In the world of lab-grown diamonds, the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) method is a sophisticated process that essentially "grows" a diamond atom by atom. It works by placing a small diamond "seed" into a vacuum chamber, introducing a carbon-rich gas like methane, and using energy to break the gas apart. This allows pure carbon atoms to settle, or "deposit," onto the seed, building up a new, larger diamond layer by layer over several weeks.
The CVD method is best understood as a high-tech "additive" process for creating diamonds. Unlike the brute-force compression of the alternative HPHT method, CVD meticulously builds a gemstone from a vaporized carbon source in a controlled, low-pressure environment.
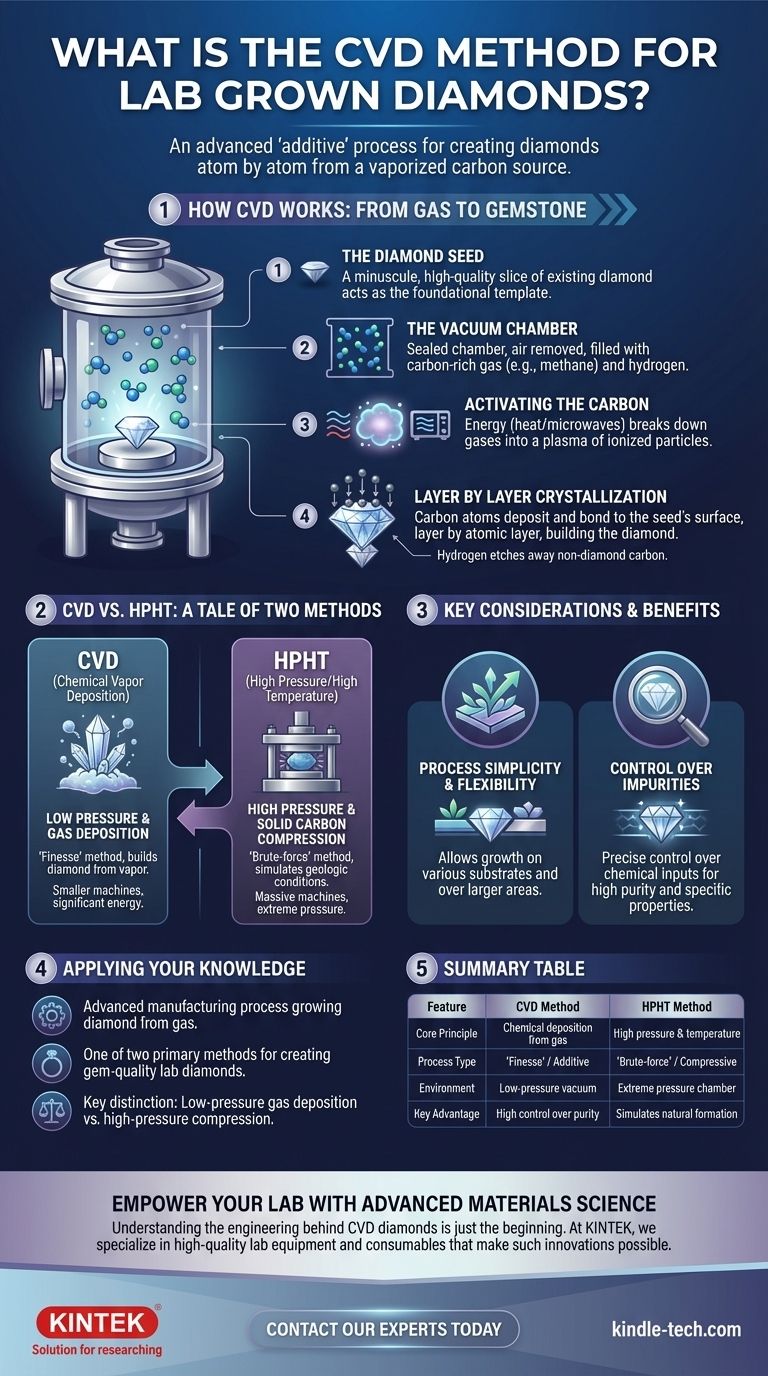
How CVD Works: From Gas to Gemstone
The CVD process is a feat of material science that mimics diamond formation found in interstellar gas clouds, but on a highly accelerated timeline. The entire process takes place inside a specialized vacuum chamber.
The Starting Point: The Diamond Seed
The process begins with a "seed," which is a minuscule, high-quality slice of an existing diamond. This seed acts as the foundational template upon which the new diamond crystal will grow.
Creating the Ideal Environment: The Vacuum Chamber
This diamond seed is placed inside a vacuum chamber. The chamber is sealed and all air is removed to prevent contamination from other elements. It is then filled with a precise mixture of gases, primarily a carbon-rich gas (like methane) and hydrogen.
The Growth Phase: Activating the Carbon
Energy, typically in the form of heat or microwaves, is introduced into the chamber. This energy superheats the gases to extreme temperatures, breaking down the molecular bonds and creating a plasma cloud of ionized particles.
Layer by Layer Crystallization
Within this plasma, carbon atoms separate from the gas molecules. These free carbon atoms are drawn down to the cooler diamond seed, bonding to its surface and replicating its crystal structure. The hydrogen gas plays a critical role by selectively etching away any non-diamond carbon (like graphite), ensuring only pure diamond forms. This meticulous process continues, layer by atomic layer, until a new, rough diamond is fully formed.
CVD vs. HPHT: A Tale of Two Methods
While other experimental methods exist, CVD and High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT) are the two dominant processes for creating lab-grown diamonds. They operate on fundamentally different principles.
The Core Difference: Pressure and Force
HPHT is a "brute-force" method that simulates the geologic conditions deep within the Earth. It subjects solid carbon to immense pressure and high temperatures, forcing it to crystallize into a diamond.
CVD, by contrast, is a "finesse" method. It uses very low pressure and relies on a chemical reaction to deposit carbon atoms from a gas, building the diamond up from a seed.
Equipment and Energy
The HPHT process requires massive, powerful machines capable of generating extreme pressure. The CVD method uses smaller machines and operates at low pressure, though it still requires significant energy to generate the necessary heat and plasma.
Suitability for Gem Quality
While both methods can produce high-quality gems, the references note that CVD is becoming an increasingly popular choice for producing gem-quality diamonds specifically for the jewelry market. The process offers excellent control over the final product's properties.
Understanding the Key Considerations
The choice of manufacturing method has tangible implications for the process and the industry. Understanding these points provides a clearer picture of why CVD has gained prominence.
Process Simplicity and Flexibility
The CVD method is described as being relatively simple and flexible. It allows for the growth of diamonds on various types of substrates and over larger areas compared to the contained environment of an HPHT press.
Control Over Impurities
A key advantage of the CVD process is the ability to precisely control the chemical inputs. This gives manufacturers a high degree of control over the purity and resulting properties of the diamond being grown.
How to Apply This to Your Understanding
Your goal determines which aspects of the CVD process are most relevant to you.
- If your primary focus is the technology: Recognize CVD as an advanced manufacturing process that "grows" a diamond from gas, fundamentally different from the compression-based HPHT method.
- If your primary focus is the final jewelry product: Know that CVD is one of the two primary, legitimate methods for creating the gem-quality lab diamonds widely available today.
- If your primary focus is comparing methods: Use the core mechanism—low-pressure gas deposition (CVD) versus high-pressure carbon compression (HPHT)—as the key point of distinction.
Understanding this process empowers you to see a lab-grown diamond not as a mere alternative, but as a marvel of modern material science.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD Method | HPHT Method |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Chemical deposition from gas | High pressure & temperature |
| Process Type | "Finesse" / Additive | "Brute-force" / Compressive |
| Environment | Low-pressure vacuum chamber | Extreme pressure chamber |
| Key Advantage | High control over purity & properties | Simulates natural formation |
Empower Your Lab with Advanced Materials Science
Understanding the precise engineering behind CVD diamonds is just the beginning. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables that make such innovations possible.
Whether you are researching advanced materials, developing new crystal growth processes, or need reliable supplies for your laboratory, KINTEK is your trusted partner. Our expertise supports the cutting-edge work that turns scientific concepts into reality.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your specific laboratory needs and help you achieve your research and development goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition



















