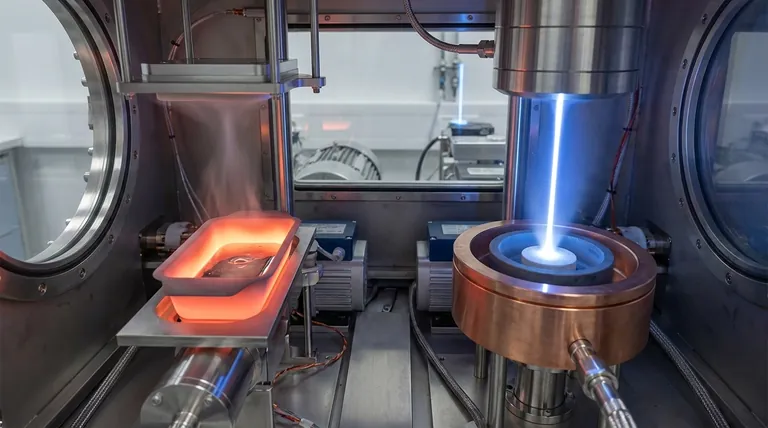
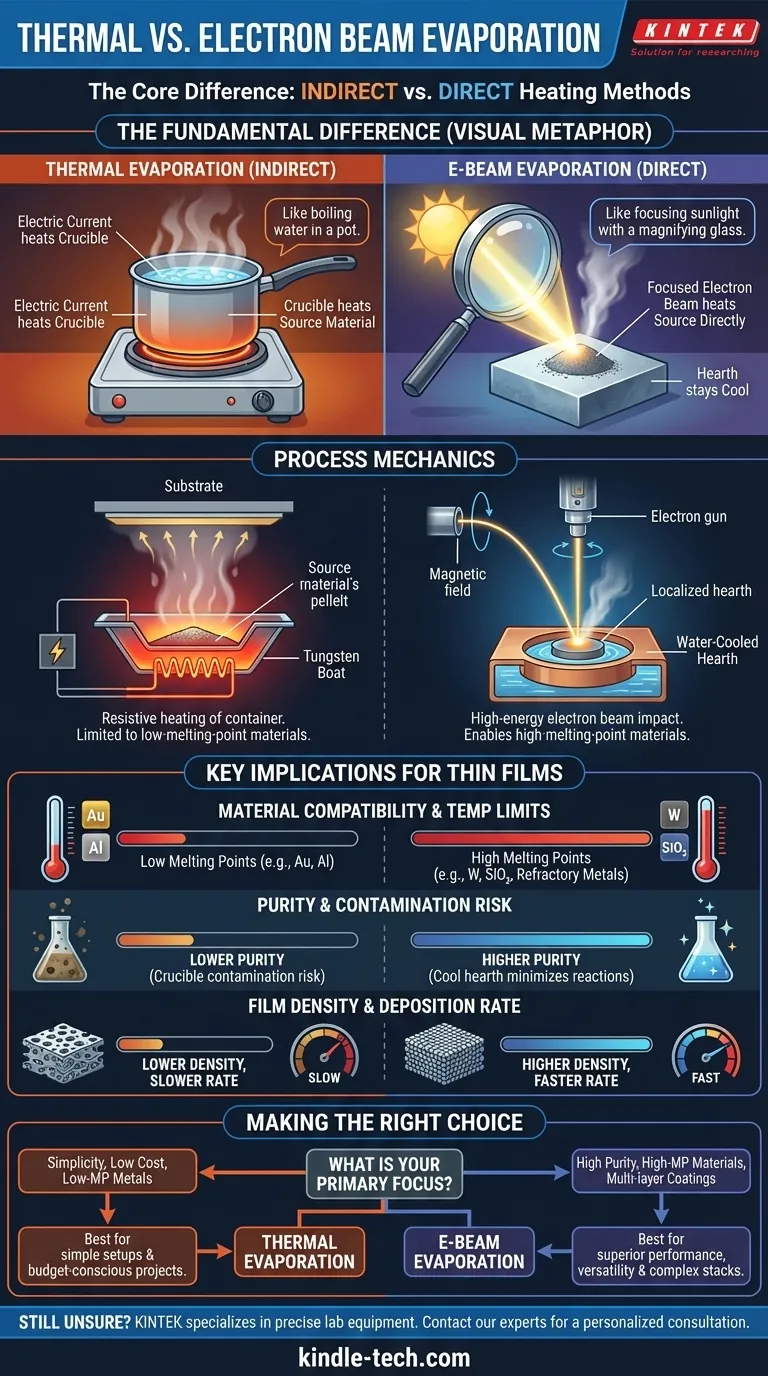
At its core, the difference is in the heating method. Thermal evaporation uses an electric current to heat a container, or "boat," which in turn heats the source material until it evaporates. In contrast, electron beam (e-beam) evaporation uses a focused, high-energy beam of electrons to heat the source material directly, bypassing the need to heat the container.
The choice between thermal and e-beam evaporation hinges on a fundamental trade-off: simplicity versus performance. While thermal evaporation is a simpler process for low-temperature materials, e-beam evaporation offers superior control, purity, and versatility for a much wider range of materials, especially those with high melting points.

The Fundamental Difference: Direct vs. Indirect Heating
The method used to deliver energy to the source material dictates the capabilities, limitations, and ultimate quality of the thin film being deposited.
How Thermal Evaporation Works
In thermal evaporation, a crucible or "boat" made of a resistive material (like tungsten) holds the source material you wish to deposit. A high electrical current is passed through this boat, causing it to heat up significantly. This heat is then transferred to the source material, raising its temperature until it begins to sublimate or evaporate.
This process is analogous to boiling water in a pot on a stove. The stove burner (electric current) heats the pot (crucible), and the pot heats the water (source material).
How E-Beam Evaporation Works
E-beam evaporation employs a much more targeted approach. A tungsten filament emits electrons, which are then accelerated and focused by magnetic fields into a high-energy beam. This beam is aimed directly at the surface of the source material, which sits in a water-cooled copper hearth. The intense, localized energy of the beam causes the material to evaporate instantly upon impact.
This is more like using a powerful magnifying glass to focus sunlight. The energy is concentrated on a tiny spot, leaving the surrounding area—including the container—relatively cool.
Key Implications for Thin Film Deposition
This difference in heating mechanism has profound consequences for the deposition process and the final quality of the film.
Material Compatibility and Temperature Limits
Thermal evaporation is limited to materials with relatively low melting points. The process temperature cannot exceed the melting point of the crucible itself.
E-beam evaporation excels with high-temperature materials. Because the heating is localized, it can vaporize refractory metals (like tungsten and tantalum) and dielectric compounds (like silicon dioxide) that are impossible to deposit using thermal methods.
Purity and Contamination Risk
With thermal evaporation, the entire crucible is heated to extreme temperatures. This creates a higher risk of contamination, as the crucible material itself can outgas or react with the source material, introducing impurities into the deposited film.
E-beam evaporation provides significantly higher purity. The water-cooled hearth stays cool, preventing it from reacting with the source material. Heating is confined only to the material being evaporated, resulting in a cleaner, purer film.
Film Density and Deposition Rate
The high energy transfer in e-beam evaporation leads to a higher deposition rate and typically produces denser, more uniform coatings.
Thermal evaporation generally has a slower deposition rate and can result in less dense films due to the lower energy of the evaporated particles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a method requires balancing process requirements with equipment complexity and cost.
Simplicity vs. Complexity
Thermal evaporation systems are mechanically simpler and often less expensive. The power supplies and control mechanisms are relatively straightforward.
E-beam systems are more complex. They require high-voltage power supplies, sophisticated magnetic fields for beam steering, and more intricate vacuum setups, making them a larger initial investment.
Process Flexibility
E-beam systems offer superior flexibility for multi-layer depositions. They often feature multi-pocket, rotating carousels that hold several different source materials. This allows an operator to deposit multiple layers sequentially in a single vacuum cycle, which is highly efficient for creating complex optical coatings or electronic devices.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your material requirements and film quality standards will ultimately determine the best method.
- If your primary focus is depositing low-melting-point metals with a simple, cost-effective setup: Thermal evaporation is a perfectly suitable choice.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-melting-point materials like refractory metals or oxides: E-beam evaporation is the necessary and superior method.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity and density: E-beam evaporation's localized heating provides a distinct and critical advantage.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, multi-layer coatings in a single process: E-beam systems with multi-pocket sources offer unmatched versatility and efficiency.
Ultimately, understanding these core differences empowers you to select the precise deposition tool that aligns perfectly with your technical goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermal Evaporation | E-Beam Evaporation |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect (heats a crucible) | Direct (focused electron beam) |
| Best For | Low-melting-point metals (e.g., Au, Al) | High-melting-point materials (e.g., W, SiO₂) |
| Film Purity | Lower (risk of crucible contamination) | Higher (water-cooled hearth minimizes contamination) |
| Process Complexity & Cost | Simpler, lower cost | More complex, higher initial investment |
| Multi-Layer Deposition | Limited | Excellent (multi-pocket sources available) |
Still Unsure Which Evaporation Method is Right for Your Project?
KINTEK specializes in providing precise lab equipment and consumables for all your thin film deposition needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal thermal or e-beam evaporation system to ensure superior film quality, purity, and process efficiency for your specific materials and application.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and unlock the full potential of your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications



















