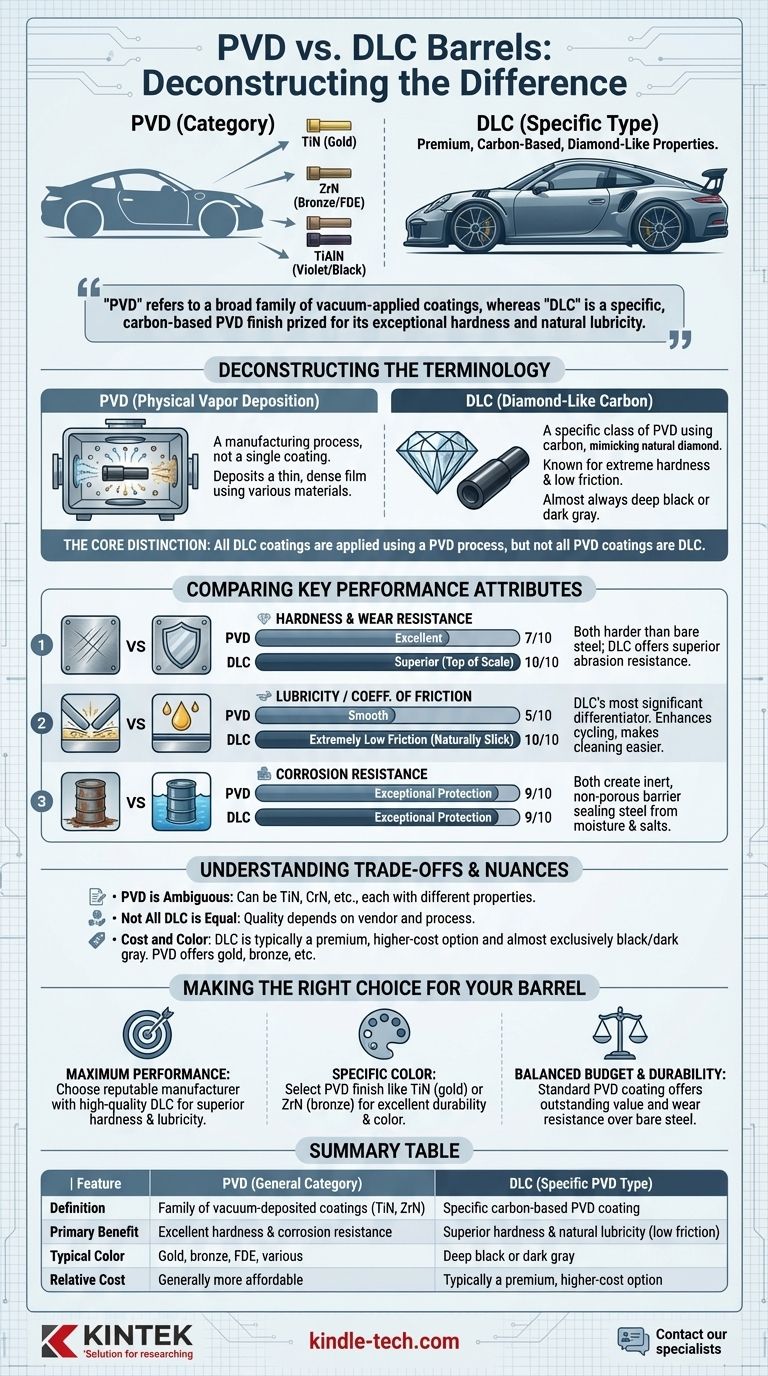
The fundamental difference is not one of opposition, but of classification. Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) is a specific, high-performance type of PVD coating. PVD, or Physical Vapor Deposition, is the broad name for a process used to apply a family of hard, durable finishes. Therefore, asking for the difference is like asking for the difference between a "sports car" and a "Porsche 911"—one is a category, and the other is a specific, premium example within that category.
While both provide a durable, corrosion-resistant finish, "PVD" refers to a broad family of vacuum-applied coatings, whereas "DLC" is a specific, carbon-based PVD finish prized for its exceptional hardness and natural lubricity.

Deconstructing the Terminology: PVD vs. DLC
To make an informed decision, you must first understand the relationship between these two terms. They are often presented as competitors, but the reality is more nuanced.
What is PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition)?
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a manufacturing process, not a single coating. It involves vaporizing a solid material in a vacuum chamber and depositing it as a thin, dense film onto the surface of a part, like a barrel.
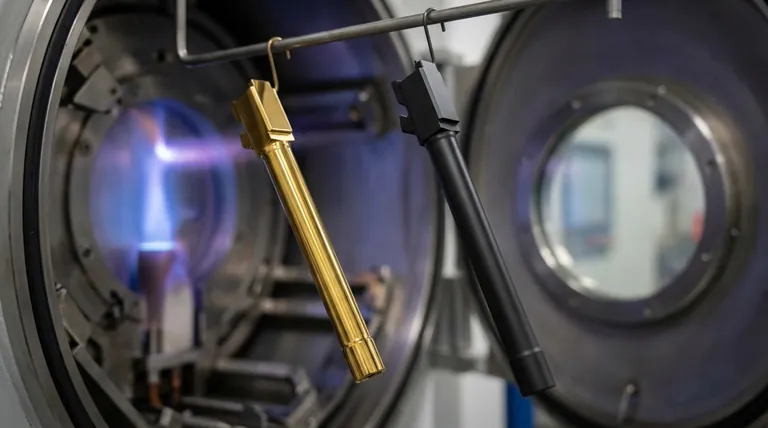
This process can use various materials to create different finishes. Common examples in the firearms industry include Titanium Nitride (TiN), which is gold-colored, and Zirconium Nitride (ZrN), which can be pale gold or flat dark earth.
When a manufacturer simply states a barrel has a "PVD finish," it is a general descriptor for a hard-wearing coating applied via this method.
What is DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon)?
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) is a specific class of PVD coating that uses carbon as its primary material. The process deposits a film with an amorphous structure that mimics many properties of natural diamond.
The key characteristics of DLC are its extreme surface hardness and an incredibly low coefficient of friction (lubricity). It is almost always a deep, rich black or dark gray color.
The Core Distinction: A Category vs. a Specific Finish
Think of it this way: PVD is the overarching family of "vacuum-deposited coatings." DLC is a specialized member of that family, renowned for its premium performance attributes.
All DLC coatings are applied using a PVD process, but not all PVD coatings are DLC.
Comparing Key Performance Attributes
While DLC is a type of PVD, its unique carbon structure gives it distinct advantages over other common PVD coatings like TiN.
Hardness and Wear Resistance
Both PVD and DLC finishes are significantly harder than bare steel or older finishes like bluing. They offer excellent protection against scratches and wear from holsters or general use.
However, high-quality DLC is typically at the absolute top of the hardness scale for firearm coatings. Its diamond-like structure provides superior resistance to abrasion and surface damage.
Lubricity (Coefficient of Friction)
This is the most significant performance differentiator. The atomic structure of DLC makes it naturally slick, resulting in an extremely low coefficient of friction.
This enhanced lubricity means the action of a firearm can cycle more smoothly with less lubrication. It also makes cleaning easier, as carbon fouling and residue have a much harder time adhering to the slick surface. While other PVD coatings are smooth, they do not match the inherent lubricity of DLC.
Corrosion Resistance
Both general PVD coatings and specific DLC coatings create an inert, non-porous barrier over the base metal. This effectively seals the steel from moisture and salts, providing exceptional corrosion resistance.
In this regard, a well-applied PVD finish and a well-applied DLC finish both offer top-tier protection.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Choosing a finish is not always as simple as picking the one with the highest specifications. Cost, quality control, and aesthetics play a crucial role.
"PVD" is an Ambiguous Term
When a product is marketed with a generic "PVD finish," it can be difficult to know exactly what you are getting. It could be TiN, CrN (Chromium Nitride), or another variant, each with slightly different properties. DLC, while it has variations, is a more specific and descriptive term.
Not All DLC is Created Equal
The quality of a DLC finish is highly dependent on the vendor and their specific process. Factors like surface preparation, chamber temperature, and the exact formulation of the carbon mixture dramatically impact the final result. A poorly applied "DLC" finish from a budget source can chip or fail, whereas a properly applied standard PVD finish will be excellent.
Cost and Color
Generally, a true, high-quality DLC coating is one of the more expensive finishing options due to the complexity of the process.
Furthermore, DLC is almost exclusively black or dark gray. If you desire a specific color like gold, bronze, or "oil slick," you must choose a different type of PVD coating, such as Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Titanium Aluminum Nitride (TiAlN).
Making the Right Choice for Your Barrel
Your decision should be guided by your primary goal for the barrel, balancing performance, aesthetics, and budget.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance: Choose a barrel from a reputable manufacturer that explicitly states it uses a high-quality DLC finish. The superior hardness and natural lubricity offer a tangible benefit.
- If your primary focus is a specific color: Select a PVD finish like TiN (gold), ZrN (FDE/bronze), or TiAlN (violet/black). You still get excellent hardness and corrosion resistance that is a major upgrade over traditional finishes.
- If your primary focus is balancing budget and durability: A standard PVD-coated barrel offers outstanding value, providing a massive leap in wear and corrosion resistance compared to bare steel or bluing.
Ultimately, choosing between PVD and DLC is about understanding your priorities and matching them to the specific capabilities of the coating.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (General Category) | DLC (Specific PVD Type) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A family of vacuum-deposited coatings (e.g., TiN, ZrN) | A specific carbon-based PVD coating |
| Primary Benefit | Excellent hardness & corrosion resistance | Superior hardness & natural lubricity (low friction) |
| Typical Color | Gold, bronze, FDE, various | Deep black or dark gray |
| Relative Cost | Generally more affordable | Typically a premium, higher-cost option |
Ready to Select the Perfect Coating for Your Laboratory Equipment?
Understanding the nuances between a general PVD finish and a high-performance DLC coating is critical for achieving optimal results in your lab. The right choice impacts wear resistance, lubricity, and the longevity of your components.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables. Let our experts guide you to the ideal surface treatment for your specific application—whether you need the broad protection of a PVD coating or the superior performance of DLC.
Contact our specialists today to discuss your project requirements and ensure your equipment performs at its best.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















