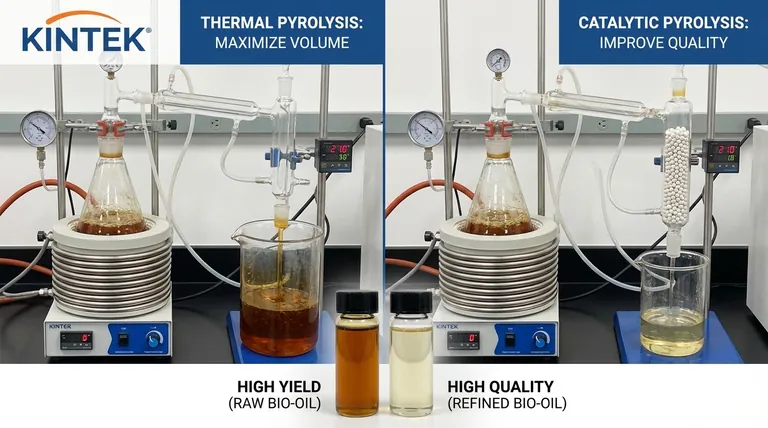
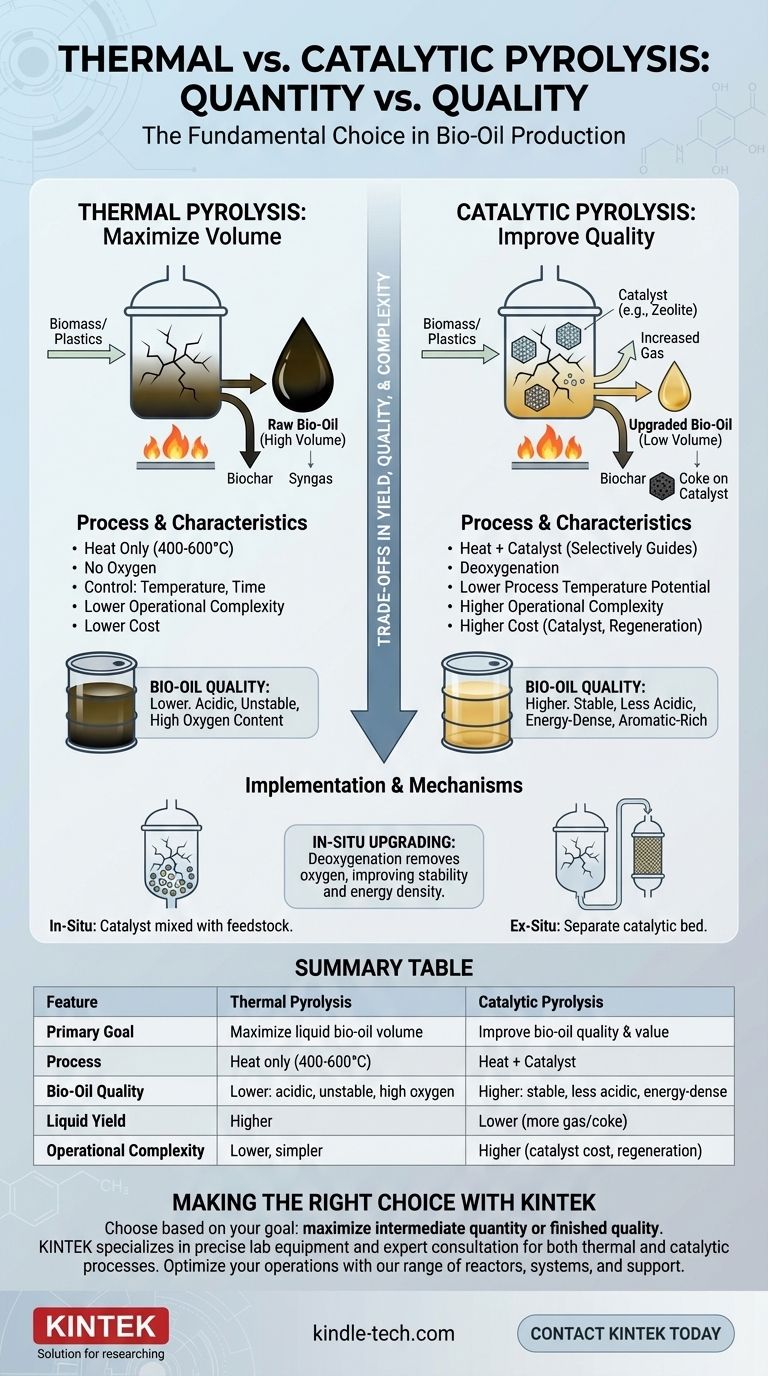
In short, thermal pyrolysis uses only heat to break down materials, while catalytic pyrolysis introduces a catalyst to selectively guide the chemical reactions. This fundamental difference leads to significant trade-offs in product yield, quality, and operational complexity.
The core distinction is a trade-off between quantity and quality. Thermal pyrolysis is designed to maximize the volume of liquid bio-oil produced, whereas catalytic pyrolysis is engineered to improve the quality and value of that oil, often at the expense of volume.
The Foundation: Understanding Thermal Pyrolysis
Thermal pyrolysis is the baseline process, representing the simplest form of converting organic material into bio-oil, biochar, and syngas.
The Core Mechanism: Heat in a Void
This process involves heating biomass or plastics to high temperatures (typically 400-600°C) in an environment completely devoid of oxygen. The absence of oxygen prevents combustion and instead causes the material's long-chain molecules to thermally crack, or break apart, into smaller, more volatile compounds.
The Typical Outcome: High Liquid Yield
The primary goal of most thermal pyrolysis operations is to maximize the yield of the liquid fraction, known as pyrolysis oil or bio-oil. While the liquid yield is high, its quality is often low. It is typically acidic, corrosive, viscous, and chemically unstable due to a high oxygen content.
The Primary Control Levers: Temperature and Time
In thermal pyrolysis, the main variables you can control are temperature, heating rate, and vapor residence time. Faster heating rates and shorter residence times generally favor the production of liquids over char and gas.
The Enhancement: How Catalytic Pyrolysis Changes the Game
Catalytic pyrolysis builds upon the thermal process by adding a catalyst to exert fine-tuned control over the chemical reactions.
Introducing the Catalyst: A Chemical "Guide"
A catalyst is a substance that accelerates a chemical reaction without being consumed by it. In pyrolysis, catalysts act as a "guide," selectively cracking the initial pyrolysis vapors and steering the reactions toward producing more desirable molecules.
The Impact on Bio-Oil Quality
The key benefit of a catalyst is in-situ upgrading. Catalysts promote deoxygenation, removing oxygen atoms from the vapors. This dramatically improves the quality of the final bio-oil, making it:
- More stable and less prone to aging.
- Less acidic and corrosive.
- Higher in energy density (higher heating value).
- Richer in valuable aromatic hydrocarbons, which are precursors for fuels and chemicals.
Implementation Methods: In-Situ vs. Ex-Situ
Catalytic pyrolysis can be performed in two main configurations.
- In-situ: The catalyst is mixed directly with the feedstock. This provides excellent contact but can make catalyst recovery and regeneration difficult.
- Ex-situ: The catalyst is placed in a separate, secondary reactor. Pyrolysis vapors from the first reactor pass through this catalytic bed for upgrading. This simplifies catalyst management but adds complexity to the overall system design.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Yield vs. Quality
Choosing between these two methods requires a clear understanding of their inherent trade-offs. Neither is universally superior; the right choice depends entirely on your end goal.
Product Distribution: Liquid vs. Gas & Coke
Thermal pyrolysis is optimized for the highest possible liquid yield. The introduction of a catalyst, however, promotes further cracking of vapors into non-condensable gases (syngas). It also often increases the formation of coke, which deactivates the catalyst.
Therefore, catalytic pyrolysis almost always results in a lower liquid bio-oil yield but a higher gas yield compared to thermal pyrolysis under similar conditions.
Processing Temperature and Energy
Because catalysts accelerate reactions, catalytic pyrolysis can often be performed at lower temperatures than thermal pyrolysis while still achieving effective conversion. This can lead to energy savings and reduced operational costs.
Operational Complexity and Cost
Thermal pyrolysis is a relatively straightforward process. Catalytic pyrolysis adds significant complexity and cost related to:
- Catalyst Cost: Procuring the initial catalyst (e.g., zeolites like ZSM-5) can be expensive.
- Catalyst Deactivation: Catalysts quickly become deactivated by coke deposits and require a regeneration cycle, which involves burning off the coke in a controlled manner.
- System Design: The need for catalyst handling and regeneration equipment adds to the plant's capital and operational expenditure.
Reactor Technology: A Shared Foundation
It is crucial to note that the physical reactor type—such as a fluidized-bed, auger, or rotary kiln—is not exclusive to either method. The choice of reactor is driven by factors like feedstock type and desired heat transfer rates, and the same reactor can often be used for both thermal and catalytic processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision must be driven by the desired characteristics of your final product and your tolerance for operational complexity and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the volume of raw bio-oil for later upgrading in a separate facility: Thermal pyrolysis is the most direct and cost-effective starting point.
- If your primary focus is producing a higher-quality, more stable bio-oil suitable for use as a "drop-in" fuel or chemical feedstock directly from the process: Catalytic pyrolysis is the necessary choice, despite its lower liquid yield and higher operational complexity.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the production of biochar: Thermal pyrolysis is typically sufficient and simpler, as the quality of the liquid co-product is a secondary concern.
Ultimately, the choice hinges on whether your priority is maximizing the quantity of an intermediate product or the quality of a finished one.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermal Pyrolysis | Catalytic Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximize liquid bio-oil volume | Improve bio-oil quality and value |
| Process | Heat only (400-600°C, no oxygen) | Heat + catalyst to guide reactions |
| Bio-Oil Quality | Lower: acidic, unstable, high oxygen | Higher: stable, less acidic, energy-dense |
| Liquid Yield | Higher | Lower (more gas/coke produced) |
| Operational Complexity | Lower, simpler system | Higher (catalyst cost, regeneration, system design) |
Ready to choose the right pyrolysis process for your lab?
The choice between thermal and catalytic pyrolysis is critical for achieving your specific product goals, whether it's maximizing yield or improving quality. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and expert consultation needed to optimize your pyrolysis operations.
We offer a range of reactors and systems suitable for both thermal and catalytic processes, along with the consumables and technical support to ensure your success. Let our experts help you design a solution that balances yield, quality, and operational efficiency.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your pyrolysis needs and discover how our solutions can advance your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- Why are quartz tubes preferred for chromium powder combustion? Superior Heat Resistance & Optical Clarity
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis



















