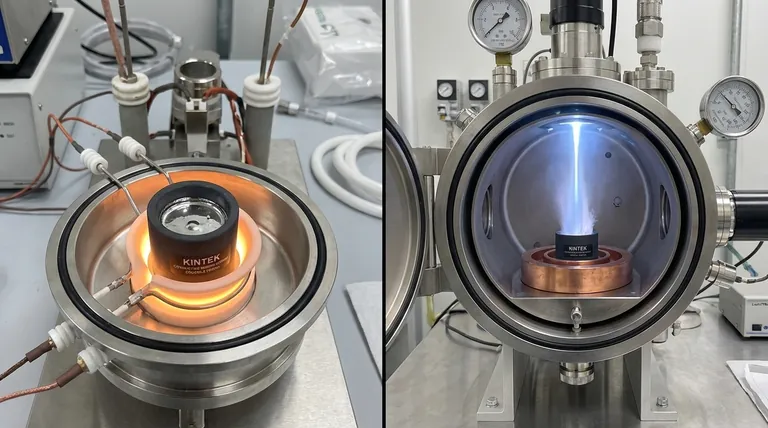
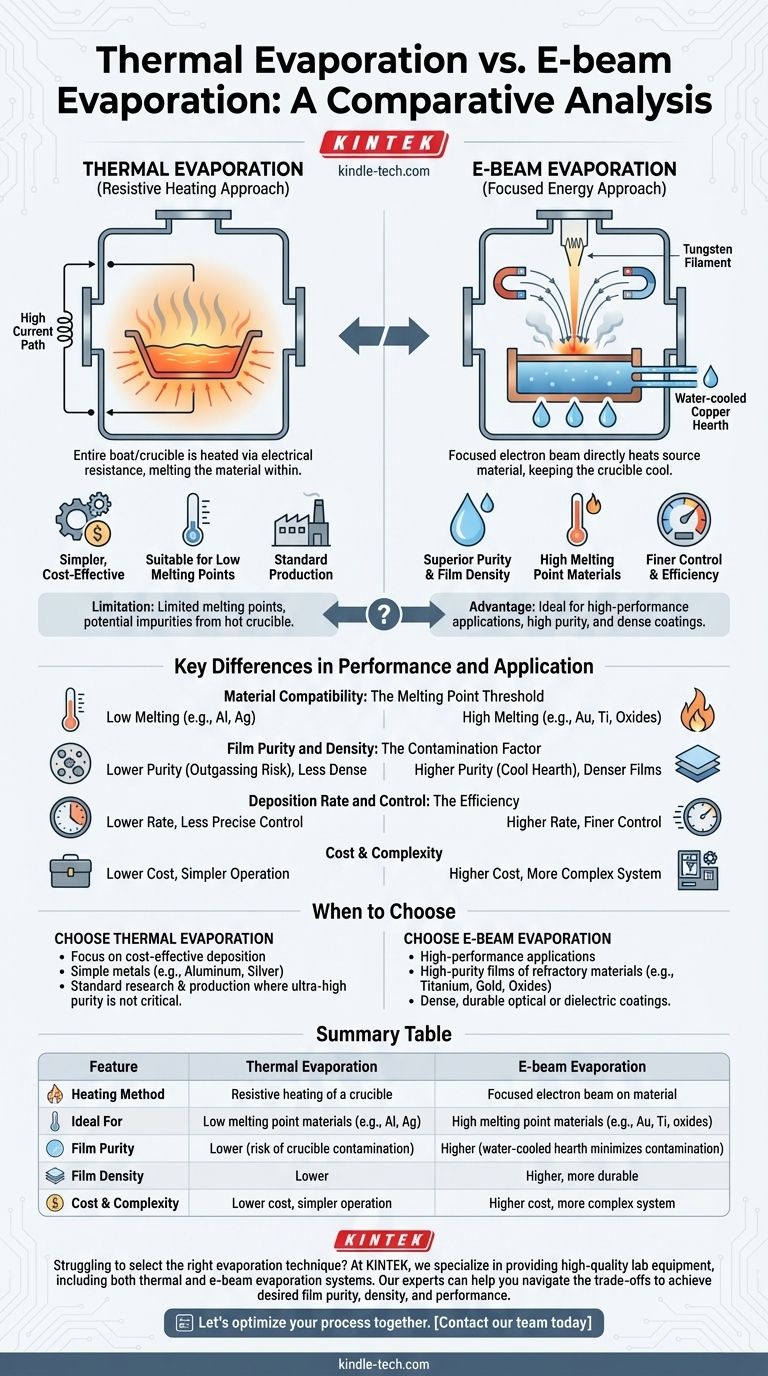
The fundamental difference between thermal evaporation and e-beam evaporation is how the source material is heated to the point of vaporization. Thermal evaporation heats an entire container (a "boat" or crucible) using electrical resistance, which in turn heats the material inside. E-beam evaporation uses a magnetically-focused beam of high-energy electrons to heat the source material directly, leaving the container comparatively cool.
This distinction is critical: e-beam evaporation offers superior purity, film density, and material versatility by targeting only the source material, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Thermal evaporation is a simpler, more cost-effective method suitable for materials with lower melting points.

The Core Mechanism: How is Heat Generated?
The heating method is the central point of divergence and dictates the capabilities and limitations of each technique.
Thermal Evaporation: The Resistive Heating Approach
In thermal evaporation, the source material is placed in a crucible, often called a "boat" or "basket," made of a resistive metal.
A high electrical current is passed through this boat. Due to its electrical resistance, the boat heats up significantly, much like a burner on an electric stove. This heat is then transferred to the source material, causing it to melt and eventually evaporate.
The entire boat and the material within reach a high temperature together.
E-beam Evaporation: The Focused Energy Approach
E-beam evaporation uses a far more direct and precise method. A tungsten filament is heated to generate a stream of electrons.
These electrons are accelerated and then guided by magnetic fields to form a high-energy beam. This beam strikes a small spot on the surface of the source material, which sits in a water-cooled copper hearth.
The intense, localized energy of the electron beam causes the material to evaporate directly from the point of impact, without significantly heating the surrounding crucible.
Key Differences in Performance and Application
The difference in heating mechanics leads to significant and predictable differences in process outcomes.
Material Compatibility: The Melting Point Threshold
Thermal evaporation is limited by the melting point of the crucible itself. It is best suited for materials with lower melting temperatures.
E-beam evaporation can generate extremely high localized temperatures, allowing it to easily vaporize materials with very high melting points, including refractory metals like gold and platinum, and dielectric materials like silicon dioxide.
Film Purity and Density: The Contamination Factor
With thermal evaporation, the hot crucible can outgas or even evaporate along with the source material, introducing impurities into the thin film. The lower-energy process can also result in less dense coatings.
E-beam evaporation produces higher purity films because the water-cooled hearth remains cool, minimizing the risk of contamination. The higher energy involved in the process also results in denser, more durable film structures.
Deposition Rate and Control: The Efficiency of the Process
E-beam evaporation generally offers a much higher deposition rate than thermal evaporation. The direct energy transfer is a more efficient method of vaporizing material.
This efficiency also provides finer control over the deposition process, allowing for more precise management of film thickness and uniformity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these methods requires acknowledging that neither is universally superior; they are tools designed for different tasks.
When to Choose Thermal Evaporation
The primary advantages of thermal evaporation are its simplicity and lower equipment cost. It is an excellent choice for depositing simple metallic films with low melting points where ultra-high purity is not the primary concern. Its straightforward operation makes it ideal for many research and standard production applications.
When to Choose E-beam Evaporation
E-beam evaporation is the choice for high-performance applications. Its ability to handle high-temperature materials, produce high-purity films, and create dense coatings is essential for advanced optics, semiconductors, and other demanding fields. This capability comes with increased equipment complexity and cost.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your material requirements and performance goals will directly point you to the correct method.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective deposition of simple metals (e.g., aluminum, silver): Thermal evaporation is the most practical and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-purity films of refractory materials (e.g., titanium, gold, oxides): E-beam evaporation is the only reliable option.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, durable optical or dielectric coatings: E-beam evaporation provides the energy necessary to achieve superior film quality.
Ultimately, selecting the right evaporation technique is about matching the tool's capabilities to your specific application's demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermal Evaporation | E-beam Evaporation |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Resistive heating of a crucible | Focused electron beam on material |
| Ideal For | Low melting point materials (e.g., Al, Ag) | High melting point materials (e.g., Au, Ti, oxides) |
| Film Purity | Lower (risk of crucible contamination) | Higher (water-cooled hearth minimizes contamination) |
| Film Density | Lower | Higher, more durable |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower cost, simpler operation | Higher cost, more complex system |
Struggling to select the right evaporation technique for your specific material and application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including both thermal and e-beam evaporation systems, to meet your precise thin-film deposition needs. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs to ensure you achieve the desired film purity, density, and performance for your project—whether in research, semiconductors, or advanced optics.
Let's optimize your process together. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the impact of substrate temperature on film properties? Optimize Density, Crystallinity & Stress
- What is the thermal evaporation method in thin film? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- How do you evaporate metal? Mastering Thermal vs. E-beam Evaporation for Thin Films
- What is the thermal evaporation of gold? A Simple Guide to Gold Thin Film Deposition
- Can metals be deposited by evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between a condenser and an evaporator? The Key to Efficient Cooling Systems
- What are the advantages of e-beam evaporation? Achieve High-Purity, High-Rate Thin Film Deposition
- What is the current of e-beam evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition



















