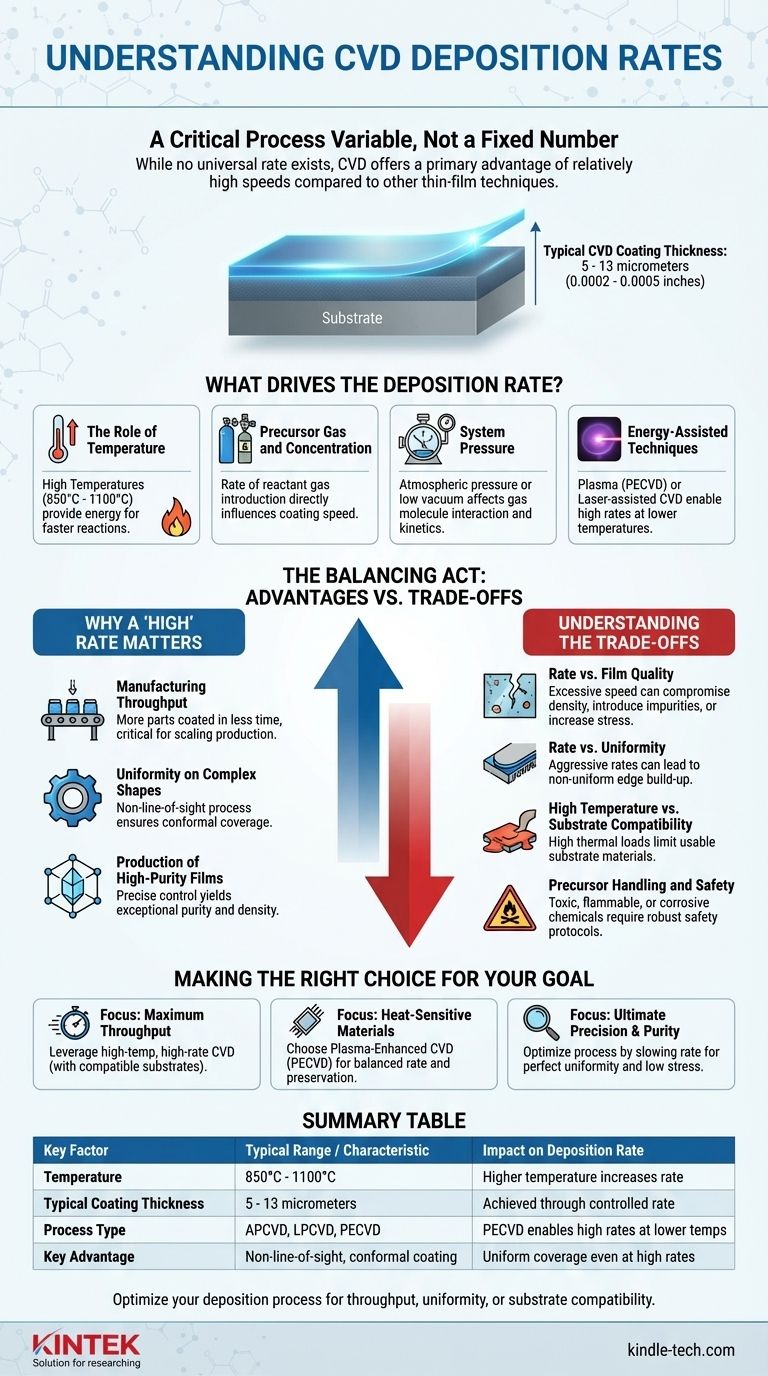
While there is no single universal number for the deposition rate of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), its rate is considered a primary advantage of the process, often described as relatively high compared to other thin-film techniques. The final thickness of a typical CVD coating ranges from .0002 to .0005 inches (approximately 5 to 13 micrometers), and the speed at which this is achieved is a carefully controlled variable dependent on multiple factors.
The deposition rate in CVD is not a fixed value but a critical process variable. Its key advantage is being relatively high, enabling efficient manufacturing, but this speed must always be balanced against the desired film properties, such as purity, uniformity, and stress.
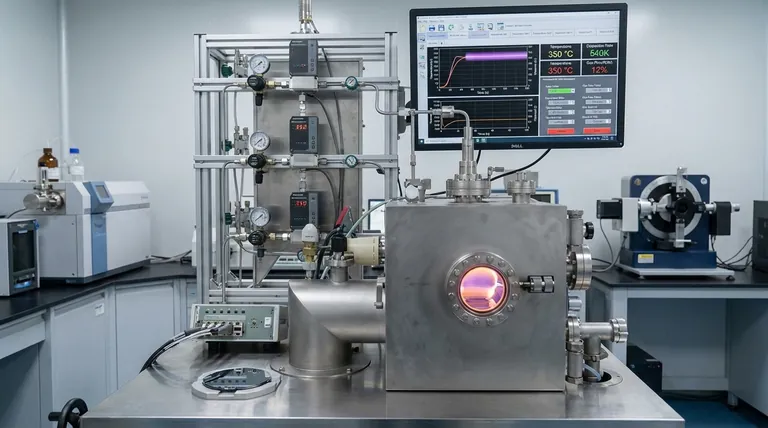

What Drives the Deposition Rate in CVD?
The speed of a CVD process is the result of a chemical reaction occurring on a substrate's surface. Several key parameters are adjusted to control the rate and quality of this reaction.
The Role of Temperature
Most CVD processes rely on high temperatures, typically between 850°C and 1100°C (around 1925°F), to provide the necessary energy to drive the chemical reactions. Generally, higher temperatures lead to faster reactions and thus higher deposition rates.
Precursor Gas and Concentration
The reactant gases, or precursors, are the building blocks of the film. The rate at which these gases are introduced into the reaction chamber and their concentration directly influence how quickly the coating can form.
System Pressure
CVD can be performed at normal atmospheric pressure or in a low vacuum. The pressure inside the chamber affects how the gas molecules travel and interact, which in turn influences the reaction kinetics and the final deposition rate.
Energy-Assisted Techniques
To overcome the limitations of high temperature, methods like plasma-enhanced CVD (PECVD) or laser-assisted CVD are used. These techniques apply energy from plasma or light to the precursor gases, allowing for high deposition rates at significantly lower temperatures.
Why a "High" Rate Matters
The "high" deposition rate of CVD is not just about speed; it's about enabling a unique combination of efficiency and quality that makes the process valuable.
Manufacturing Throughput
For industrial applications, a higher deposition rate means more parts can be coated in less time. This efficiency is critical for scaling production and managing costs.
Uniformity on Complex Shapes
CVD is a non-line-of-sight process. Because the coating is formed from a gas, it can uniformly cover highly complex and intricate surfaces. A well-controlled rate ensures this conformal coating is even across the entire component.
Production of High-Purity Films
Despite its speed, CVD is capable of producing films with exceptional purity and density. The process builds the coating molecule by molecule through a chemical reaction, allowing for precise control over the final material's composition and crystal structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A high deposition rate is desirable, but it comes with critical trade-offs that must be managed to achieve the desired outcome.
Rate vs. Film Quality
Pushing for the maximum possible deposition rate can compromise the quality of the film. Excessively high rates can introduce impurities, create a less dense structure, or increase residual stress in the coating.
Rate vs. Uniformity
An overly aggressive deposition rate can lead to non-uniformity. One common issue is a higher rate of edge build-up, where the coating becomes thicker on the edges of a component than in the center.
High Temperature vs. Substrate Compatibility
The very high temperatures that enable fast deposition rates also limit the types of materials that can be coated. Many substrates cannot withstand the thermal load without being damaged or deformed.
Precursor Handling and Safety
The chemicals used in CVD are often toxic, flammable, or corrosive. A process designed for high throughput requires robust safety protocols for handling and disposing of these potentially hazardous materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal deposition rate is determined entirely by the goals of your specific application. You must treat the rate as a tunable parameter to be balanced against other requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput for robust components: You can leverage the high-temperature, high-rate capabilities of traditional CVD, provided your substrate material can handle the heat.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials: A lower-temperature process like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the superior choice, balancing a good deposition rate with substrate preservation.
- If your primary focus is ultimate precision and film purity: You will need to carefully optimize the process, likely slowing the deposition rate to ensure perfect uniformity, low stress, and the highest possible quality.
Ultimately, viewing the deposition rate as a flexible parameter, rather than a fixed number, is the key to successfully applying CVD technology.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Typical Range / Characteristic | Impact on Deposition Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 850°C - 1100°C | Higher temperature increases rate |
| Typical Coating Thickness | 5 - 13 micrometers | Achieved through controlled rate |
| Process Type | APCVD, LPCVD, PECVD | PECVD enables high rates at lower temps |
| Key Advantage | Non-line-of-sight, conformal coating | Uniform coverage even at high rates |
Need to optimize your deposition process for throughput, uniformity, or substrate compatibility?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables to precisely control your CVD parameters. Whether you are scaling up production or require the highest film purity for R&D, our expertise can help you achieve the perfect balance between speed and quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific CVD needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















