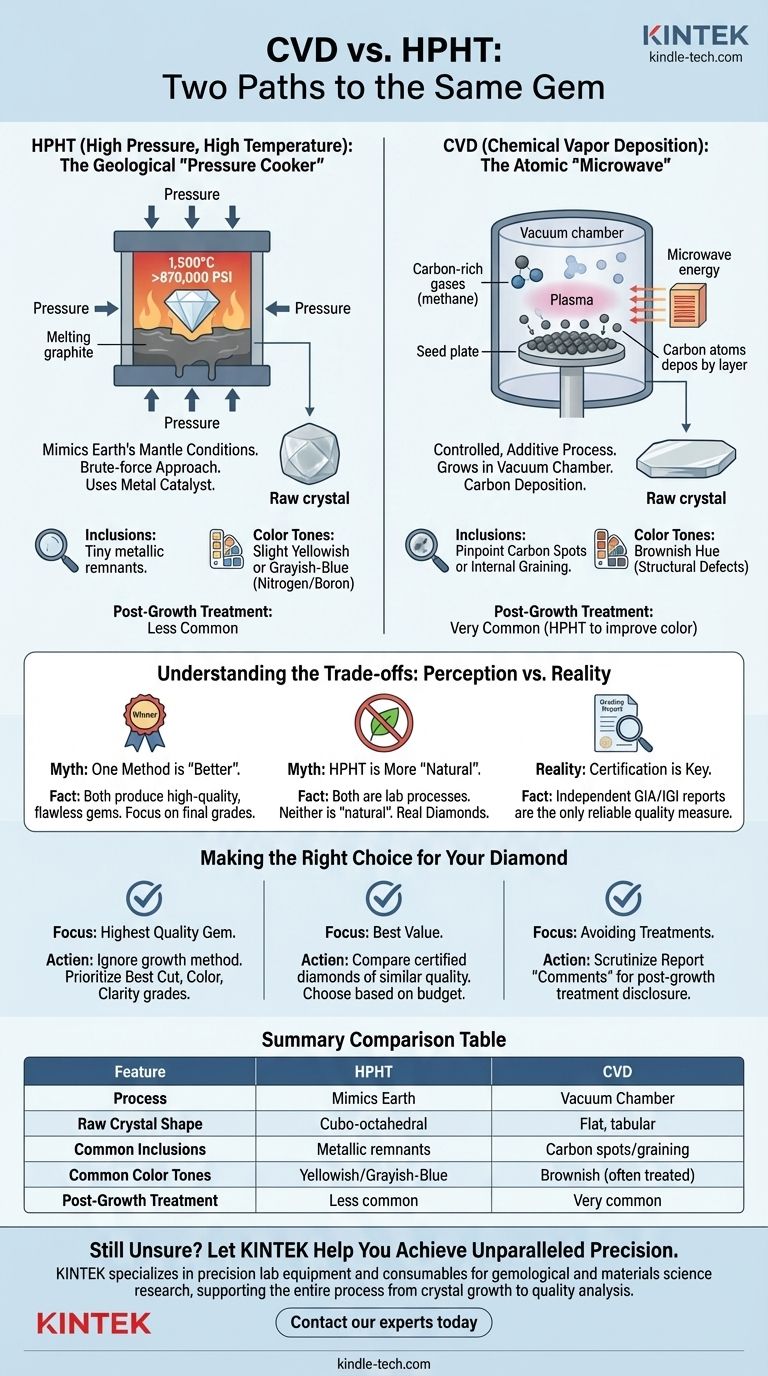
At a fundamental level, the difference between CVD and HPHT is the manufacturing process. HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature) mimics the natural geological conditions that form diamonds deep within the Earth, using immense pressure and heat. In contrast, CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) grows a diamond in a vacuum chamber, depositing carbon atoms layer by layer onto a diamond seed.
While their scientific origins are entirely different, neither method is inherently superior. Both HPHT and CVD are capable of producing flawless, high-quality diamonds that are physically and chemically identical to natural ones. The final quality of the gem you purchase depends on the specific manufacturer's skill and subsequent treatments, not the growth method itself.

How Each Process Works: Two Paths to the Same Gem
To understand the subtle differences in the final product, you must first understand the two distinct manufacturing environments.
HPHT: The Geological "Pressure Cooker"
The HPHT process is a brute-force approach that recreates the conditions of the Earth's mantle. A small diamond "seed" is placed in a chamber with a carbon source, typically graphite.
This chamber is then subjected to extreme pressures (over 870,000 pounds per square inch) and very high temperatures (around 1,500°C). Under these conditions, the carbon melts and crystallizes around the diamond seed, forming a larger, gem-quality diamond. The resulting raw crystal typically has a cubo-octahedral shape, similar to natural diamonds.
CVD: The Atomic "Microwave"
The CVD method is a more controlled, additive process. It begins with a thin slice of a diamond, called a seed plate, which is placed inside a vacuum chamber.
The chamber is filled with carbon-rich gases (like methane) and heated to a high temperature. Microwave energy is then used to ionize these gases into a plasma, which releases carbon atoms. These atoms "rain down" and deposit onto the seed plate, building up the diamond one atomic layer at a time. This results in a flatter, tabular-shaped raw crystal.
Key Differentiating Characteristics
While visually indistinguishable to the naked eye when cut and polished, HPHT and CVD diamonds can have subtle identifying markers that are detectable with advanced gemological equipment.
Inclusions and Internal Features
Because the HPHT process uses a metal catalyst to dissolve the carbon, HPHT diamonds can sometimes contain tiny metallic inclusions. These are remnants of the growth environment.
CVD diamonds, grown in a carbon-gas environment, do not have metallic inclusions. Instead, they can sometimes feature very small pinpoint carbon spots or internal graining lines related to their layered growth.
Color Tones and Growth Patterns
HPHT diamonds, especially older or lower-quality ones, sometimes have a slight yellowish or grayish-blue tint due to the way nitrogen or boron is incorporated during growth.
CVD diamonds are more prone to a brownish hue, which is a result of structural defects at the atomic level. However, modern advancements have greatly reduced these tendencies in both methods.
The Role of Post-Growth Treatments
This is a critical point of understanding. Many lab-grown diamonds, especially CVD diamonds, undergo a secondary treatment to improve their color.
Most commonly, a CVD diamond with a brownish tint is subjected to an HPHT process after it is grown. This "post-growth treatment" permanently removes the brown coloration, dramatically improving its quality. This is a standard, stable, and accepted industry practice, and it is always disclosed on a reputable grading report.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Perception vs. Reality
Marketing narratives can create confusion. Focusing on the facts is the best way to navigate your decision.
Myth: Is One Method "Better" Than the Other?
No. This is the most common misconception. Both methods can produce the full spectrum of quality, from low-grade industrial material to flawless, D-color gems. A high-quality CVD diamond is far superior to a low-quality HPHT diamond, and vice versa.
Myth: Is HPHT More "Natural"?
While HPHT mimics the Earth's conditions, it is no more "natural" than CVD. Both are sophisticated technological processes conducted in a laboratory. The final product from both is a real diamond, but neither is a "natural diamond."
Reality: The Importance of Certification
The growth method is a piece of background information, not a measure of quality. The only reliable measure of a diamond's quality is its independent grading report from a respected gemological lab like GIA or IGI. This report details the 4 Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, Carat) and will note the origin as "Laboratory-Grown," often disclosing the specific method and any detectable post-growth treatments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Diamond
Your focus should be on the final quality of the gem, not its manufacturing history.
- If your primary focus is obtaining the highest quality gem: Ignore the growth method entirely and focus on finding a diamond with the best grades for Cut, Color, and Clarity on its certificate.
- If your primary focus is finding the best value: Compare certified diamonds of similar quality from both methods, as market prices can fluctuate. Choose the stone that best meets your budget and aesthetic preferences.
- If your primary focus is avoiding treatments: Scrutinize the "Comments" section of the grading report. It will state if the diamond has undergone post-growth treatment to improve its color.
Ultimately, judging the diamond by its final, certified quality—not its origin story—is the key to making a confident and informed decision.
Summary Table:
| Feature | HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Mimics Earth's mantle: extreme pressure & heat | Grows in a vacuum chamber: carbon deposition |
| Raw Crystal Shape | Cubo-octahedral | Flat, tabular |
| Common Inclusions | Metallic remnants from catalyst | Pinpoint carbon spots or graining |
| Common Color Tones | Slight yellowish or grayish-blue | Can have a brownish hue (often treated) |
| Post-Growth Treatment | Less common | Very common (HPHT treatment to improve color) |
Still Unsure Which Lab-Grown Diamond is Right for You?
Understanding the nuances of CVD and HPHT is the first step. The next is finding a trusted partner to provide the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed to create and certify these exceptional gems.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving the exacting needs of laboratories in the gemological and materials science industries. Whether you are researching, developing, or certifying lab-grown diamonds, our reliable products support the entire process, from crystal growth to quality analysis.
Let us help you achieve unparalleled precision and reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's specific requirements with our high-performance solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- How does a continuous, single layer of graphene form from carbon species? Master the 4 Stages of Graphene Growth
- What are the features and benefits of Low Pressure Chemical Vapour Deposition (LPCVD)? Expert Guide to Film Uniformity
- Why are CVD or sintering furnaces necessary for SiC cladding? Unlock the Future of Accident Tolerant Fuel
- Why is film thickness important? It's the key to controlling material performance.
- How does deposition occur in DC sputtering? Master the Kinetic Process for Superior Thin Films
- What is the high temperature for CVD? Unlock Optimal Film Quality for Your Lab
- What is the layer method of deposition? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What are the steps of sputtering? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition



















