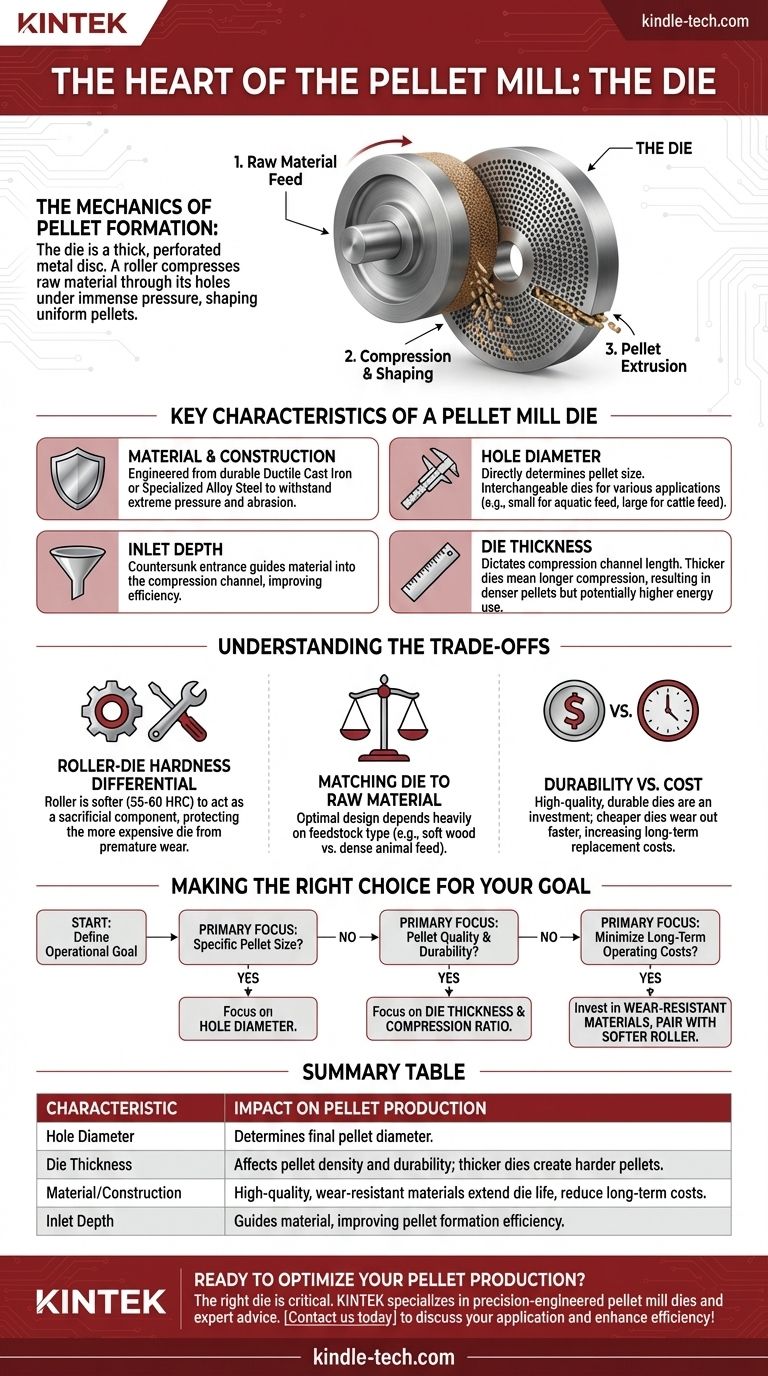
In simple terms, the die is the heart of a pellet mill. It is a thick, perforated metal disc that works with a roller to compress and shape raw materials into uniform pellets. The die's design is the single most critical factor in determining the quality of the final pellets and the overall efficiency of the production process.
The pellet mill die is not just a component; it is the molding tool that dictates the final pellet's size, density, and quality. Understanding its characteristics is essential for controlling production outcomes and minimizing operational costs.

The Mechanics of Pellet Formation
A pellet mill functions by forcing raw material through the holes of the die under immense pressure. This process relies on the precise interaction between the die and one or more rollers.
The Die and Roller Partnership
As raw materials are fed into the pelletizing chamber, they are spread across the face of the die. A rotating roller then travels over the material, creating a powerful force that presses the feedstock into the die's holes. The larger the roller, the more effectively it can grab material and force it into the die.
The Extrusion and Shaping Process
Once inside the die holes, the material is intensely compressed. The length and shape of these holes determine the final density and durability of the pellet. As the compressed material is extruded out the other side, it is typically cut to a consistent length, resulting in the final, uniform pellets.
The Value of Visibility
Modern pellet mills often include a visibility feature. This allows operators to directly observe the interaction between the roller and the die, making it easier to identify and troubleshoot issues like uneven feed distribution or blockages in real-time.
Key Characteristics of a Pellet Mill Die
The performance of a die is defined by several critical design specifications. Each one has a direct impact on the final product.
Material and Construction
The die is typically a disc made from highly durable materials like ductile cast iron or specialized alloy steel. It is engineered to withstand extreme pressure and abrasion during operation.
Hole Diameter
The diameter of the holes in the die directly determines the diameter of the pellets. Dies are interchangeable, allowing a single mill to produce pellets of various sizes by simply swapping out the die. For example, smaller diameters are used for aquatic feed, while larger diameters are common for cattle feed.
Inlet Depth
Each hole has a countersunk or beveled entrance known as the inlet depth. This design helps guide raw material into the compression channel, improving the efficiency of the pelletizing process.
Die Thickness
The overall thickness of the die dictates the length of the compression channel (the hole). A thicker die provides a longer compression time, which can lead to denser, more durable pellets, but may also require more energy and reduce output.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting and maintaining a die involves balancing competing factors. Making the wrong choice can lead to poor pellet quality and increased operational costs.
The Roller-Die Hardness Differential
To maximize the lifespan of the more expensive die, the roller is intentionally made from a softer alloy steel (typically 55-60 HRC). The roller is designed as a sacrificial component that wears out faster, protecting the die from premature failure.
Durability vs. Cost
A high-quality, durable die is a significant investment. While a cheaper die lowers initial costs, it will wear out faster, leading to more frequent replacements and higher long-term costs per ton of pellets produced.
Matching Die to Raw Material
There is no universal die. The optimal design—including hole diameter, thickness, and inlet depth—depends heavily on the type of raw material being processed. A die designed for soft wood biomass will perform poorly with dense animal feed formulations, and vice versa.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational goal should guide your die selection and management strategy.
- If your primary focus is producing a specific pellet size: The die's hole diameter is the non-negotiable specification you must match to your requirement.
- If your primary focus is pellet quality and durability: Pay close attention to the die's thickness and compression ratio, ensuring it is optimized for your feedstock.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operating costs: Invest in a die made from superior, wear-resistant materials and pair it correctly with a slightly softer roller.
Ultimately, mastering your pellet production begins with understanding and respecting the central role of the die.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Impact on Pellet Production |
|---|---|
| Hole Diameter | Determines the final pellet diameter (e.g., small for fish feed, large for cattle feed). |
| Die Thickness | Affects pellet density and durability; thicker dies create harder pellets but may reduce output. |
| Material/Construction | High-quality, wear-resistant materials (e.g., alloy steel) extend die life and reduce long-term costs. |
| Inlet Depth | Guides material into compression channels, improving the efficiency of the pellet formation process. |
Ready to optimize your pellet production? The right die is critical for achieving high-quality, durable pellets while controlling operational costs. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision-engineered pellet mill dies and expert advice. Let our specialists help you select the perfect die for your specific raw materials and production goals. Contact us today to discuss your application and enhance your pelletizing efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Ring Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Twin Screw Extruder Plastic Granulation Machine
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- How does temperature affect forging? Master Hot, Cold, and Warm Forging for Optimal Results
- Who made the first hydraulic press? Joseph Bramah's 1795 Invention Explained
- What is the function of a precision hydraulic press in MEA fabrication? Optimize Fuel Cell Bonding and Efficiency
- How powerful is hydraulic pressure? Generate Immense Force for Heavy-Duty Applications
- Why is 127 MPa Pressure Required for LZP Green Pellets? Unlock High-Density Solid Electrolyte Performance
- What is the limitation of XRF? Understanding the Key Constraints for Accurate Analysis
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in testing conductivity? Enhancing Nanoparticle Powder Analysis
- What is a hydraulic cooler? The Essential Guide to Protecting Your Hydraulic System



















