on your specific requirements.
Contact KINTEL today for a personalized consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction and temperature control mechanism of a laboratory tube furnace? Master Precision Heating for Your Lab
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing



















