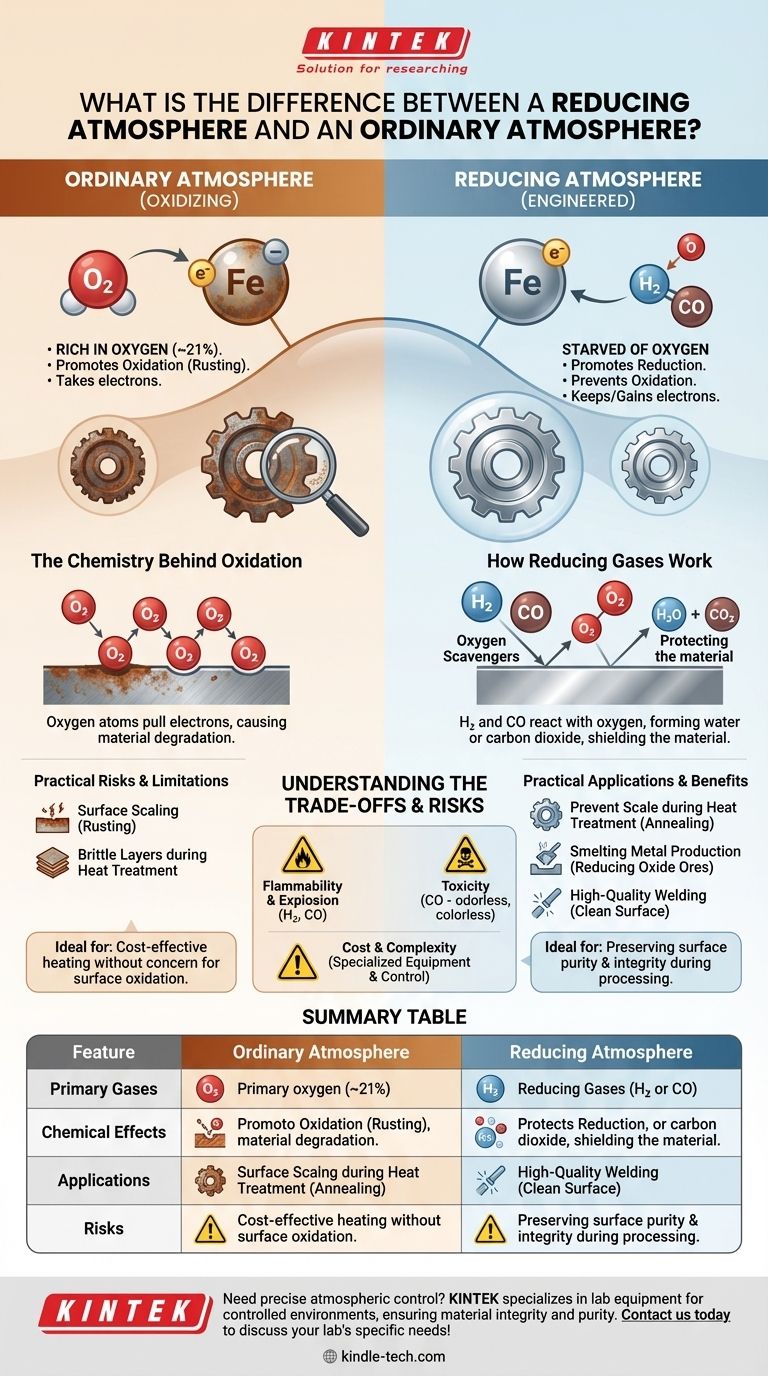
At its core, the difference is about chemical reactivity. An ordinary atmosphere, rich in oxygen, actively promotes oxidation—the process responsible for rust and combustion. A reducing atmosphere is an engineered environment that does the opposite; it is starved of oxygen and often contains specific gases that prevent or even reverse oxidation by promoting chemical reduction.
An ordinary atmosphere causes materials to oxidize by taking their electrons. A reducing atmosphere creates a chemical environment that prevents this, forcing materials to either keep their electrons or gain new ones.

The Chemistry Behind Each Atmosphere
An atmosphere's behavior is defined by its potential to either donate or accept electrons from a material. This single principle governs whether an object will rust, burn, or remain pure.
The Oxidizing Nature of Ordinary Air
Our normal atmosphere is approximately 21% oxygen, a highly reactive element. This makes our environment inherently oxidizing.
Oxygen atoms have a strong tendency to pull electrons from other elements. This process, known as oxidation, is fundamental to reactions like the rusting of iron (forming iron oxide) or the burning of wood.
The Protective Nature of a Reducing Atmosphere
A reducing atmosphere is a gaseous environment where oxidation is actively suppressed. This is achieved in two main ways.
First, oxygen and other oxidizing agents are removed or significantly diluted. Second, gases that promote reduction—the chemical opposite of oxidation—are introduced. Common reducing gases include hydrogen (H₂) and carbon monoxide (CO).
How Reducing Gases Work
These gases act as "oxygen scavengers." For example, at high temperatures, any stray oxygen will preferentially react with hydrogen to form water (H₂O) or with carbon monoxide to form carbon dioxide (CO₂).
This effectively protects a material from reacting with the oxygen itself. In this environment, an atom is more likely to gain an electron (reduction) than to lose one (oxidation).
Practical Applications and Use Cases
The choice between an ordinary and reducing atmosphere is critical in many industrial and scientific processes where material integrity is paramount.
Preventing Scale During Heat Treatment
When metals are heated to high temperatures in ordinary air, their surface rapidly oxidizes, forming a brittle layer called "scale."
Using a reducing atmosphere during annealing or hardening prevents this scale from forming, resulting in a cleaner, higher-quality finished product.
Smelting and Metal Production
The very process of extracting metals like iron from their natural ore (iron oxide) requires a powerful reducing atmosphere.
In a blast furnace, burning coke creates a carbon monoxide-rich environment. The carbon monoxide strips the oxygen atoms from the iron oxide, "reducing" it back to pure, molten iron.
Welding and Brazing
High-quality welding requires shielding the molten metal from the air. While often done with inert gases like argon, a gas mixture containing reducing gases like hydrogen can be used.
This not only shields the weld pool but also actively cleans the surface by reducing any existing light oxides, leading to a stronger bond.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While powerful, creating and maintaining a reducing atmosphere involves significant challenges and hazards compared to simply using ambient air.
Flammability and Explosion Hazards
The primary gases used to create reducing atmospheres, hydrogen and carbon monoxide, are highly flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. This requires specialized equipment and strict safety protocols.
Toxicity of Reducing Agents
Carbon monoxide is an extremely toxic gas that is colorless and odorless. Any process using it must incorporate robust ventilation and continuous air monitoring to protect personnel.
Cost and Complexity
Generating a specific gas mixture and maintaining its purity and pressure within a furnace or chamber is far more complex and expensive than using an ordinary atmosphere. The process requires precise control systems and a reliable supply of high-purity gases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal atmosphere is determined entirely by the desired outcome for your material or process.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective heating without concern for surface oxidation: An ordinary atmosphere is the simplest and cheapest solution.
- If your primary focus is preserving the surface purity of a metal during heat treatment: A reducing atmosphere is necessary to prevent scale and maintain the material's integrity.
- If your primary focus is chemically transforming an oxide back into its pure element (e.g., smelting): A strong reducing atmosphere is not just beneficial, it is a fundamental requirement of the process.
Ultimately, mastering the atmospheric conditions gives you direct control over the fundamental chemical fate of your material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ordinary Atmosphere (Air) | Reducing Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Gas | ~21% Oxygen | Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Monoxide (CO) |
| Chemical Effect | Promotes Oxidation (Rusting) | Promotes Reduction (Prevents Rusting) |
| Key Application | General Heating | Metal Heat Treatment, Smelting, Welding |
| Main Risk | Surface Scaling/Oxidation | Flammability, Toxicity (CO) |
Need precise atmospheric control for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for creating controlled environments for heat treatment, welding, and material synthesis. Our expertise ensures your materials maintain integrity and purity. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What is an inert condition? A Guide to Preventing Fires and Explosions
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab



















