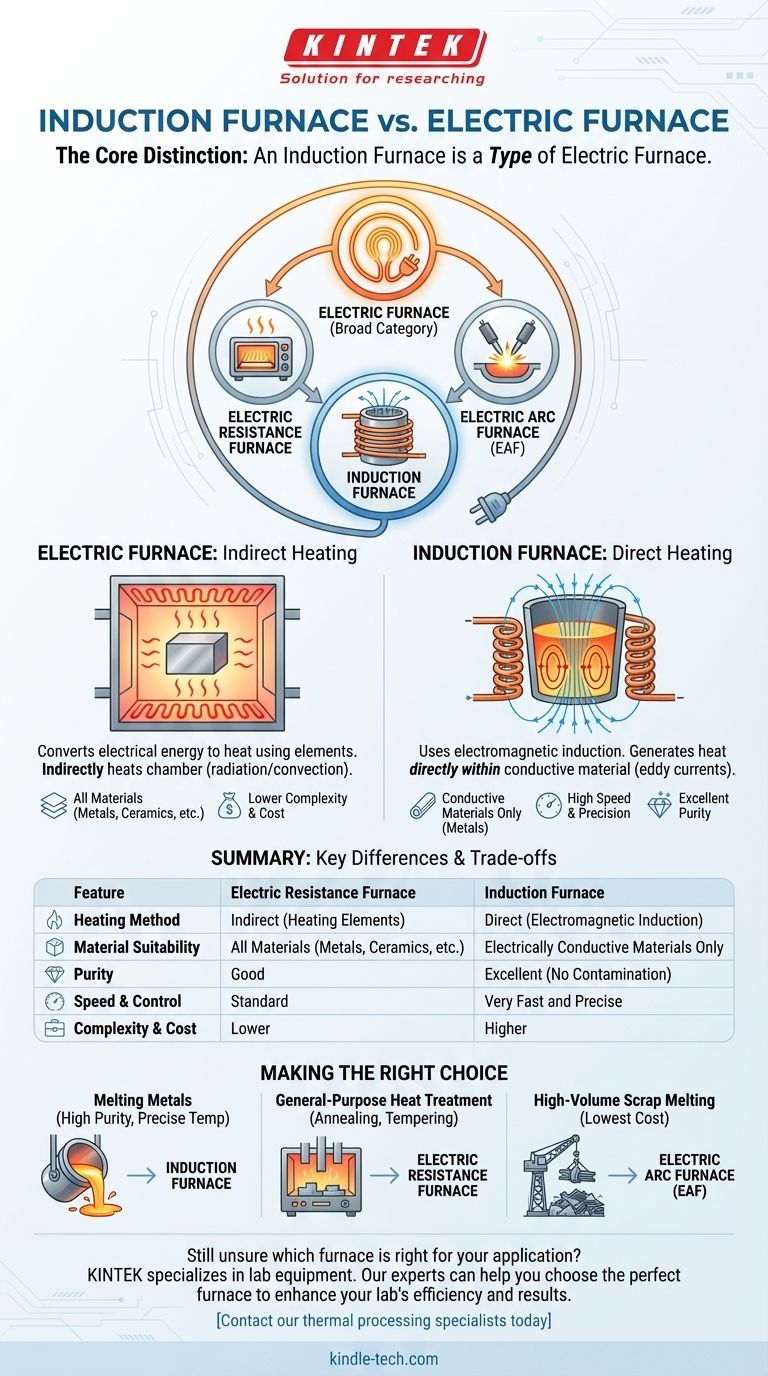
The core distinction is that an induction furnace is a type of electric furnace. The term "electric furnace" refers to any furnace that uses electricity as its energy source, which is a very broad category. An induction furnace is a specific, advanced type of electric furnace that uses a unique heating method based on electromagnetic induction.
The essential difference lies in the heating mechanism. Most common electric furnaces use resistive heating elements to heat a chamber (indirect heating), much like a kitchen oven. In contrast, an induction furnace uses a magnetic field to generate heat directly within the material itself (direct heating), offering greater speed, precision, and purity.

What is an Electric Furnace? A Broad Category
An electric furnace is any device that converts electrical energy into heat for industrial or laboratory processes. This classification is based on the energy source, distinguishing them from furnaces powered by gas, oil, or coal.
The Fundamental Principle
All electric furnaces operate by passing electricity through a component to generate heat. However, how they do this varies significantly, leading to different furnace types with distinct applications.
Major Types of Electric Furnaces
The three primary types of industrial electric furnaces are:
- Electric Resistance Furnaces: These are the most common type. They work like a toaster or oven, passing electricity through high-resistance heating elements. These elements glow hot and heat the furnace chamber through radiation and convection.
- Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF): These use a high-power electric arc between electrodes to generate intense heat. The arc itself can reach thousands of degrees, making EAFs ideal for melting scrap steel and other high-volume materials.
- Induction Furnaces: These use electromagnetic principles to heat conductive materials without any direct contact or arc.
How an Induction Furnace Works
An induction furnace operates on the principles of a transformer. It uses a powerful, alternating magnetic field to induce electrical currents directly within the metal charge, which generates heat.
The Principle of Electromagnetic Induction
A water-cooled copper coil acts as the primary winding of a transformer, powered by a high-frequency AC supply. The conductive material to be heated (the "charge") is placed inside this coil and effectively becomes the secondary winding.
The rapidly changing magnetic field from the coil induces powerful electrical currents, called eddy currents, within the charge. The material's natural resistance to these currents generates immense and precise heat.
Advantages of Direct Heating
Because heat is generated inside the material, the induction process is incredibly fast and efficient. It avoids the slow process of transferring heat from external elements to the furnace chamber and then to the product.
This direct heating method also allows for exceptional purity. Since there is no electric arc or burning fuel, the risk of introducing carbon or other impurities into the melt is significantly reduced, making it crucial for producing high-quality alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a conventional resistance furnace and an induction furnace involves clear trade-offs in capability, cost, and application.
Heating Method and Purity
A standard electric resistance furnace heats indirectly, which is slower and can be less uniform. An induction furnace heats directly and internally, offering superior speed, temperature control, and the ability to operate in controlled atmospheres (like a vacuum) for high-purity results.
Material Constraints
This is a critical distinction. Induction furnaces only work on electrically conductive materials, like metals. Electric resistance furnaces are material-agnostic; they can heat metals, ceramics, composites, and other non-conductive materials with equal effectiveness.
Complexity and Cost
Simple electric resistance furnaces are generally less complex, easier to maintain, and have a lower initial purchase price. Induction furnaces require sophisticated high-frequency power supplies and cooling systems, making them more complex and typically more expensive to acquire.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice depends entirely on your specific material and processing objective.
- If your primary focus is melting metals with high purity and precise temperature control: The induction furnace is the superior technology due to its direct, clean, and rapid heating.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment (like annealing or tempering) for a wide variety of materials: A conventional electric resistance furnace offers greater versatility and is often more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is melting massive quantities of scrap steel at the lowest possible cost: An Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is the industry standard for this high-volume application.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental heating mechanism is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific thermal processing task.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electric Resistance Furnace | Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect (heating elements) | Direct (electromagnetic induction) |
| Material Suitability | All materials (metals, ceramics, etc.) | Electrically conductive materials only |
| Purity | Good | Excellent (no contamination) |
| Speed & Control | Standard | Very fast and precise |
| Complexity & Cost | Lower | Higher |
Still unsure which furnace is right for your application?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you choose the perfect furnace—whether it's a versatile electric resistance model for general heat treatment or a high-purity induction furnace for precise metal melting—to enhance your lab's efficiency and results.
Contact our thermal processing specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation



















