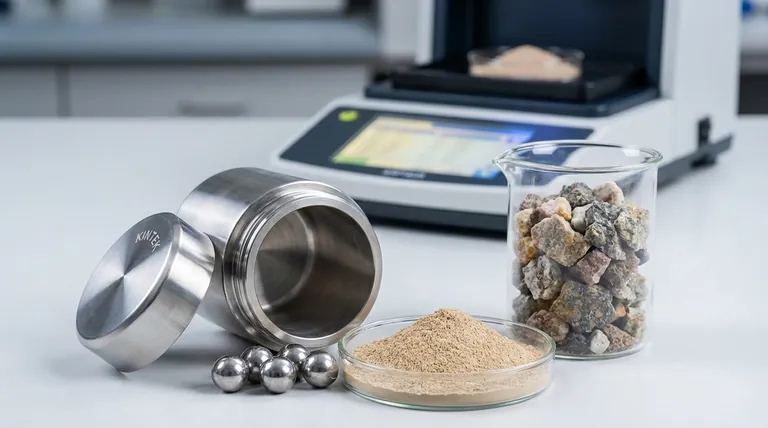
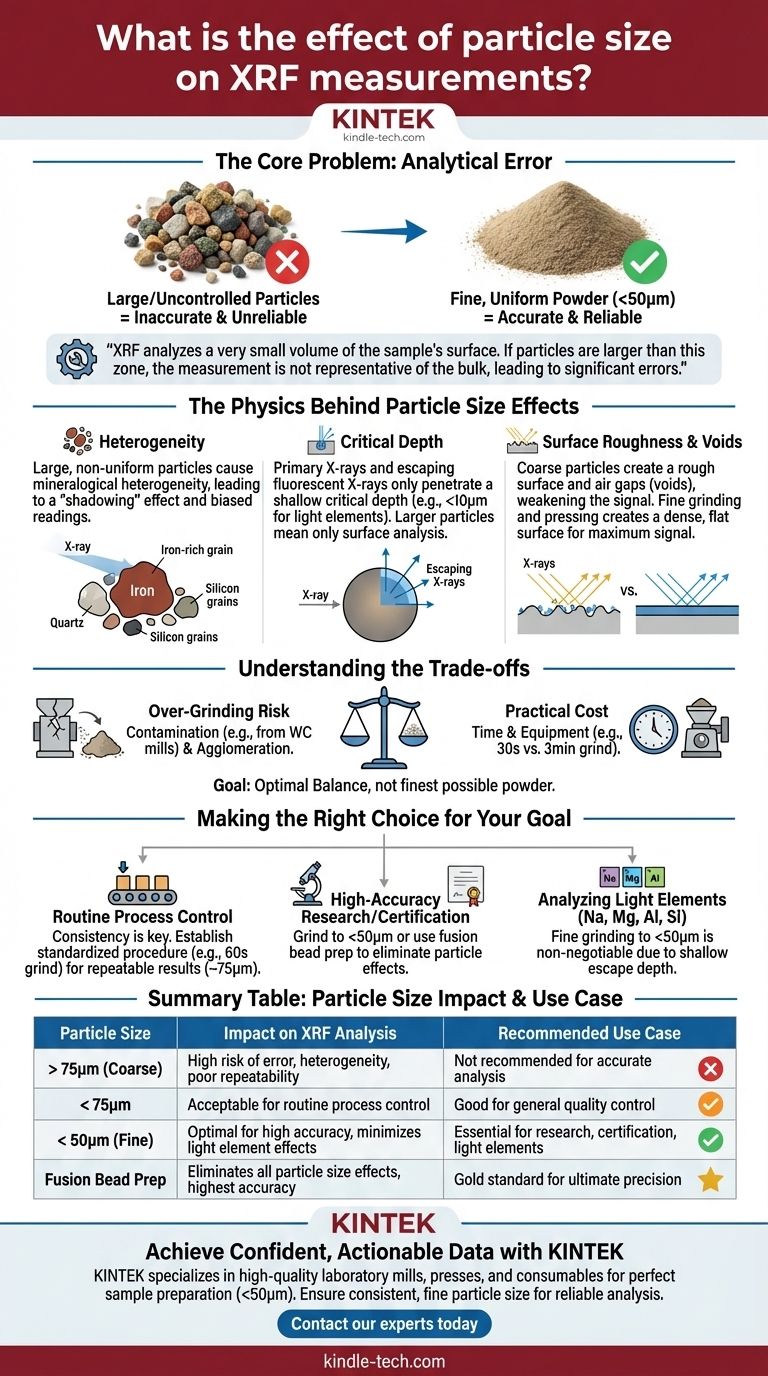
In X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) analysis, particle size is one of the most significant sources of analytical error. Uncontrolled or oversized particles in a sample directly lead to inaccurate and unreliable measurements because they create physical and chemical inconsistencies that distort the X-ray signal. For best results, samples should be ground to a fine, uniform powder, typically less than 50 microns (µm).
The core issue is that XRF analyzes a very small volume of the sample's surface. If the individual particles are larger than this analysis zone or are not uniformly distributed, the measurement will not be representative of the bulk material, leading to significant errors.

The Physics Behind Particle Size Effects
To achieve accurate results, you must first understand how particle size physically interferes with the XRF measurement process. The primary issues stem from sample heterogeneity and surface imperfections.
The Problem of Heterogeneity
A powdered sample is rarely a single substance; it is a mixture of different minerals or phases. Each phase has a unique elemental composition.
Large, non-uniform particles cause mineralogical heterogeneity. Imagine a sample with large grains of quartz (SiO₂) mixed with smaller grains of hematite (Fe₂O₃). The X-ray beam might hit a large iron-rich grain, artificially inflating the iron reading, while missing the silicon entirely.
This "shadowing" effect means the analysis is biased toward whichever particles happen to be on the very top surface, making the results highly variable and non-repeatable.
X-ray Penetration and "Critical Depth"
The primary X-rays from the instrument only penetrate a shallow layer of the sample, and the fluorescent X-rays that escape to the detector come from an even shallower depth, known as the critical depth.
For heavier elements, this depth can be hundreds of microns, but for critical light elements (like Na, Mg, Al, Si), it can be less than 10 microns.
If your sample particles are larger than this critical depth, the analysis is only measuring the composition of that single grain, not the average composition of the sample. Grinding the sample to a size smaller than the critical depth of the lightest element of interest is essential for a representative analysis.
Surface Roughness and Void Spaces
A sample made of coarse, irregular particles will have a rough surface and significant air gaps, or voids, between particles.
This roughness changes the take-off angle of the fluorescent X-rays, altering the path length to the detector and weakening the signal. The voids act as dead space, reducing the overall density of the sample presented to the beam, which systematically lowers the intensity counts for all elements.
Fine grinding and pressing the sample into a pressed pellet minimizes these voids, creating a dense, flat analytical surface that ensures maximum signal and repeatability. This is why smaller particles create better binding under pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While fine grinding is critical, there are practical limits and potential downsides to consider. The goal is an optimal balance, not necessarily grinding to the finest possible powder.
The Risk of Over-Grinding
Excessively long grinding times can introduce problems. The most common issue is contamination from the grinding vessel itself. Mills made of tungsten carbide (WC), for example, can introduce trace amounts of tungsten and cobalt into the sample.
Some materials can also begin to "cake" or agglomerate if ground too finely, re-introducing a form of heterogeneity.
The Practical Cost: Time and Equipment
Grinding is a preparatory step that costs time and requires specific equipment, such as a ring-and-puck mill or ball mill.
For high-throughput industrial environments, the time spent on grinding must be balanced against the required analytical precision. A 30-second grind might be sufficient for process control, while a 3-minute grind might be necessary for certification.
The General Rule: <75µm to <50µm
For the vast majority of pressed pellet XRF applications, grinding to a particle size of less than 75 microns is acceptable.
However, for achieving high accuracy, especially when analyzing light elements, the gold standard is to grind to less than 50 microns. This size provides the best compromise between reducing particle effects and minimizing contamination risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your grinding strategy should be tailored to your specific analytical needs. There is no single answer that fits every situation.
- If your primary focus is routine process control: Consistency is key. Establish a standardized grinding procedure (e.g., 60 seconds in a specific mill) that produces a repeatable particle size distribution, even if it is closer to 75µm.
- If your primary focus is high-accuracy research or certification: Grind to <50µm and consider using fusion bead preparation, which completely dissolves the sample in a flux. This eliminates all particle size and mineralogical effects, providing the highest possible accuracy.
- If your primary focus is analyzing light elements (Na, Mg, Al, Si): Fine grinding to <50µm is non-negotiable. The extremely shallow escape depth for these elements makes their analysis acutely sensitive to particle size effects.
Mastering sample preparation is the foundation of trustworthy XRF analysis; it turns your instrument's potential into confident, actionable data.
Summary Table:
| Particle Size | Impact on XRF Analysis | Recommended Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| > 75µm (Coarse) | High risk of error, mineral heterogeneity, poor repeatability | Not recommended for accurate analysis |
| < 75µm | Acceptable for routine process control where consistency is key | Good for general quality control |
| < 50µm (Fine) | Optimal for high accuracy, minimizes effects for light elements | Essential for research, certification, light element analysis |
| Fusion Bead Prep | Eliminates all particle size effects, highest accuracy | Gold standard for ultimate precision |
Achieve Confident, Actionable Data with KINTEK
Don't let particle size undermine your XRF results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory mills, presses, and consumables designed specifically for perfect sample preparation. Our equipment ensures you achieve the consistent, fine particle size (<50µm) necessary for reliable analysis of light elements and bulk composition.
Contact our experts today to find the ideal grinding and pressing solution for your specific application—from routine process control to high-accuracy certification.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Sealed Hammer Crusher for Efficient Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
People Also Ask
- What is the product size of a ball mill? Achieve Micron-Level Precision for Your Materials
- What affects ball mill efficiency? Optimize Grinding Speed, Media, and Material for Peak Performance
- What is the average speed of a ball mill? Optimize Grinding with Critical Speed Calculations
- What are the factors affecting grinding efficiency? Optimize Your Process for Maximum Output
- What are the disadvantages of a ball mill? High Energy Use, Noise, and Contamination Risks



















