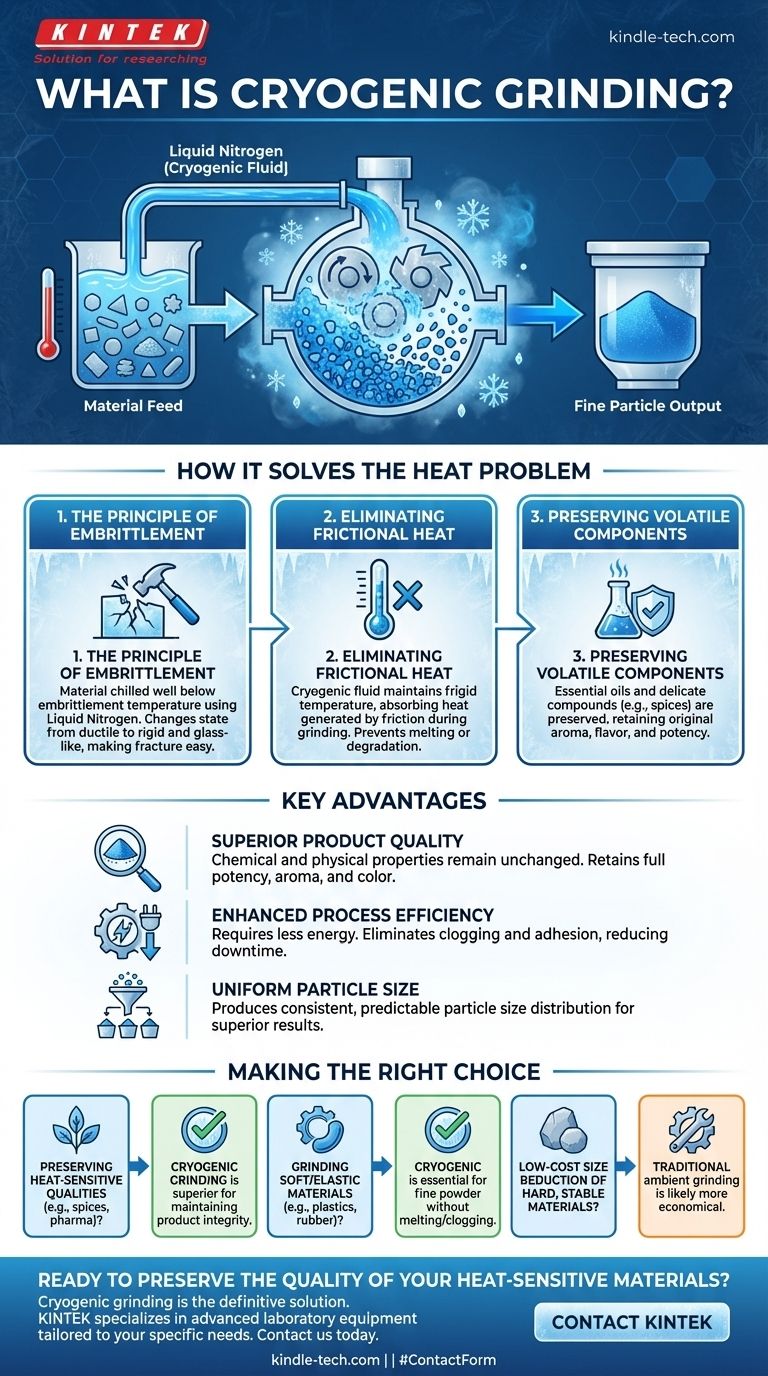
In essence, cryogenic grinding is a size-reduction process where a material is first chilled to extremely low temperatures with a cryogenic fluid, most commonly liquid nitrogen, and then fractured into fine particles. This chilling makes the material brittle, allowing it to be ground more effectively while preventing the heat damage common in traditional grinding methods.
The core purpose of cryogenic grinding is not simply to make particles smaller, but to do so while perfectly preserving the material's original quality. It leverages extreme cold to overcome the destructive heat and mechanical stress that plague conventional grinding, especially for sensitive or soft materials.

How Cryogenic Grinding Solves the Heat Problem
Traditional grinding generates immense frictional heat, which can degrade or destroy the material being processed. Cryogenic grinding fundamentally changes the equation by making the material itself resistant to heat damage.
The Principle of Embrittlement
Many materials, particularly polymers and organic matter, are tough or elastic at room temperature. Forcing them through a grinder causes them to soften, smear, and clog the machinery.
By introducing a cryogenic fluid like liquid nitrogen, the material is cooled well below its embrittlement temperature. This changes its physical state from ductile to rigid and glass-like, making it easy to fracture with minimal force.
Eliminating Frictional Heat
The cryogenic fluid serves a dual purpose. It not only embrittles the material before it enters the mill but also maintains a frigid temperature inside the grinding zone itself.
This constant cooling absorbs the heat generated by friction as it occurs, ensuring the material's temperature never rises to a point where it could melt, soften, or degrade.
Preserving Volatile Components
This process is critical for materials whose value lies in their heat-sensitive components, such as spices.
Volatile oils, which create the distinct aroma and flavor of a spice, are easily lost when exposed to the heat of conventional grinding. Cryogenic grinding preserves these delicate compounds, resulting in a final product with superior quality.
Key Advantages of the Cryogenic Method
By fundamentally altering the material's properties before grinding, the cryogenic process delivers several distinct advantages over ambient-temperature methods.
Superior Product Quality
Because the material is ground in an inert, super-cooled state, its chemical and physical properties remain unchanged. This means the final powder retains the full potency, aroma, and color of the original material.
Enhanced Process Efficiency
Grinding a brittle material requires significantly less energy than grinding a soft or elastic one. Furthermore, issues like clogging and adhesion are eliminated, leading to more consistent operation and less downtime for cleaning.
Uniform Particle Size
The clean, brittle fractures produced by cryo-grinding result in a more uniform and predictable particle size distribution. Advanced systems can be paired with classifiers to simultaneously sort the output into fine, medium, and coarse powders in a single pass.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, cryogenic grinding is a specialized technique with unique operational requirements. It is not a universal solution for all size-reduction tasks.
The Cost of Cryogens
The primary trade-off is the ongoing operational cost of liquid nitrogen. This consumable expense must be factored in and weighed against the value gained from improved product quality and efficiency.
System Complexity
Cryogenic grinding systems are more complex than their ambient counterparts. They require insulated vessels, specialized delivery systems for the cryogenic fluid, and precise temperature controls, which can increase the initial capital investment.
Material Suitability
This method provides the most significant benefit for materials that are difficult or impossible to grind at room temperature. This includes elastomers, tough polymers, and heat-sensitive organic materials. For hard, inert materials like minerals, the benefits may not justify the added cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct grinding method depends entirely on the properties of your material and your final goal.
- If your primary focus is preserving heat-sensitive qualities (e.g., spices, pharmaceuticals): Cryogenic grinding is the superior method for maintaining product integrity.
- If your primary focus is grinding soft or elastic materials (e.g., plastics, rubber): This process is essential for achieving a fine powder without melting or clogging machinery.
- If your primary focus is low-cost size reduction of hard, stable materials (e.g., ceramics, rocks): Traditional ambient grinding is likely the more economical and straightforward choice.
Ultimately, choosing cryogenic grinding is an investment in preserving the inherent value of your material through the size-reduction process.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Cryogenic Grinding Benefit |
|---|---|
| Heat Management | Eliminates frictional heat, preventing material degradation. |
| Material Embrittlement | Makes tough or elastic materials brittle for easier grinding. |
| Quality Preservation | Maintains potency, aroma, and color of heat-sensitive materials. |
| Process Efficiency | Reduces energy use, clogging, and machine downtime. |
| Particle Uniformity | Produces a consistent, predictable particle size distribution. |
Ready to preserve the quality of your heat-sensitive materials?
Cryogenic grinding is the definitive solution for processing sensitive materials like spices, polymers, and pharmaceuticals without compromising their essential properties. If your goal is to achieve a fine, uniform powder while retaining volatile oils, flavors, and chemical integrity, this method is essential.
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory equipment, including cryogenic grinding systems tailored to your specific needs. Our solutions help you enhance product quality, improve process efficiency, and protect your valuable materials.
Contact us today to discuss how a cryogenic grinding system from KINTEK can benefit your laboratory. Let's find the perfect solution for your size-reduction challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill with Screw Feeder
- lab cryogenic grinding use liquid-nitrogen for pulverizing plastic raw materials and heat sensitive materials
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is cryogenic grinding used? To pulverize tough, heat-sensitive materials effectively.
- Which tool could be used to pulverize an object? Match the Tool to Your Material's Hardness and Brittleness
- How do laboratory grinders and standard sieving systems ensure the quality of feedstock for torrefaction?
- What is the purpose of the grinding process for Titanium Dioxide? Maximize Surface Area and Photocatalytic Efficiency
- What is the purpose of a pulverizer? Unlock Material Potential with Fine Grinding


















