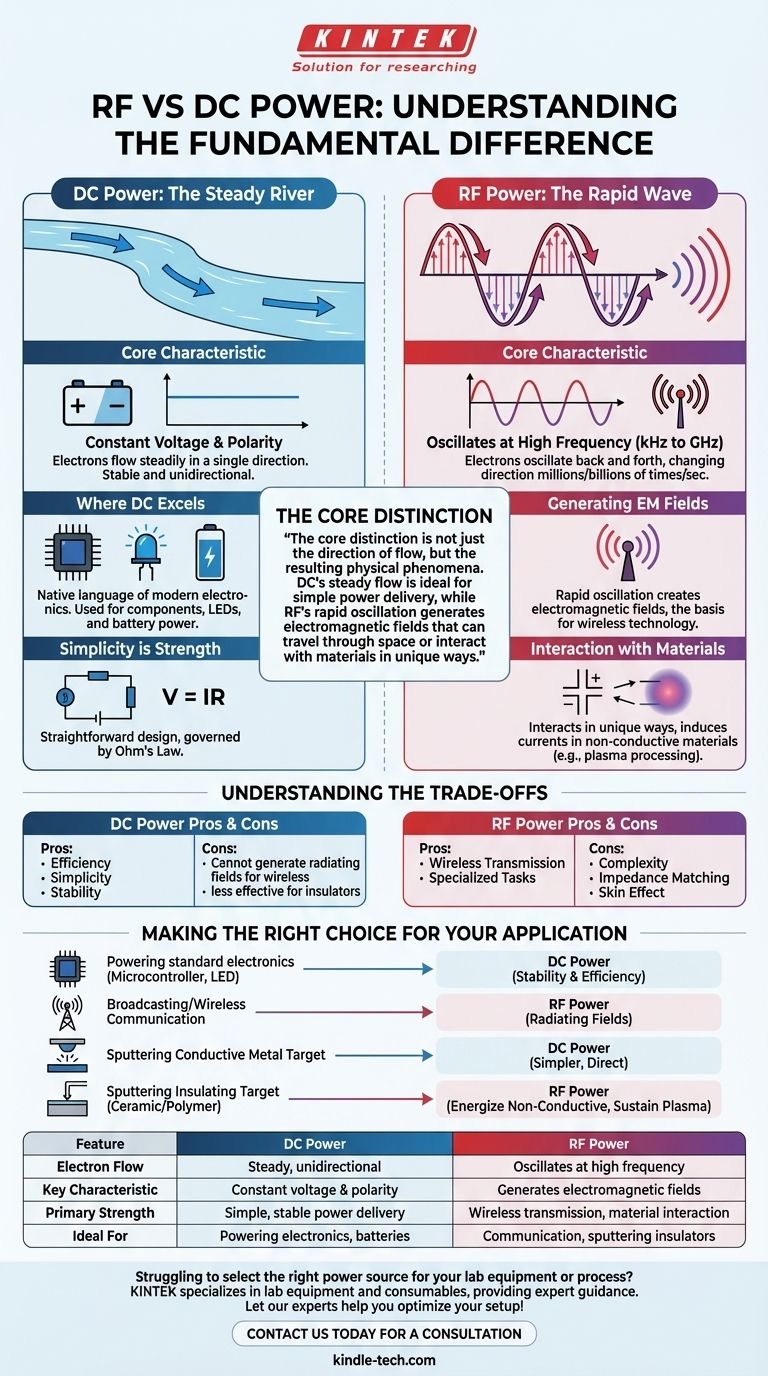
The fundamental difference between DC and RF power lies in the behavior of electrons. In Direct Current (DC) power, electrons flow steadily in a single direction. In Radio Frequency (RF) power, which is a form of Alternating Current (AC), electrons oscillate back and forth at a very high frequency, changing direction millions or billions of times per second.
The core distinction is not just the direction of flow, but the resulting physical phenomena. DC's steady flow is ideal for simple power delivery, while RF's rapid oscillation generates electromagnetic fields that can travel through space or interact with materials in unique ways.

The Nature of DC Power: The Steady River
Direct Current is the simplest form of electrical power, defined by its consistency and predictability. It behaves like a river flowing constantly in one direction.
Constant Voltage and Polarity
The most defining characteristic of DC power is its constant voltage and fixed polarity. One terminal is always positive, and the other is always negative. This creates a stable and unidirectional flow of energy.
Where DC Excels
DC is the native language of most modern electronics. It is used for powering computer components, LEDs, and anything running on a battery, as batteries naturally store and deliver DC power. Its stability is essential for digital logic circuits.
Simplicity is its Strength
DC circuits are generally straightforward to design and analyze. The principles of resistance, voltage, and current (Ohm's Law) govern their behavior without the complexities introduced by high frequencies.
The World of RF Power: The Rapid Wave
RF power is a high-frequency form of Alternating Current (AC). Instead of a steady flow, it behaves like a rapidly oscillating wave, reversing its direction at a specific frequency.
The Critical Role of Frequency
Unlike simple AC that powers your home (at 50 or 60 Hz), RF operates at frequencies from thousands (kHz) to billions (GHz) of cycles per second. This speed is what gives RF its unique properties.
Generating Electromagnetic Fields
The most important consequence of this rapid oscillation is the creation of electromagnetic (EM) fields. As the current accelerates back and forth, it radiates energy away from the conductor in the form of waves. This is the foundational principle behind all wireless technology.
Interaction with Materials
RF energy can interact with materials in ways DC cannot. For example, it can induce currents in non-conductive (dielectric) materials through a process called capacitive coupling. This is critical for applications like plasma generation for processing insulating materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between DC and RF is not about which is "better," but which is the right tool for a specific job. Each has distinct advantages and inherent complexities.
DC Power: Pros and Cons
The strength of DC is its efficiency and simplicity for direct power delivery. It is stable and easy to manage. Its primary limitation is its inability to generate the radiating fields necessary for wireless communication or to effectively energize insulating materials in plasma processes.
RF Power: Pros and Cons
RF's great advantage is its ability to transmit information wirelessly and perform specialized industrial tasks. However, this comes at the cost of complexity. RF circuits require careful design to manage impedance matching, prevent signal reflection, and account for phenomena like the "skin effect," where current flows only on the surface of a conductor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal determines the correct form of power. The application's requirements will make the choice clear.
- If your primary focus is powering standard electronics like a microcontroller or an LED: Use DC for its stability and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is broadcasting a signal or enabling wireless communication: RF is the only choice, as its radiating fields are necessary to carry information through the air.
- If your primary focus is sputtering a conductive metal target in a vacuum chamber: DC is the simpler and more direct method.
- If your primary focus is processing or sputtering an insulating ceramic or polymer target: RF is required to energize the non-conductive material and sustain a plasma.
Understanding this core distinction empowers you to select the right tool for any electrical task, from powering a simple circuit to transmitting a signal across the globe.
Summary Table:
| Feature | DC Power | RF Power |
|---|---|---|
| Electron Flow | Steady, unidirectional | Oscillates at high frequency |
| Key Characteristic | Constant voltage & polarity | Generates electromagnetic fields |
| Primary Strength | Simple, stable power delivery | Wireless transmission, material interaction |
| Ideal For | Powering electronics, batteries | Communication, sputtering insulators |
Struggling to select the right power source for your lab equipment or process? The choice between DC and RF power is critical for the success of applications like thin-film deposition, plasma treatment, and materials processing. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and reliable solutions for your specific laboratory needs. Let our experts help you optimize your setup—contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What materials are sintered? From Metals to Ceramics, Unlocking Advanced Material Properties
- What is plasma melting? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Processing for High-Performance Alloys
- What are the important parameters in thin film deposition with magnetron sputtering technique? Master Your Film's Properties
- How do you measure thin film SEM thickness? A Direct Visual Guide for Accurate Analysis
- Why must cold traps and drying tubes be configured for WGS gas analysis? Protect Your Micro-GC from Moisture Damage.
- Can plastic waste be converted into fuel? Discover the methods, benefits, and risks.
- How long does it take to do a heat treatment? A Full Day for a 100% Bed Bug Kill Rate
- Why is a constant temperature orbital shaker essential for bioleaching? Optimize Enargite Mineral Recovery Today



















