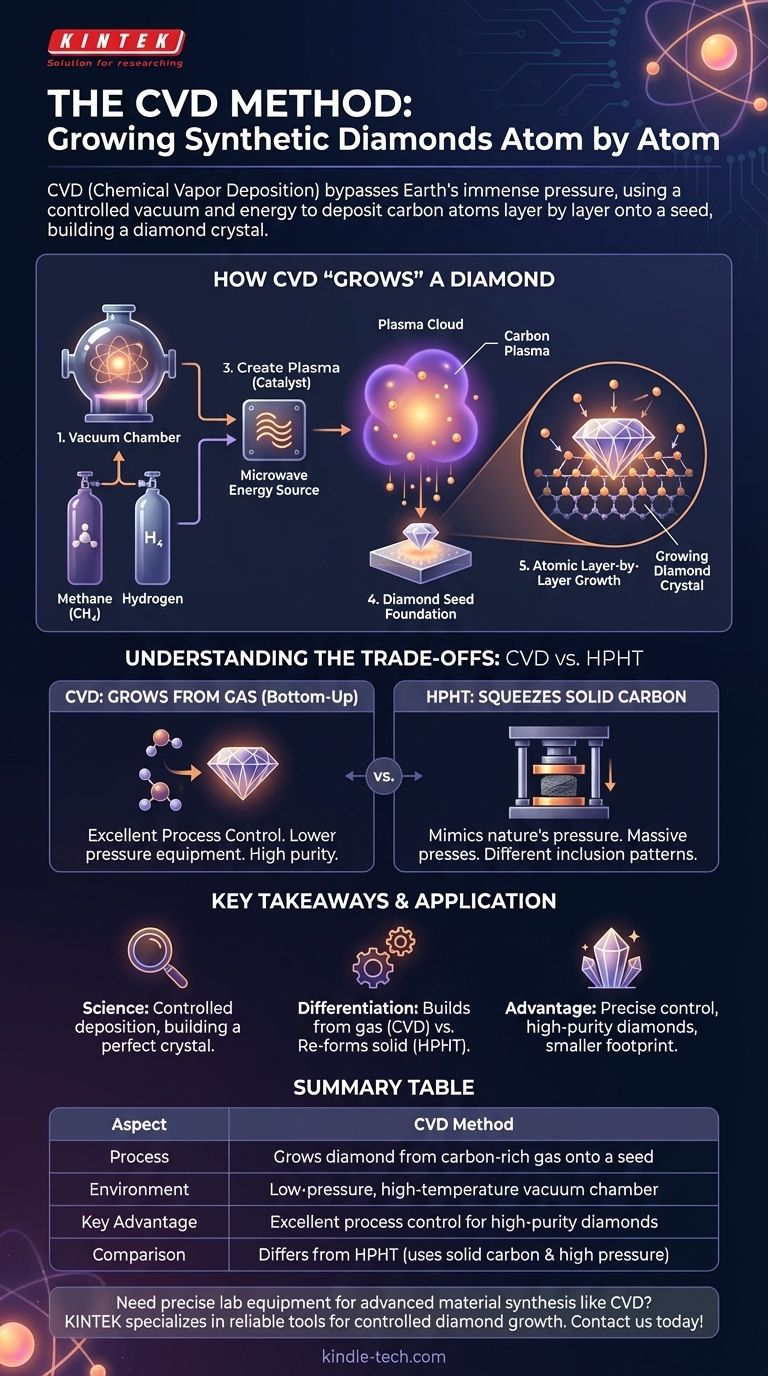
In essence, the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) method is a process for "growing" synthetic diamonds atom by atom. It involves placing a diamond seed crystal in a vacuum chamber, introducing a carbon-rich gas like methane, and using an energy source like microwaves to break down the gas molecules. This allows pure carbon atoms to deposit onto the seed, slowly building up a new, larger diamond crystal that is chemically identical to a natural one.
While natural diamonds are formed by immense pressure deep within the Earth, CVD technology bypasses this requirement entirely. It instead creates the ideal low-pressure, high-temperature conditions to build a diamond layer by layer, offering remarkable control over the final product.
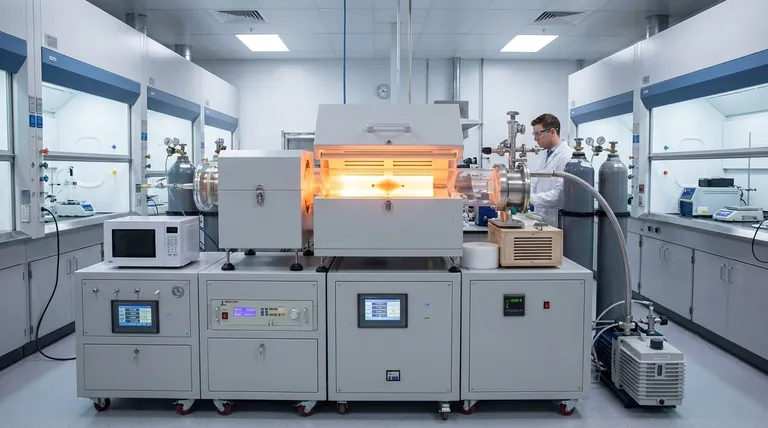

How CVD "Grows" a Diamond from Gas
The CVD process is a highly controlled, technical procedure that replicates the conditions needed for carbon atoms to bond into a diamond crystal structure, but without the geological force of nature.
The Chamber: Creating a Vacuum
The entire process takes place inside a sealed vacuum chamber. The pressure is reduced significantly, creating an environment that can be precisely managed and is free of contaminants that could disrupt crystal growth.
The Ingredients: Carbon-Rich Gas
A carefully measured mixture of gases is introduced into the chamber. This is typically a hydrocarbon gas, like methane (CH₄), which serves as the source of carbon, and hydrogen gas.
The Catalyst: Creating Carbon Plasma
An energy source, most commonly microwaves, is used to heat the gases to extreme temperatures (around 800°C or higher). This intense energy splits the gas molecules apart, creating a cloud of chemically reactive carbon and hydrogen atoms known as plasma.
The Foundation: The Diamond Seed
A small, thin slice of a previously created diamond (either natural or synthetic) is placed on a substrate in the chamber. This "seed" crystal provides the foundational template for the new diamond's crystal lattice.
The Result: Atomic Layer-by-Layer Growth
Within the plasma, carbon atoms are drawn to the cooler surface of the diamond seed. They bond to the seed's existing crystal structure, meticulously building new layers and expanding the diamond, atom by atom. The process continues for weeks until the desired size is achieved.
Understanding the Trade-offs: CVD vs. HPHT
CVD is one of two dominant methods for producing gem-quality synthetic diamonds. The other is High-Pressure/High-Temperature (HPHT). Understanding their differences is key to understanding the technology.
The Core Principle: Growth vs. Compression
The fundamental difference is in the approach. CVD "grows" a diamond from a gas in a bottom-up process. In contrast, HPHT mimics nature by "squeezing" solid carbon (like graphite) under immense pressure and high temperatures until it crystallizes into a diamond.
Equipment and Control
The CVD method generally requires a smaller equipment footprint than the massive presses used for HPHT. As noted in technical analyses, the CVD process allows for excellent process control, giving manufacturers a high degree of influence over the diamond's growth and purity.
Resulting Diamond Characteristics
Because the growth environments are so different, the two methods can produce diamonds with distinct characteristics. The types and patterns of inclusions (internal flaws) often differ, which is one way gemological labs can distinguish between CVD and HPHT synthetic diamonds.
How to Apply This to Your Understanding
Your reason for investigating CVD diamonds determines which details are most important. Use these points to focus your knowledge.
- If your primary focus is the fundamental science: See CVD as a controlled deposition technique where carbon atoms are selectively "rained" down from a plasma onto a template to build a perfect crystal.
- If your primary focus is differentiating synthetic methods: The key is that CVD builds a diamond up from a gas, while HPHT re-forms a solid carbon source under force.
- If your primary focus is the commercial and technical advantage: The value of CVD lies in its precise process control and its ability to produce high-purity diamonds without the colossal machinery required for HPHT.
Ultimately, understanding the CVD process reveals how human ingenuity can replicate one of nature's most extreme creation events in a highly controlled laboratory setting.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | CVD Method |
|---|---|
| Process | Grows diamond from carbon-rich gas onto a seed crystal |
| Environment | Low-pressure, high-temperature vacuum chamber |
| Key Advantage | Excellent process control for high-purity diamonds |
| Comparison | Differs from HPHT, which uses high pressure and temperature on solid carbon |
Need precise, high-quality lab equipment for advanced material synthesis like CVD? KINTEK specializes in supplying reliable laboratory equipment and consumables to support your research and production. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools for controlled processes like diamond growth. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating



















