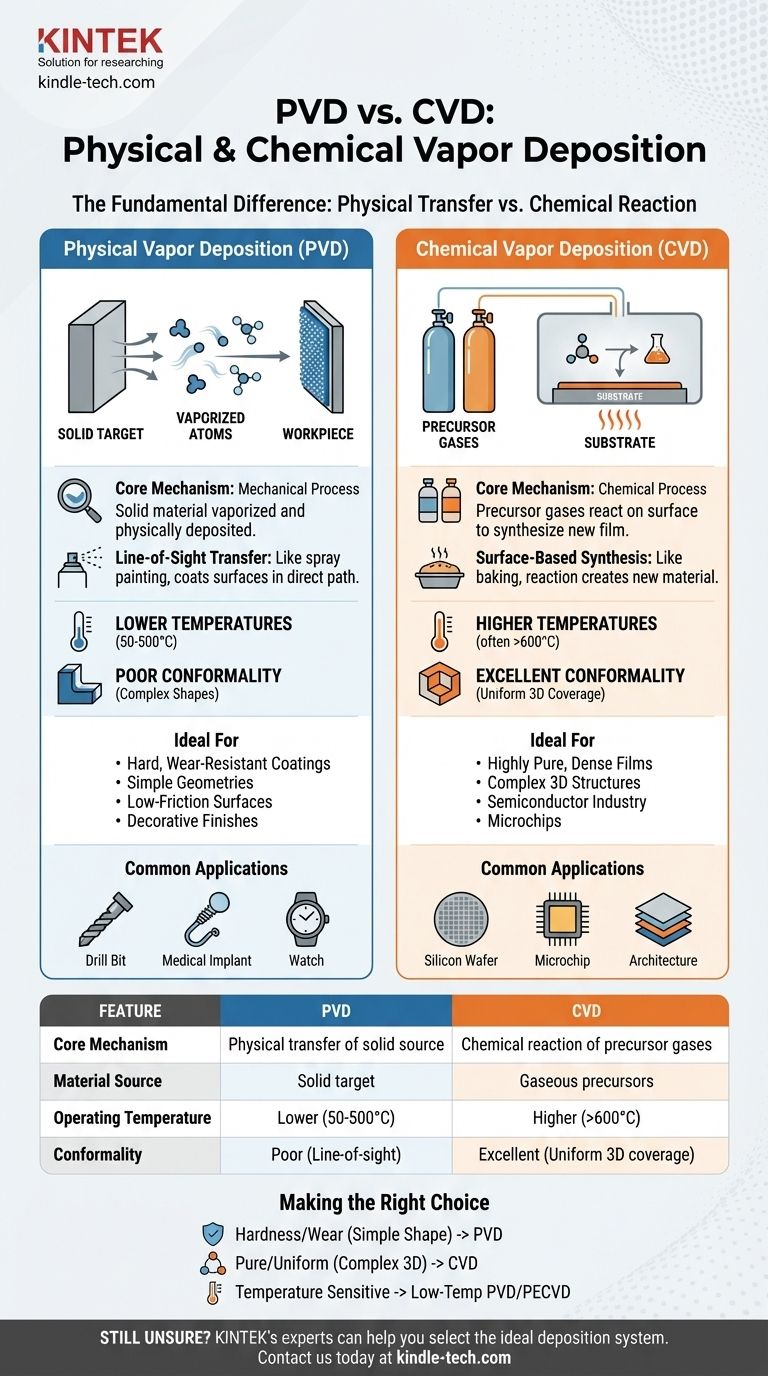
The fundamental difference between Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) lies in how the coating material arrives and forms on a surface. PVD is a mechanical process where a solid material is vaporized into atoms or molecules and physically deposited onto a substrate. In contrast, CVD is a chemical process where precursor gases are introduced into a chamber and react on the substrate's surface to synthesize a new solid film.
While both processes create high-performance thin films, the choice between them hinges on one key distinction: PVD physically transports a source material, whereas CVD chemically creates an entirely new material directly on the target surface.
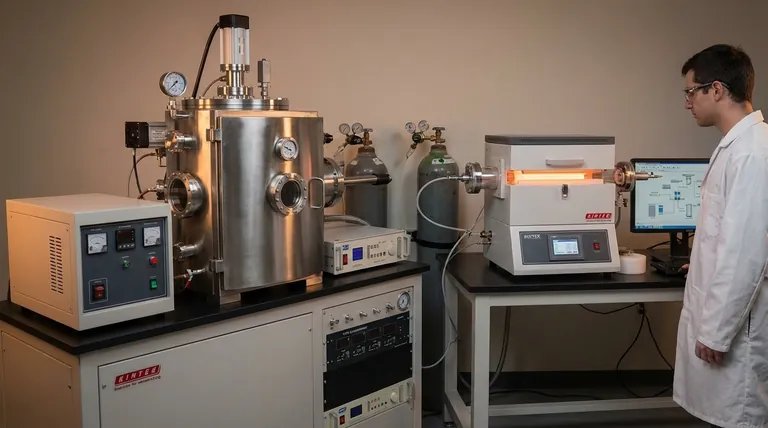

The Core Mechanism: Physical Transfer vs. Chemical Reaction
Understanding the underlying process is the first step to choosing the correct method. The two techniques are not interchangeable; they represent fundamentally different approaches to building a film layer by layer.
How PVD Works: A Line-of-Sight Transfer
In Physical Vapor Deposition, the coating begins as a solid source material, often called a "target." This material is converted into a vapor through purely physical means.
Common methods include evaporation, where the material is heated in a vacuum until it vaporizes, or sputtering, where the target is bombarded with high-energy ions, ejecting atoms that travel toward the substrate.
These vaporized atoms or molecules travel in a straight line—a "line-of-sight"—and condense on the cooler workpiece, forming the solid thin film. Think of it like spray painting, where particles travel directly from the nozzle to the surface.
How CVD Works: A Surface-Based Synthesis
In Chemical Vapor Deposition, the process begins with volatile precursor gases. These gases, which contain the elements required for the final film, are fed into a reaction chamber.
Energy, typically in the form of high heat, is applied to the substrate. This energy causes the precursor gases to react or decompose on the hot surface, forming the desired solid coating. Unwanted byproduct gases are then pumped out of the chamber.
This is less like painting and more like baking a cake. The raw ingredients (gases) are mixed and transformed by heat on the pan's surface (the substrate) to create something new (the film).
Comparing Key Process Parameters
The differences in mechanism lead to distinct process characteristics, each with significant implications for the final product.
Material Source and State
PVD uses a solid source material (e.g., a block of titanium nitride) that is transformed into a vapor. The final film has the same chemical composition as the source material.
CVD uses gaseous precursor chemicals. The final film is the product of a chemical reaction and may be completely different from any of the individual starting gases.
Operating Temperature
CVD typically requires very high temperatures (often >600°C) to provide the activation energy needed to drive the chemical reactions.
PVD processes can often be performed at much lower temperatures (50-500°C), making them suitable for coating materials that cannot withstand the intense heat of a standard CVD process.
Deposition Conformality
This is a critical distinction. Because CVD involves gases that flow and diffuse freely, it can uniformly coat highly complex, three-dimensional surfaces. This property is known as excellent conformality.
PVD is a line-of-sight process. Surfaces not in the direct path of the vapor source receive little to no coating, resulting in poor conformality on intricate shapes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
The choice between PVD and CVD is dictated by the desired properties of the coating and the geometry of the part being coated.
PVD: Hardness and Line-of-Sight Precision
PVD is the go-to process for creating extremely hard, wear-resistant, and low-friction coatings. It is widely used for cutting tools, engine components, and medical implants.
The line-of-sight nature, while a limitation for complex shapes, provides precise control for coating flat surfaces. Decorative finishes on watches and fixtures often use PVD for its durability and wide range of colors.
CVD: Purity and Conformal Coverage
CVD excels at producing exceptionally pure, dense, and uniform films. Its ability to conformally coat complex structures makes it the backbone of the semiconductor industry for building the intricate, layered architecture of microchips.
Specialized techniques like Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD) and Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) expand its capabilities, with PECVD allowing for lower deposition temperatures.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
A common mistake is choosing a method based on the coating material alone. The geometry of the part is equally critical. Using PVD on a part with deep recesses or internal channels will result in an incomplete, non-functional coating.
Conversely, using high-temperature CVD on a heat-sensitive substrate, like certain plastics or tempered alloys, can damage or destroy the part itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your primary technical objective and the physical constraints of your part.
- If your primary focus is creating a hard, wear-resistant coating on a relatively simple shape: PVD is often the more direct, lower-temperature, and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is depositing a highly pure, uniform film on a complex 3D surface: CVD is the superior choice due to its unparalleled ability to coat conformally.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material: A low-temperature PVD process or a specialized technique like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is required.
Understanding this core distinction between physical transport and chemical synthesis is the key to selecting the right deposition technology for your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Physical transfer of a solid source material | Chemical reaction of precursor gases on the substrate surface |
| Material Source | Solid target (e.g., titanium block) | Gaseous precursors |
| Operating Temperature | Lower (50-500°C) | Higher (often >600°C) |
| Conformality | Poor (line-of-sight process) | Excellent (uniform 3D coverage) |
| Ideal For | Hard, wear-resistant coatings on simple shapes | Pure, dense films on complex 3D structures |
| Common Applications | Cutting tools, medical implants, decorative finishes | Semiconductor manufacturing, microelectronics |
Still unsure whether PVD or CVD is right for your project?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and R&D facilities. Our experts can help you select the ideal deposition system to achieve your specific coating goals—whether you require the hardness of PVD or the conformal coverage of CVD.
Contact our technical team today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your research and development processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the process of chemical vapor infiltration? A Guide to Creating High-Performance CMCs
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Superior Thin Films for Your Lab
- What does flexibility mean in the context of a deposition system? Optimize Your R&D Adaptability
- What is physical vapor deposition for jewelry? A Durable, High-Tech Finish for Modern Wear
- What is the history of CVD process? The Evolution of Modern Thin-Film Coating Technology
- What are the methods used to deposit thin films? A Guide to Physical vs. Chemical Deposition
- What are the advantages of using a hot-wall CVD reactor? Optimize Tantalum Carbide Coatings for Semiconductor Purity



















