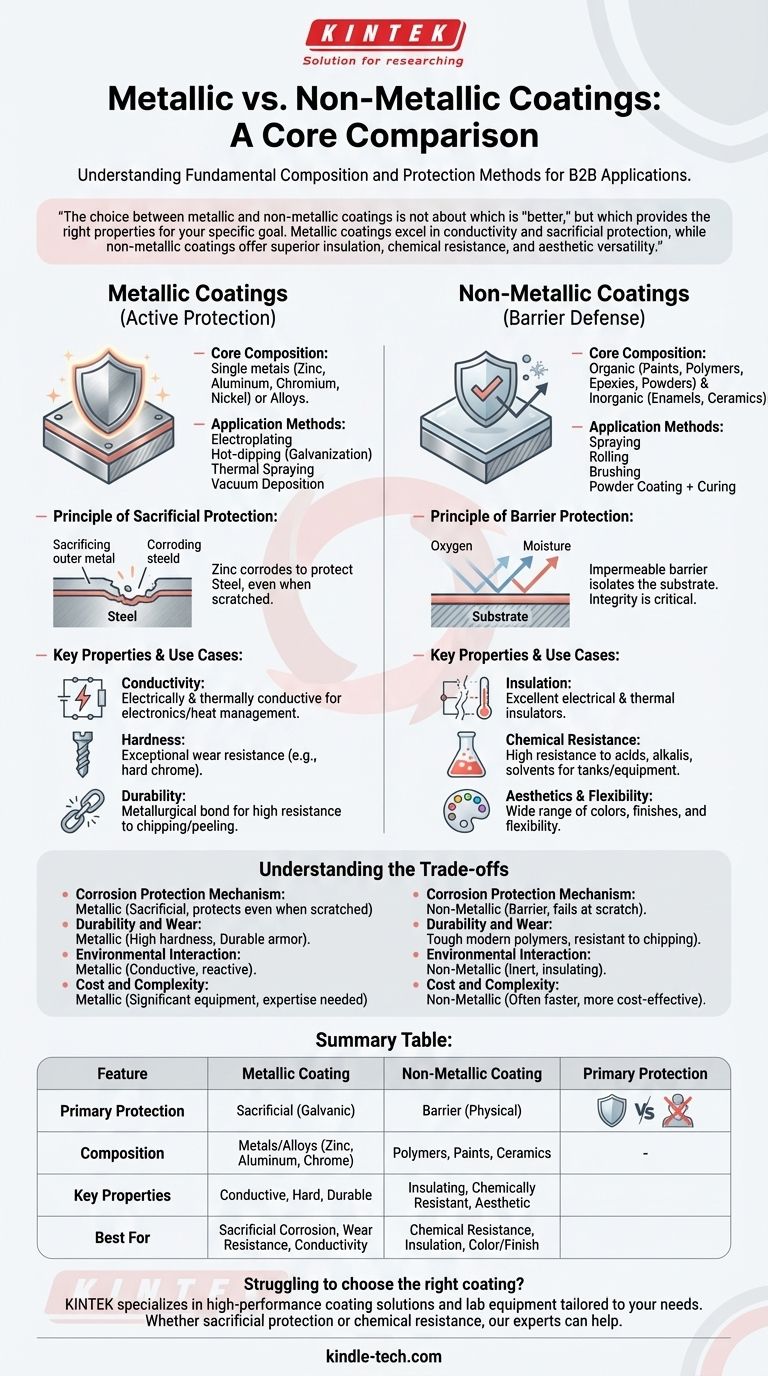
At their core, the difference between metallic and non-metallic coatings lies in their fundamental composition and method of protection. Metallic coatings are composed of metals or metal alloys and are often applied to a substrate to provide sacrificial corrosion protection or enhance hardness. In contrast, non-metallic coatings are made from organic or inorganic compounds like polymers, paints, or ceramics, and typically work by creating an inert physical barrier between the substrate and its environment.
The choice between metallic and non-metallic coatings is not about which is "better," but which provides the right properties for your specific goal. Metallic coatings excel in conductivity and sacrificial protection, while non-metallic coatings offer superior insulation, chemical resistance, and aesthetic versatility.
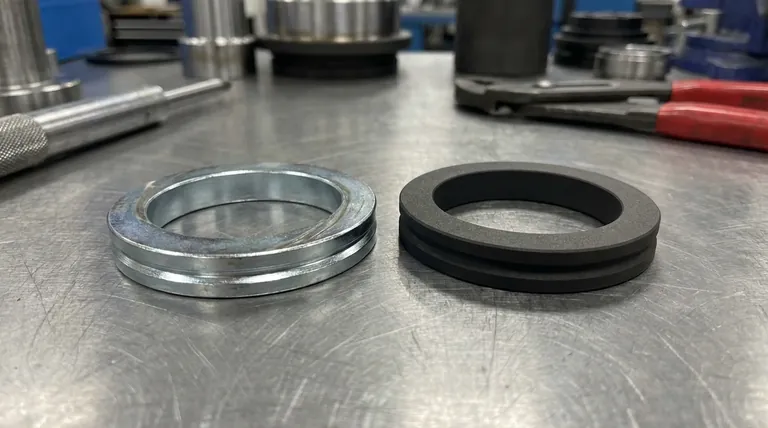

Understanding Metallic Coatings: Active Protection
Metallic coatings involve depositing a layer of metal onto a base material (the substrate). The goal is to lend the surface the properties of the coating metal, such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, or conductivity.
Core Composition and Application
These coatings are made from single metals like zinc, aluminum, chromium, and nickel, or from various alloys.
Common application methods include electroplating, hot-dipping (like galvanization), thermal spraying, and advanced methods like vacuum deposition, which produce strong, thin protective layers.
The Principle of Sacrificial Protection
The primary advantage of many metallic coatings is their ability to provide sacrificial (or galvanic) protection.
When a more reactive metal (like zinc) coats a less reactive one (like steel), the zinc coating will corrode first when exposed to the elements. It essentially sacrifices itself to protect the underlying steel, even if the coating gets scratched.
Key Properties and Use Cases
- Conductivity: Metallic coatings are electrically and thermally conductive, making them essential for electronic components and heat management applications.
- Hardness: Hard chrome plating provides exceptional wear resistance for industrial rollers, hydraulic cylinders, and machine tools.
- Durability: They form a metallurgical bond with the substrate, making them highly resistant to chipping or peeling.
Understanding Non-Metallic Coatings: Barrier Defense
Non-metallic coatings encompass a vast range of materials, from simple paints to advanced polymers and ceramics. Their primary function is to isolate the substrate from its environment.
Core Composition and Application
This category includes organic coatings like paints, plastics, epoxies, and powders, as well as inorganic coatings such as enamels and ceramics.
Application is typically straightforward, involving spraying, rolling, brushing, or powder coating followed by curing.
The Principle of Barrier Protection
Unlike sacrificial metallic coatings, non-metallic coatings act as an impermeable barrier. They physically block oxygen, moisture, and chemicals from reaching the substrate.
The integrity of this barrier is critical. If the coating is scratched or breached, corrosion can begin at the point of damage and spread underneath the coating.
Key Properties and Use Cases
- Insulation: They are excellent electrical and thermal insulators, used to prevent short circuits and reduce heat transfer.
- Chemical Resistance: High-performance polymer coatings offer unmatched resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents, making them ideal for chemical tanks and processing equipment.
- Aesthetics & Flexibility: Non-metallic coatings are available in a nearly infinite range of colors and finishes. Many are also flexible, allowing them to bend with the substrate without cracking.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a coating requires comparing their distinct advantages and disadvantages for your specific context.
Corrosion Protection Mechanism
A metallic coating like zinc actively protects the base metal even when scratched. A non-metallic paint layer loses all protective ability at the site of a scratch, relying entirely on its physical integrity.
Durability and Wear
High-performance metallic coatings, such as those applied in a vacuum, are often harder and more durable than most non-metallic options. They act as a durable "armor" for parts, as mentioned in the reference. However, many modern polymer coatings are extremely tough and resistant to chipping and cracking.
Environmental Interaction
Metallic coatings are conductive and react galvanically with their environment. Non-metallic coatings are inert and insulating. This is often the single most important factor in the selection process, especially for electrical applications.
Cost and Complexity
Applying a simple paint or powder coat is often faster and more cost-effective than complex processes like electroplating or thermal spraying. The required equipment and expertise for many metallic coating processes are significant.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be guided by the primary performance requirement of the coated part.
- If your primary focus is sacrificial corrosion protection for outdoor steel: Choose a metallic coating like zinc (galvanizing) or an aluminum alloy.
- If your primary focus is electrical or thermal insulation: A non-metallic polymer or ceramic coating is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is resistance to harsh chemicals: Select a high-performance non-metallic coating like an epoxy or fluoropolymer.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: A hard metallic coating like chrome plating or a specialized vacuum-deposited coating is ideal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective color and aesthetics: Non-metallic paints and powder coats offer the most versatility and value.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference in how these coatings protect—sacrificially versus as a barrier—is the key to selecting the right technology for your needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Metallic Coating | Non-Metallic Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Protection | Sacrificial (Galvanic) | Barrier (Physical) |
| Composition | Metals/Alloys (Zinc, Aluminum, Chrome) | Polymers, Paints, Ceramics |
| Key Properties | Conductive, Hard, Durable | Insulating, Chemically Resistant, Aesthetic |
| Best For | Sacrificial Corrosion, Wear Resistance, Conductivity | Chemical Resistance, Insulation, Color/Finish |
Struggling to choose the right coating for your lab equipment or industrial parts? KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance coating solutions and lab equipment tailored to your specific needs. Whether you require the sacrificial protection of a metallic coating or the chemical resistance of a non-metallic one, our experts can help you select the perfect solution to enhance durability, performance, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory and industrial requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- High Purity Gold Platinum Copper Iron Metal Sheets
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer










