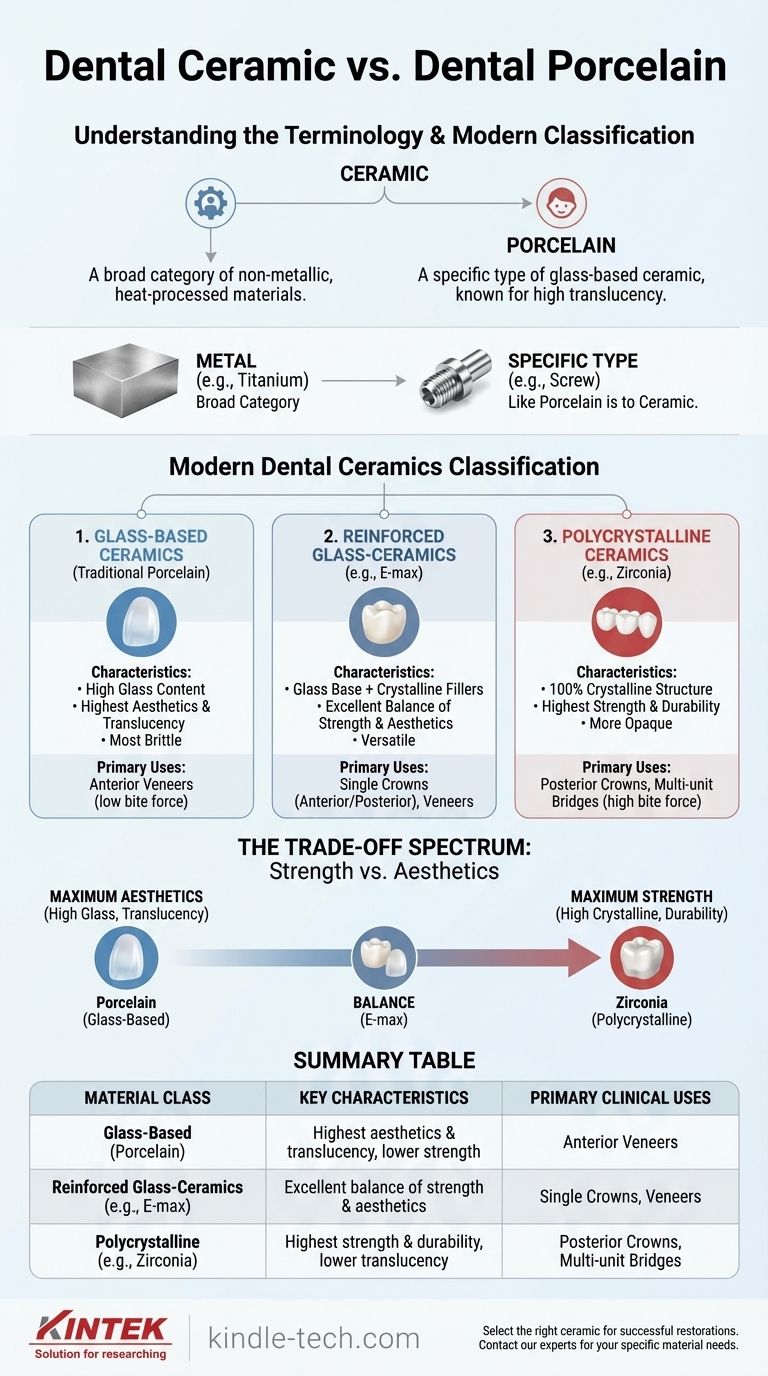
In practice, there is no difference because dental porcelain is a specific type of dental ceramic. The terms are often used interchangeably in clinical conversation, but "ceramic" is the broader, more accurate scientific term that encompasses a wide range of materials, including porcelain.
Think of "ceramic" as the parent category, like "metal." "Porcelain" is a specific type within that category, like "titanium." While all porcelain is ceramic, modern dentistry now uses many advanced, non-porcelain ceramics (like zirconia) that offer different properties for specific clinical needs.

Deconstructing the Terminology: Ceramic vs. Porcelain
Understanding the distinction begins with a clear definition of each term within the context of material science.
The Broad Category: Dental Ceramics
A dental ceramic is any inorganic, non-metallic material that is processed and hardened by heating at high temperatures. This is the overarching classification that covers all glass-like and crystalline restorative materials used in dentistry.
The Specific Subtype: Dental Porcelain
Dental porcelain refers to a specific subtype of ceramic that is glass-based. Its primary component is feldspar, which, when fired, creates a highly translucent, vitreous (glass-like) structure that mimics the appearance of natural tooth enamel exceptionally well.
A Modern Classification of Dental Ceramics
The confusion between terms often arises because the field has evolved far beyond traditional porcelain. Modern dental ceramics are best understood by their composition, which directly dictates their strength and appearance.
Group 1: Glass-Based Ceramics (Traditional Porcelain)
This group includes materials like feldspathic porcelain. It contains a high concentration of glass, making it the most aesthetically pleasing and translucent option available. However, this glass content also makes it the most brittle of the ceramic classes.
Its unmatched beauty makes it the gold standard for cosmetic applications like anterior veneers, where biting forces are low.
Group 2: Reinforced Glass-Ceramics (e.g., E-max)
These materials, such as lithium disilicate (E-max), start with a glass base but are reinforced with crystalline fillers. This process significantly increases the material's strength and fracture resistance without sacrificing excellent aesthetics.
They represent a versatile middle ground, offering a superb balance of beauty and durability for applications like single crowns (front or back) and veneers.
Group 3: Polycrystalline Ceramics (e.g., Zirconia)
This group is fundamentally different. Materials like zirconia contain no glass at all; they are composed entirely of a dense, tightly packed crystalline structure.
This makes them the strongest and most durable ceramics available, but also the most opaque. Because of their immense strength, they are the material of choice for posterior crowns and multi-unit bridges where chewing forces are greatest.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Aesthetics
The choice of a specific dental ceramic is always a deliberate clinical decision based on a fundamental trade-off between mechanical performance and visual appearance.
The Aesthetic Spectrum
A ceramic's aesthetic potential is directly tied to its glass content. The more glass in the material's matrix, the more light can pass through it, resulting in the life-like translucency seen in natural teeth. Porcelain sits at the peak of this spectrum.
The Strength Spectrum
Strength is determined by the crystalline content. Crystalline structures are highly organized and robust, effectively stopping cracks from propagating through the material. Zirconia, being fully crystalline, is the undisputed leader in strength and fracture resistance.
Clinical Application Drives the Choice
This inverse relationship is the core of modern dental material selection. A cosmetic case on a front tooth demands the beauty of a glass-ceramic. A bridge in the back of the mouth that must withstand immense chewing forces requires the brute strength of a polycrystalline ceramic like zirconia.
Making the Right Choice for the Restoration
Understanding the different classes of ceramics allows clinicians to select the optimal material to meet the specific functional and aesthetic demands of each case.
- If your primary focus is maximum aesthetics for anterior teeth (veneers): Glass-based ceramics like feldspathic porcelain or reinforced glass-ceramics like lithium disilicate are the gold standard.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and beauty for single crowns: Lithium disilicate (E-max) is often the ideal choice for its versatility and proven clinical success.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength for posterior crowns or bridges: Polycrystalline ceramics like zirconia are the most durable and reliable option to withstand heavy occlusal forces.
Ultimately, knowing the distinct properties of each ceramic empowers you to move beyond interchangeable terms and select the precise material that ensures a predictable, beautiful, and long-lasting result.
Summary Table:
| Material Class | Key Characteristics | Primary Clinical Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Glass-Based (Porcelain) | Highest aesthetics & translucency, but lower strength | Anterior Veneers |
| Reinforced Glass-Ceramics (e.g., E-max) | Excellent balance of strength & aesthetics | Single Crowns (Anterior/Posterior), Veneers |
| Polycrystalline (e.g., Zirconia) | Highest strength & durability, but lower translucency | Posterior Crowns, Multi-unit Bridges |
Selecting the right dental ceramic is critical for a successful, long-lasting restoration. KINTEK specializes in high-quality dental ceramics and lab equipment, providing the materials you need for predictable, beautiful results. Whether you're crafting delicate veneers or strong posterior bridges, we support your laboratory's success.
Let's discuss your specific material needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your cases.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results



















