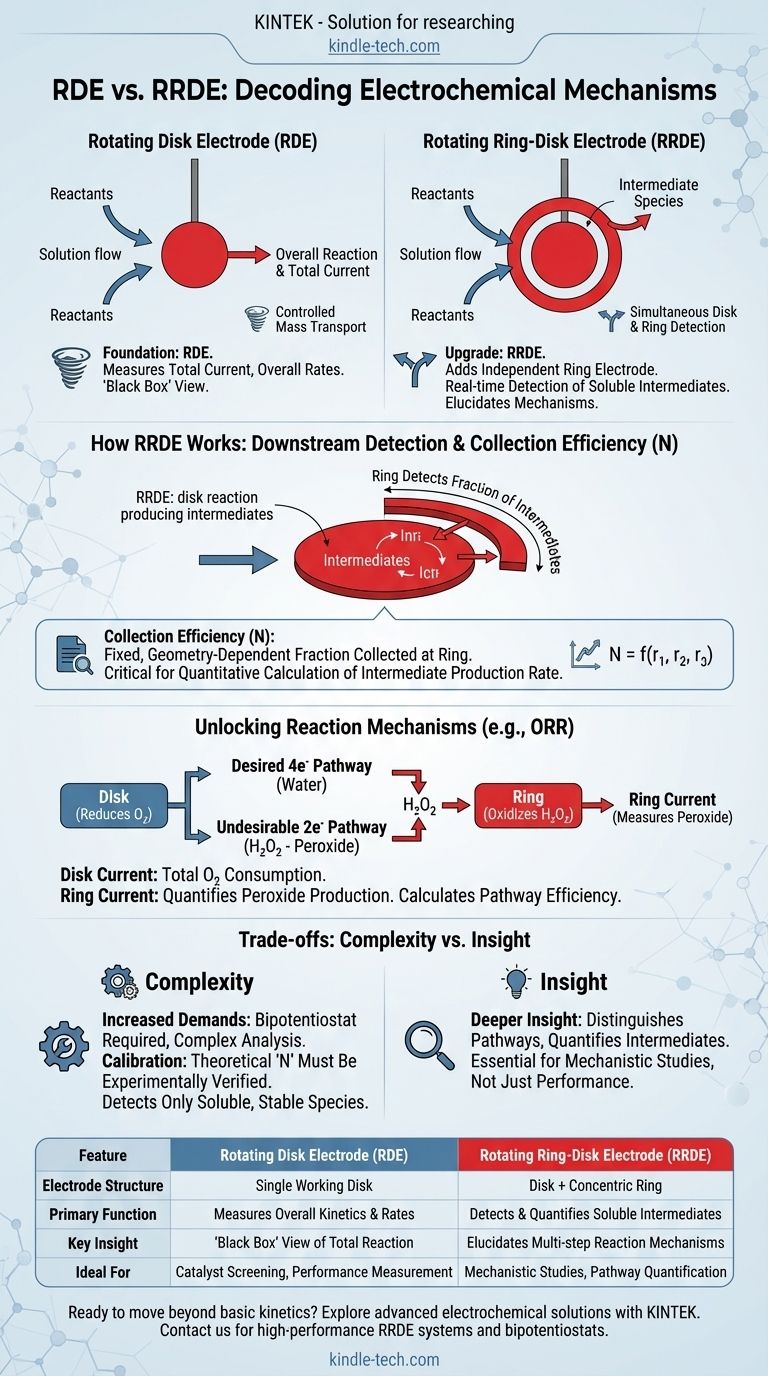
The fundamental difference between a Rotating Disk Electrode (RDE) and a Rotating Ring-Disk Electrode (RRDE) is the addition of a second, independent working electrode. In an RRDE, the central disk is surrounded by a concentric ring electrode, which is electrically insulated from the disk, allowing it to function as a downstream detector for products generated at the disk.
While both techniques use controlled hydrodynamics to study reaction kinetics, the RRDE's ring electrode adds a critical capability: the real-time detection and quantification of soluble reaction intermediates. This transforms it from a tool for measuring overall reaction rates into a powerful device for elucidating multi-step reaction mechanisms.

The Foundation: The Rotating Disk Electrode (RDE)
An RDE is a foundational tool in electrochemistry used to study reaction rates under highly controlled and reproducible conditions.
Creating Controlled Mass Transport
The rotation of the electrode pulls the solution towards its surface and then flings it outwards radially. This creates a very thin, well-defined diffusion boundary layer whose thickness is inversely proportional to the square root of the rotation rate.
This precise control over mass transport allows for the separation of mass-transport effects from the intrinsic kinetics of the electrochemical reaction occurring at the electrode surface.
What an RDE Measures
An RDE experiment measures the total current flowing through the disk electrode as a function of the applied potential.
From this data, you can determine key kinetic parameters for the overall reaction, such as the limiting current, the kinetic current, and the total number of electrons transferred (n).
The Core Limitation
The RDE acts as a "black box." It can tell you the overall efficiency and speed of a reaction (e.g., that oxygen was reduced using an average of 3.9 electrons per molecule), but it cannot tell you how it happened. It cannot distinguish between a direct 4-electron pathway and a 2-electron pathway that produces an intermediate which is then further reduced.
The Upgrade: The Rotating Ring-Disk Electrode (RRDE)
The RRDE builds directly upon the RDE by adding the ring electrode, which acts as a sensitive downstream sensor.
The Ring as a Downstream Detector
As reactants are consumed at the disk, any soluble products or intermediates are swept outwards by the centrifugal force of the rotation. A fraction of these species passes over the ring electrode before being dispersed into the bulk solution.
By setting the potential of the ring to a value where it can detect a specific intermediate (e.g., by oxidizing it), the ring measures a current that is proportional to the amount of that intermediate being produced at the disk.
The Concept of Collection Efficiency (N)
The collection efficiency (N) is a critical, pre-calibrated constant for any given RRDE. It is determined purely by the geometry of the electrode (the radii of the disk and the inner and outer edges of the ring).
N represents the fixed fraction of material generated at the disk that is geometrically guaranteed to be "collected" (i.e., detected) at the ring. Knowing this allows you to quantitatively calculate the rate of intermediate production at the disk based on the current measured at the ring.
Unlocking Reaction Mechanisms
The RRDE allows you to simultaneously run two experiments. For example, in the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR):
- The Disk: Is set to a potential where it reduces oxygen. The current tells you the total rate of oxygen consumption.
- The Ring: Is set to a potential where it oxidizes hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), a common intermediate.
By measuring both the disk and ring currents, you can precisely calculate what percentage of the reaction proceeds via the undesirable 2-electron pathway (producing peroxide) versus the desirable 4-electron pathway (producing water directly).
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the RRDE introduces additional complexity that is not always necessary.
Increased Experimental Demands
An RRDE experiment requires a bipotentiostat, an instrument capable of independently controlling the potential and measuring the current at two separate working electrodes (the disk and the ring) simultaneously. Data analysis is also inherently more complex.
Calibration is Not Optional
The theoretical collection efficiency N is based on perfect geometry. In practice, it must be experimentally verified using a well-behaved, reversible redox couple before you can trust your quantitative results for an unknown system.
Only Detects Soluble, Stable Species
The ring can only detect intermediates that are soluble and stable enough to survive the transit time from the disk to the ring. It cannot provide information about species that remain adsorbed on the disk's surface or that decompose instantly.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Experiment
Your choice depends entirely on the question you need to answer.
- If your primary focus is screening new catalysts or measuring overall performance: An RDE is often sufficient, simpler, and provides the necessary kinetic data like limiting current and overall electron transfer number.
- If your primary focus is understanding a reaction pathway or quantifying intermediate production: An RRDE is essential, as the ring electrode is the only way to directly detect and quantify these soluble species in real time.
- If you are developing a fundamental understanding of an electrochemical process: The RRDE provides a much deeper level of insight that is critical for mechanistic studies, far beyond the "black box" view of an RDE.
By understanding this difference, you can select the precise tool needed to move from simply measuring performance to truly decoding the underlying chemical mechanism.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rotating Disk Electrode (RDE) | Rotating Ring-Disk Electrode (RRDE) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrode Structure | Single working disk electrode | Disk electrode + concentric ring electrode |
| Primary Function | Measures overall reaction kinetics & rates | Detects & quantifies soluble reaction intermediates |
| Key Insight | "Black box" view of total reaction | Elucidates multi-step reaction mechanisms |
| Ideal For | Catalyst screening, performance measurement | Mechanistic studies, pathway quantification |
Ready to move beyond basic kinetics and decode complex electrochemical mechanisms?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced laboratory equipment you need to push the boundaries of your research. Whether you are developing next-generation catalysts, studying fuel cell reactions, or investigating complex electron transfer processes, our range of high-performance RRDE systems and bipotentiostats are designed to deliver the precision and reliability required for groundbreaking discoveries.
Our experts understand the critical importance of accurate data in mechanistic studies. We provide not only top-tier equipment but also the support to ensure you can confidently quantify reaction intermediates and validate your collection efficiency.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our solutions can empower your specific research goals and bring unparalleled clarity to your electrochemical analysis.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between ring disk electrode and rotating disk electrode? Unlock Deeper Electrochemical Insights
- Why is a high-precision Rotating Ring-Disk Electrode (RRDE) essential for ORR? Unlock Precise Catalytic Kinetics
- What is the function of a Laboratory RDE system for OER catalysts? Optimize Kinetic Activity Screening
- What are the technical advantages of RRDE for electrochemical studies? Unlock Real-Time Intermediate Detection
- What is the application of RRDE? Unlock Quantitative Catalyst and Reaction Insights



















