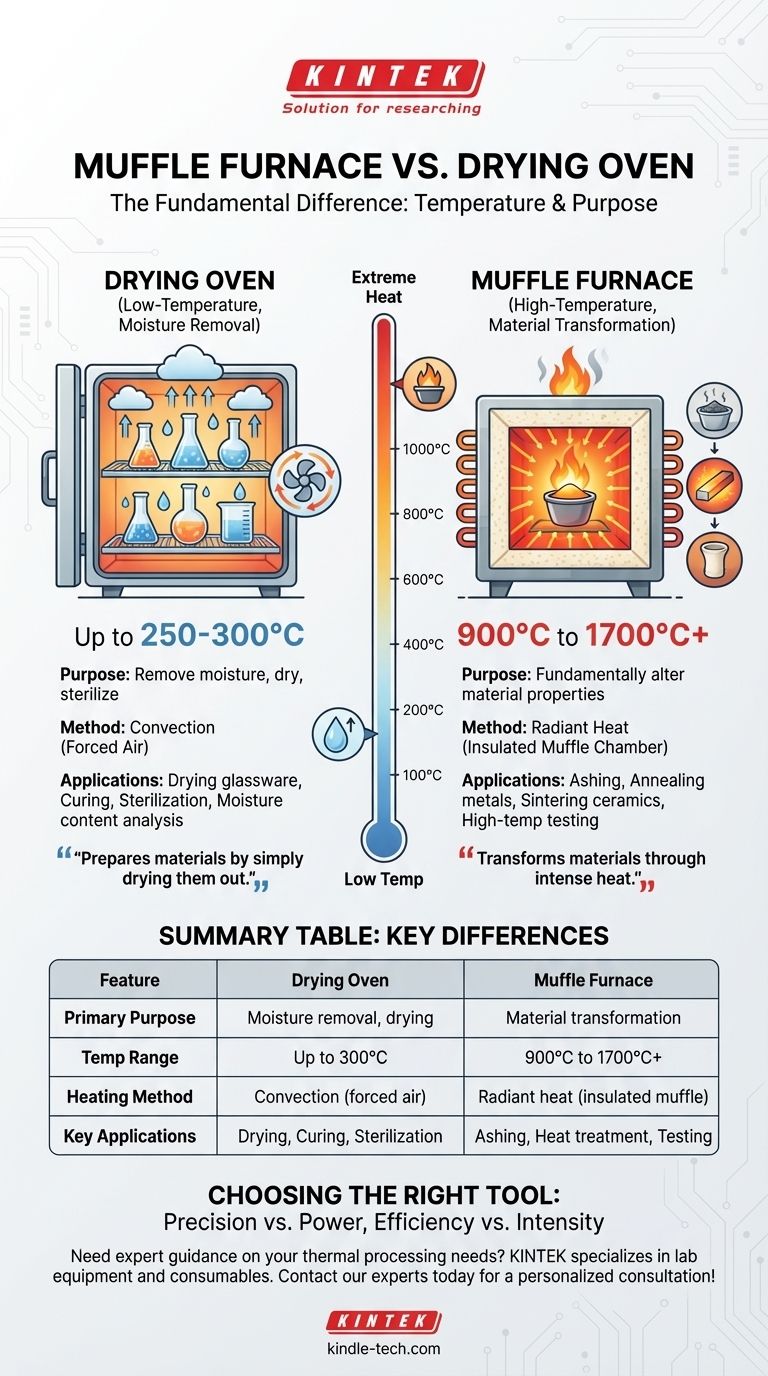
At its core, the primary difference is temperature and purpose. A muffle furnace is a high-temperature chamber designed to fundamentally alter a material's chemical or physical properties, reaching temperatures over 1000°C. A drying oven is a low-temperature device, typically operating below 300°C, designed specifically for removing moisture.
The decision between a muffle furnace and a drying oven is not about which is superior, but about aligning the tool with the thermal process. A furnace transforms materials through intense heat, while an oven prepares them by simply drying them out.

Core Functional Difference: Heat Intensity and Purpose
The most significant distinction lies not just in their maximum temperature but in the scientific goal each piece of equipment is built to achieve.
Drying Ovens: Low-Temperature Moisture Removal
A laboratory drying oven typically operates in a range from slightly above ambient temperature up to 250°C or 300°C.
Its function is straightforward: to heat a sample enough to evaporate and remove water or other volatile solvents. Common applications include drying laboratory glassware, sterilizing equipment, and performing moisture content analysis.
Muffle Furnaces: High-Temperature Material Transformation
A muffle furnace is designed for processes that require extreme heat, often from 900°C to 1700°C or higher.
At these temperatures, the goal is not merely to dry a sample but to fundamentally change it. This includes applications like ashing (burning off organic material to determine inorganic content), annealing metals, or sintering ceramics.
How They Achieve Different Temperatures
The vast difference in temperature capability stems from fundamentally different design principles and construction materials.
The Insulated Chamber (The "Muffle")
The name "muffle furnace" comes from its core design feature: the muffle. This is a highly insulated chamber, often made of refractory ceramic materials, that contains the sample.
Crucially, the heating elements are positioned outside this chamber. They heat the muffle, which then radiates heat uniformly onto the sample. This separation protects the sample from direct contact with the heating elements and any potential contaminants.
Advanced Heating Elements
To reach extreme temperatures, muffle furnaces rely on specialized heating elements.
The choice of element depends on the target temperature range:
- Electric heating wires are used for temperatures up to 1200°C.
- Silicon-carbon rods are used for temperatures up to 1400°C.
- Silicon molybdenum rods are required for the highest ranges, from 1400°C to 1700°C and beyond.
The Convection Principle in Ovens
Drying ovens use simpler heating elements and typically rely on convection. A fan circulates hot air throughout the chamber to ensure even, gentle heating, which is ideal for moisture removal without damaging the sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong instrument can lead to failed experiments, damaged equipment, or significant safety hazards.
Precision vs. Power
Ovens provide excellent temperature stability and control within their lower range, making them ideal for sensitive drying or curing processes. Furnaces provide immense thermal power, which requires more sophisticated control systems and safety protocols to manage.
Energy Consumption and Safety
Due to the extreme temperatures, a muffle furnace consumes significantly more energy than a drying oven. It also presents greater safety risks, including severe burns and the potential for hazardous off-gassing from samples during high-temperature processes.
Contamination Control
The indirect heating design of a muffle furnace is a key advantage for analytical work. By keeping the heating elements separate from the sample chamber, it prevents any potential contamination, ensuring the purity of the sample for subsequent analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be dictated entirely by the thermal requirements of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is drying glassware, sterilizing instruments, or curing coatings below 300°C: A drying oven is the correct, energy-efficient tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is ashing samples, annealing metals, or testing materials at extreme temperatures: A muffle furnace is the only instrument capable of achieving the necessary heat.
Ultimately, choosing the right equipment begins with a clear understanding of whether your goal is to remove moisture or fundamentally transform your material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Drying Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Moisture removal, drying, sterilizing | Material transformation (ashing, annealing, sintering) |
| Typical Temp Range | Up to 250-300°C | 900°C to 1700°C+ |
| Heating Method | Convection (forced air) | Radiant heat (insulated muffle chamber) |
| Key Applications | Drying glassware, curing, sterilization | Ashing, heat treatment, high-temperature testing |
Still unsure which thermal processing equipment is right for your application?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect muffle furnace or drying oven based on your specific temperature requirements and process goals, ensuring safety, efficiency, and accurate results.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the burning temperature of a furnace? From 200°C to 3000°C, It Depends on Your Needs
- How hot does a furnace get in Celsius? From 1100°C to 1800°C for Your Lab Needs
- What is the temperature of furnace exhaust? A Key Indicator of Efficiency and Safety
- What is a muffle furnace used to estimate? A Key Tool for Precise Ash Determination
- What are the disadvantages of wet ashing? Key Safety & Contamination Risks



















