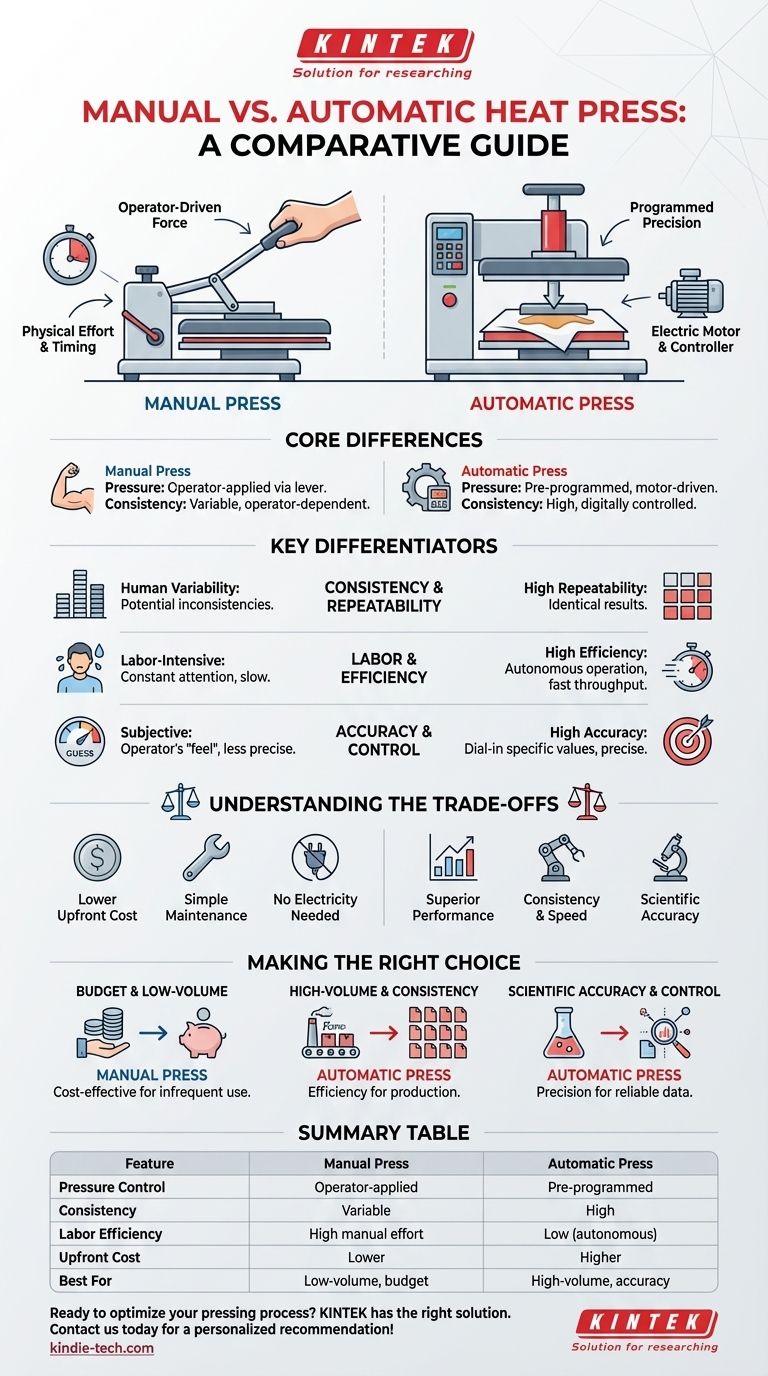
The fundamental difference between a manual and an automatic heat press lies in how pressure is applied and controlled. A manual press requires the operator to physically exert force using a lever to apply pressure, while an automatic press uses an electric motor and hydraulic pump to apply a precise, pre-set amount of pressure for a specific duration.
The decision between a manual and automatic press is not about which is universally superior, but which tool aligns with your specific goals. The choice hinges on a critical trade-off between upfront cost, labor efficiency, and the need for repeatable precision.

How Each Press Achieves its Goal
The operational mechanics of each press type directly influence its suitability for different tasks. Understanding this is key to choosing the right one for your workflow.
The Manual Press: Operator-Driven Force
A manual hydraulic press is a purely mechanical device. The operator uses a hand-operated lever or pump to generate the hydraulic force needed to press the sample or garment.
There are no electronic components controlling the process. The pressure applied and the time it is held are entirely dependent on the operator's physical effort and timing.
The Automatic Press: Programmed Precision
An automatic hydraulic press incorporates an electric motor to drive a pump and an electronic controller. This system automates the application of force.
The operator can pre-program the exact desired pressure and holding time. Once activated, the machine executes these parameters precisely without further human intervention, ensuring every press cycle is identical.
Key Differentiators for Your Workflow
The mechanical differences translate into significant practical implications for consistency, speed, and overall output quality.
Consistency and Repeatability
Automatic presses offer exceptionally high repeatability. Because the pressure and time are digitally controlled, the conditions for each sample are virtually identical, which is critical for consistent results in production or lab settings.
Manual presses, by contrast, are subject to human variability. The force applied can differ between operators or even with the same operator over a long day, leading to potential inconsistencies in the final product.
Labor and Efficiency
A manual press is inherently labor-intensive and time-consuming. It requires constant operator attention and physical effort, making it less efficient for high-volume or frequent use.
Automatic presses significantly reduce labor. Once programmed, they operate autonomously, freeing the operator to prepare the next sample. This dramatically improves workflow and throughput in busy environments like factories or labs processing many samples.
Accuracy and Control
Automatic presses provide a high degree of accuracy. The ability to dial in a specific pressure value ensures the process meets exact specifications, which is essential for sensitive materials or scientific applications.
With a manual press, the applied pressure is subjective and cannot be measured with the same precision. It relies on the operator's "feel" rather than a calibrated setting.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While automatic presses offer clear advantages in performance, the manual press holds its ground in specific scenarios, primarily due to its simplicity and cost.
The Cost Factor
The most significant advantage of a manual press is its lower upfront cost. The absence of motors, pumps, and electronic controllers makes it a much more affordable initial investment.
Simplicity and Maintenance
Manual presses are mechanically simple. With fewer moving parts and no electronics, they are often easier to maintain and troubleshoot than their more complex automatic counterparts.
Power and Placement
An automatic press requires an electrical source to power its motor and controller. A manual press needs no electricity, offering greater flexibility in where it can be set up and operated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select the press that directly serves your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is budget and low-volume, infrequent use: A manual press is the most cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and consistent output: An automatic press will deliver the efficiency and repeatability you need.
- If your primary focus is scientific accuracy and process control: The precision of an automatic press is non-negotiable for reliable data.
By understanding these core differences, you are empowered to invest in the tool that will best achieve your objectives.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Manual Press | Automatic Press |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Control | Operator-applied via lever | Pre-programmed, motor-driven |
| Consistency | Variable (operator-dependent) | High (digitally controlled) |
| Labor Efficiency | High manual effort | Low (autonomous operation) |
| Upfront Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Best For | Low-volume, budget-focused tasks | High-volume production, scientific accuracy |
Ready to optimize your pressing process? Whether you need the budget-friendly simplicity of a manual press or the precision of an automated system, KINTEK has the right solution for your laboratory. Our experts will help you select the ideal equipment to enhance your workflow, ensure consistent results, and boost your productivity. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is hot press lamination? The Ultimate Guide to Strong, Durable Material Bonding
- What does a hot press machine do? Permanently Bond, Form, or Transfer Materials with Precision
- Why is a laboratory hot press necessary for all-solid-state battery assembly? Reduce Impedance and Enhance Performance
- What is the function of columns in a hot press? Prevent Deflection for Superior Material Quality
- What is the hot pressing process polymer? Achieve Maximum Density and Strength for Critical Parts
- What is the standard temperature for heat press? Master the Perfect Settings for Durable Transfers
- What is machine press plywood? The Key to Modern Plywood's Strength and Stability
- How does the hot pressing process enhance Li7P2S8I0.5Cl0.5 stability? Boost Solid-State Battery Life and Safety



















