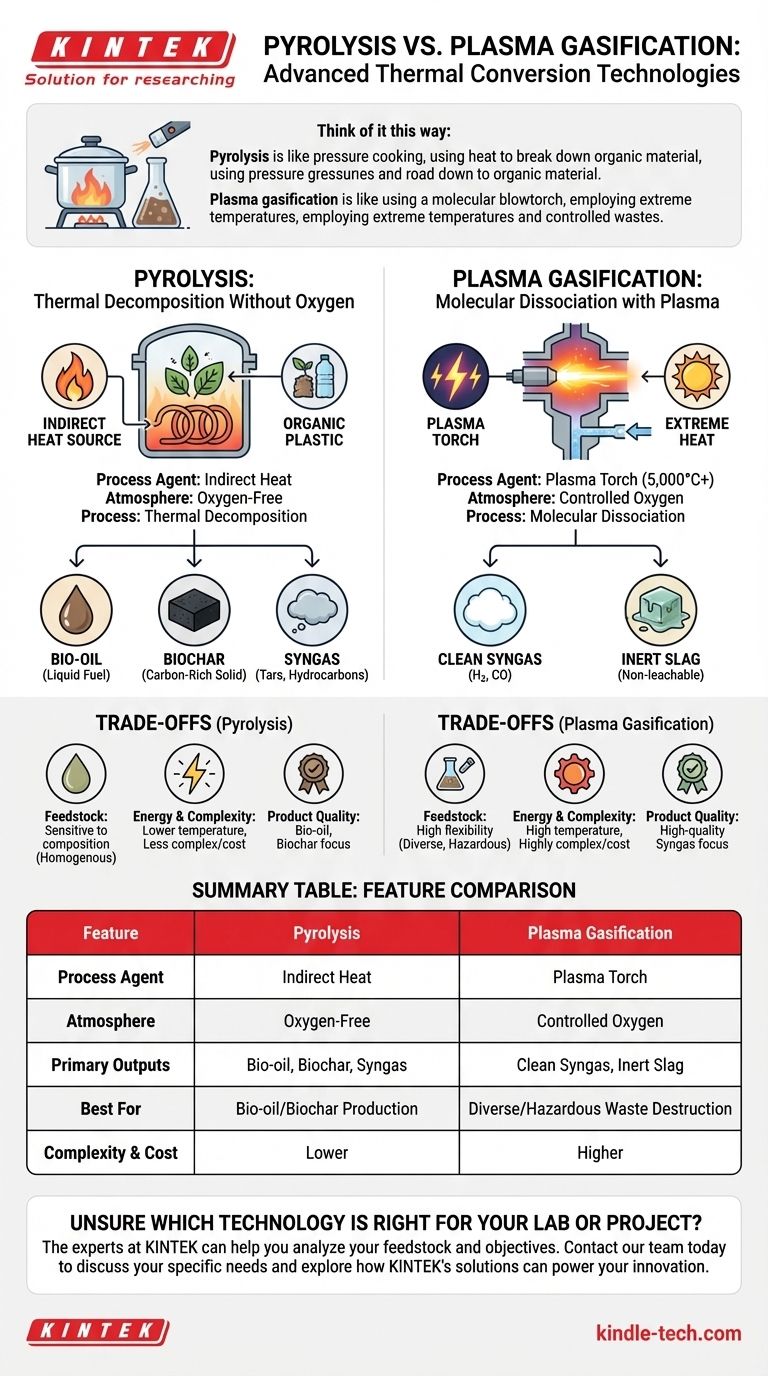
At its core, the primary difference between pyrolysis and plasma gasification lies in the agent used to break down the material. Pyrolysis uses indirect heat in a completely oxygen-free environment to thermally decompose materials, while plasma gasification uses an extremely hot, electrically charged gas (plasma) to molecularly dissociate materials in a controlled-oxygen environment.
Think of it this way: Pyrolysis is like pressure cooking, using heat to break down organic material into simpler components without burning it. Plasma gasification is like using a molecular blowtorch, employing extreme temperatures to shatter molecules into their most basic building blocks.

The Fundamental Difference: Heat and Atmosphere
The core distinction between these two advanced thermal conversion technologies comes down to how they apply energy and the environment in which they do it.
Pyrolysis: Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is a process that heats organic materials (like biomass or plastics) to a high temperature, but in the complete absence of oxygen.
Because there is no oxygen, the material does not combust. Instead, the heat breaks the complex chemical bonds, decomposing the material into three distinct products: a liquid (bio-oil), a solid (biochar), and a gas (syngas).
This process is endothermic, meaning it requires a constant input of external heat to sustain the reaction.
Plasma Gasification: Molecular Dissociation with Plasma
Plasma gasification uses a plasma torch to generate temperatures exceeding 5,000°C—hotter than the surface of the sun.
This intense energy field doesn't just decompose the material; it dissociates it, tearing molecules apart into their fundamental elements.
Unlike pyrolysis, this process uses a controlled amount of an oxidant (like oxygen or air), which makes it a form of gasification, not combustion.
A Comparison of Process Outputs
The radical difference in process conditions leads to fundamentally different outputs, which dictates how they can be used.
Pyrolysis Products: Bio-oil, Syngas, and Biochar
The primary goal of many pyrolysis systems is to maximize the production of bio-oil, a liquid fuel, or biochar, a valuable carbon-rich solid.
The resulting syngas is often a secondary product containing tars and other complex hydrocarbons, which typically require significant secondary processing or "reforming" to become clean enough for high-value applications.
Plasma Gasification Products: Clean Syngas and Inert Slag
Plasma gasification is designed to maximize the output of a high-quality, hydrogen-rich syngas.
The extreme temperatures instantly destroy any tars or complex hydrocarbons, resulting in a very clean gas mixture (primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide).
Any inorganic materials in the feedstock, like glass or metal, are melted down into an inert, non-leachable glassy slag, which is safe for disposal or use as construction aggregate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is universally superior; their suitability depends entirely on the feedstock and the desired outcome.
Feedstock Flexibility
Plasma gasification is the clear winner in terms of flexibility. Its extreme temperatures allow it to process nearly any carbon-containing material, including municipal solid waste, hazardous materials, and industrial byproducts, with minimal pre-treatment.
Pyrolysis is more sensitive to the feedstock's composition and moisture content and works best with more homogenous materials like agricultural waste or specific types of plastic.
Energy Consumption and Complexity
Pyrolysis is a simpler and significantly less energy-intensive process. It operates at much lower temperatures and does not require the massive electrical input needed to power plasma torches.
Plasma gasification is a highly complex and energy-intensive technology with a higher capital and operational cost, primarily due to the electricity demand of the plasma system.
Quality of the Final Product
If the goal is a clean, versatile syngas ready for chemical synthesis or power generation, plasma gasification excels. It produces a high-quality gas directly from the reactor.
If the goal is to produce bio-oil or biochar, pyrolysis is the only viable option between the two, as plasma gasification destroys these more complex compounds.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision between these technologies is a strategic one based on your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is creating bio-oils or biochar from specific biomass: Pyrolysis is the purpose-built technology for this goal.
- If your primary focus is eliminating diverse or hazardous waste streams to create clean syngas: Plasma gasification offers the most robust and complete conversion solution.
- If your primary focus is lower operational cost for processing a consistent, clean feedstock: Pyrolysis is generally the more economical and less complex choice.
Choosing the right thermal technology means matching the process to your specific input material and desired output.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis | Plasma Gasification |
|---|---|---|
| Process Agent | Indirect Heat | Plasma Torch (5,000°C+) |
| Atmosphere | Oxygen-Free | Controlled Oxygen |
| Primary Outputs | Bio-oil, Biochar, Syngas | Clean Syngas, Inert Slag |
| Best For | Bio-oil/Biochar Production | Diverse/Hazardous Waste Destruction |
| Complexity & Cost | Lower | Higher |
Unsure which thermal conversion technology is right for your lab or project? The experts at KINTEK can help you analyze your feedstock and objectives to determine the optimal solution. As a specialist in laboratory equipment and consumables, we provide the insights and technology to advance your research in waste valorization and sustainable energy.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and explore how KINTEK's solutions can power your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role do industrial vacuum ovens play in LPBF powder pretreatment? Optimize Your Metal Additive Manufacturing
- Why Use Vacuum Furnaces for MAX Phase Cladding? Achieve High Purity & Superior Oxidation Resistance
- How do pyrolysis reactor dimensions influence plastic conversion? Optimize Geometry for Higher Liquid Yields
- What is vacuum based deposition? Achieve High-Purity, Performance Coatings for Your Products
- How does sintering affect mechanical properties? Master the Key to Stronger, Denser Materials
- What is the hardening process in simple words? A Guide to Boosting Metal Hardness and Strength
- What is the role of a high-temperature heat treatment furnace in T4 treatment? Optimize (WC+B4C)p/6063Al Strength
- What does bond strength depend on in braze welding? Master the 3 Keys to a Strong Joint



















