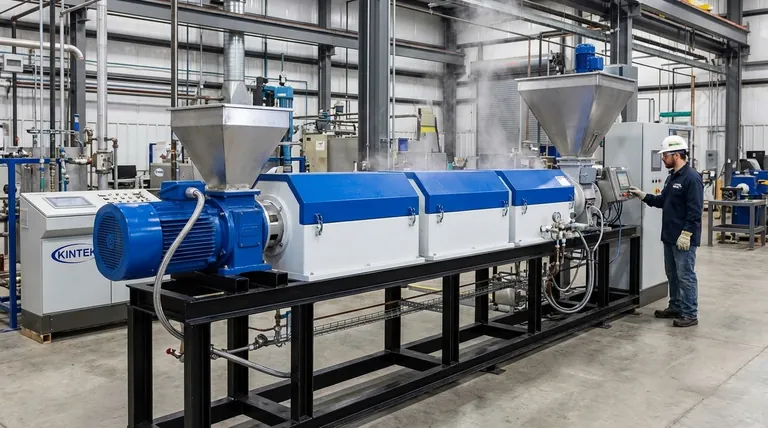
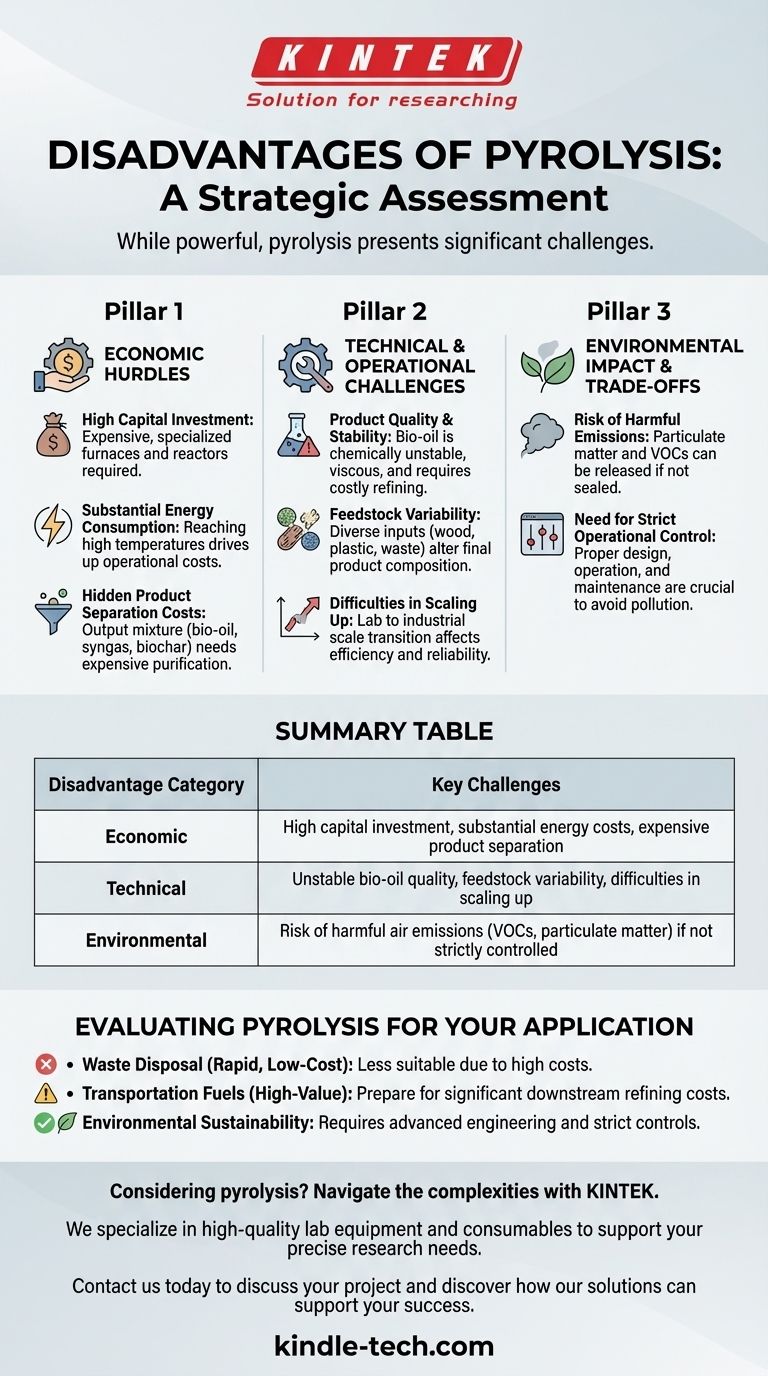
While a powerful technology, pyrolysis is not a simple solution. Its main disadvantages are significant economic costs, high energy consumption, the technical complexity of handling its products, and the potential for creating harmful air emissions if not managed with precision.
While pyrolysis can transform waste into valuable resources, its practical viability is often challenged by high capital and operational costs, coupled with the technical difficulty of refining its unstable outputs into market-ready products.

The Economic Hurdles of Pyrolysis
The most immediate barriers to adopting pyrolysis are financial. The process demands a substantial upfront investment and incurs significant ongoing expenses that can impact its overall profitability.
High Capital Investment
Deploying a pyrolysis system requires expensive, specialized equipment and machinery. The furnaces and reactors needed to withstand high temperatures in an oxygen-free environment contribute to a high initial capital cost.
Substantial Energy Consumption
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process. Reaching and maintaining the necessary high temperatures, sometimes over long periods, consumes a large amount of energy, driving up operational costs.
The Hidden Costs of Product Separation
The output of pyrolysis is not a single, clean product. It's a mixture of bio-oil, syngas, and biochar that requires an efficient, and often expensive, separation and purification process before the components can be used.
Technical and Operational Challenges
Beyond the costs, pyrolysis presents several engineering and chemical challenges that must be addressed for a project to be successful.
The Problem of Product Quality and Stability
The liquid bio-oil produced is a primary challenge. It is chemically unstable and tends to increase in viscosity or even separate into different phases over time.
Heating this oil can cause it to rapidly form solids and release volatile organic compounds, meaning it almost always requires further costly refining before it can be used as a stable transportation fuel.
Feedstock Variability
The final products of pyrolysis are highly dependent on the initial material, or feedstock, being processed. Variations in the type and quality of feedstock (like wood, plastic, or agricultural waste) can alter the composition of the bio-oil and other outputs, making consistent production difficult.
Difficulties in Scaling Up
Moving a pyrolysis process from a laboratory setup to a large-scale industrial operation is technically challenging. Issues that are manageable on a small scale can become significant obstacles, impacting efficiency and reliability at commercial volumes.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Environmental Impact
While often framed as a "green" technology, the environmental benefits of pyrolysis are conditional and depend entirely on system design and operation.
The Risk of Harmful Emissions
The process itself can produce emissions that negatively impact air quality. Pollutants such as particulate matter and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can be released if the system is not perfectly sealed and managed.
The Need for Strict Operational Control
To be environmentally sound, a pyrolysis facility requires proper furnace design, diligent operation, and rigorous maintenance. Without these controls, the process can shift from being a solution to pollution to becoming a source of it.
Evaluating Pyrolysis for Your Application
Understanding these disadvantages is the key to determining if pyrolysis is the right technology for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid, low-cost waste disposal: The high initial investment and operational energy costs of pyrolysis may make it less suitable than simpler methods like landfilling or incineration.
- If your primary focus is creating high-value transportation fuels: Be prepared for the significant downstream costs and technical challenges associated with refining, upgrading, and stabilizing the raw bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: Recognize that achieving a truly "green" process demands advanced engineering and strict operational controls to mitigate the inherent risk of air pollution.
A successful pyrolysis strategy depends on a clear-eyed assessment of these economic and technical realities from the outset.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| Economic | High capital investment, substantial energy costs, expensive product separation |
| Technical | Unstable bio-oil quality, feedstock variability, difficulties in scaling up |
| Environmental | Risk of harmful air emissions (VOCs, particulate matter) if not strictly controlled |
Considering pyrolysis for your lab or facility? The technical and economic challenges require specialized equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories. Our team can help you navigate the complexities of thermal conversion processes. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















