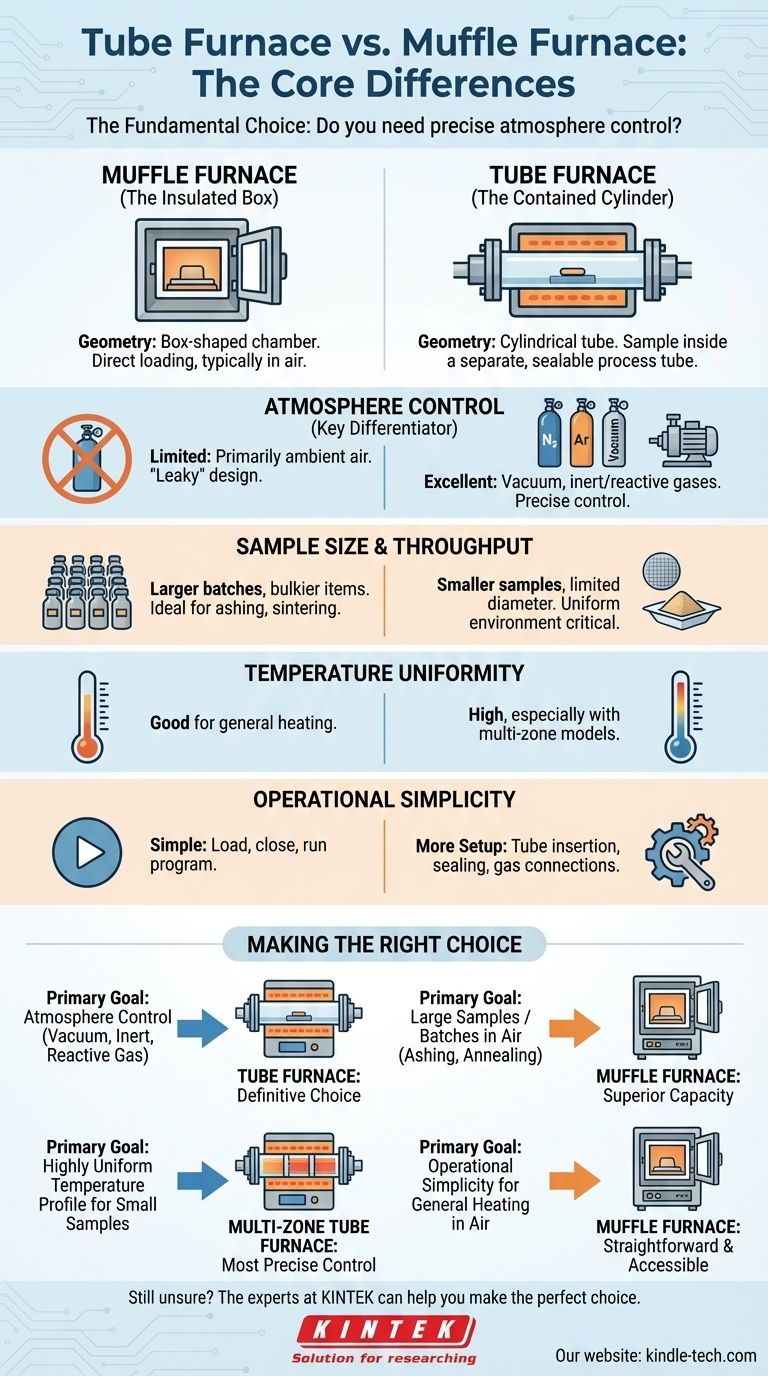
At its core, the difference is geometry. A muffle furnace is a box-shaped chamber where materials are placed directly inside for heating, typically in air. A tube furnace, by contrast, heats a separate cylindrical tube that passes through the insulated heating zone, a design that makes it exceptionally well-suited for controlling the sample's atmosphere.
The fundamental choice between these furnaces comes down to a single question: do you need to control the atmosphere around your sample? A tube furnace is designed for precise atmospheric control (vacuum, inert gas), while a muffle furnace is built for simplicity and larger capacity heating in ambient air.

The Core Architectural Difference: Chamber vs. Tube
The distinct shapes of these furnaces are not arbitrary; they directly dictate how each is used and what applications they excel at.
The Muffle Furnace: The Insulated Box
A muffle furnace is a type of box furnace. Its defining feature is a front-loading door that opens to a single, spacious chamber.
The sample or crucible is placed directly onto the hearth floor. These furnaces are typically insulated with high-efficiency ceramic fiber, allowing for rapid heating and cooling cycles.
This design makes them simple to load and ideal for processing multiple samples at once or handling larger, bulkier items.
The Tube Furnace: The Contained Cylinder
A tube furnace features a cylindrical heating cavity. A separate process tube, often made of quartz, alumina, or another ceramic, is placed through this heated cylinder.
Your material sample is then placed inside this process tube. The tube can be sealed at the ends with flanges, allowing for precise control over the internal environment.
This contained setup is naturally more compact and focuses the heat energy on a smaller, more defined area.
How Design Dictates Application
The architectural differences create clear advantages for each furnace type in specific scientific and industrial tasks.
Atmosphere Control: The Key Differentiator
This is the most critical distinction. The ability to seal the ends of the process tube makes the tube furnace the definitive choice for any work requiring a non-air atmosphere.
You can easily connect gas lines to flow inert (nitrogen, argon) or reactive gases over the sample, or connect a vacuum pump to remove the atmosphere entirely.
A muffle furnace is designed primarily for operation in ambient air. While some models can be modified for gas flow, they are inherently "leaky" and cannot achieve the high-purity atmosphere or vacuum levels of a tube furnace.
Sample Size and Throughput
The large chamber of a muffle furnace makes it superior for applications requiring larger sample volumes. It's perfect for ashing, gravimetric analysis, sintering, and heat-treating multiple parts in a single batch.
Tube furnaces have a much smaller usable diameter. They are ideal for processing small samples, powders, or wafers where a uniform environment is critical.
Temperature Uniformity
Due to their cylindrical geometry, tube furnaces often provide a more uniform and stable temperature zone along the central length of the tube.
Multi-zone tube furnaces, which have separate heating elements along the tube's length, offer even more precise control over the temperature gradient.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
Choosing between these furnaces also involves considering their day-to-day operation and versatility.
Operational Simplicity
A muffle furnace is generally easier to operate. You open the door, place the sample, close it, and run the temperature program.
A tube furnace requires more setup, especially when using atmosphere control. This involves inserting the process tube, loading the sample into the correct position, and properly sealing the flanges and connecting gas lines.
Interchangeability
A tube furnace can perform most of the basic functions of a muffle furnace if the sample is small enough to fit and you are simply heating it in air.
However, a muffle furnace cannot replicate the primary function of a tube furnace: high-purity atmosphere or vacuum control.
Heating Elements
Both furnace types use the same technologies to achieve high temperatures. The choice of heating element depends on the maximum required temperature, not the furnace style.
Common elements include electric heating wires (up to 1200°C), silicon carbide (SiC) rods (up to 1400°C), and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) rods (up to 1700°C or higher).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your furnace based on the non-negotiable requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is atmosphere control (vacuum, inert, or reactive gas): The tube furnace is the only suitable option.
- If your primary focus is heating larger samples or batches in air (e.g., ashing, annealing): The muffle furnace provides superior capacity and simplicity.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly uniform temperature profile for small samples: A multi-zone tube furnace offers the most precise control.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity for general-purpose heating in air: The muffle furnace is the more straightforward and accessible choice.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is about matching the tool's inherent design to the specific environmental and physical needs of your application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Design | Cylindrical tube for sample containment | Box-shaped chamber for direct loading |
| Atmosphere Control | Excellent (vacuum, inert/reactive gases) | Limited (primarily ambient air) |
| Sample Size/Capacity | Smaller samples, limited diameter | Larger batches, bulkier items |
| Temperature Uniformity | High, especially with multi-zone models | Good for general heating |
| Best For | Precise atmosphere work, small samples | Ashing, sintering, large-volume heating in air |
Still unsure which furnace is right for your specific application? The experts at KINTEK can help you make the perfect choice. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including both tube and muffle furnaces, tailored to meet the precise needs of your laboratory. Whether you require advanced atmosphere control or high-capacity batch processing, we have the solution.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and let KINTEK enhance your lab's capabilities with the ideal heating equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What is the function of alumina tubes and alumina wool in a pyrolysis furnace? Optimize Your Biochar Production Quality
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?



















