In short, temperature is the single most critical factor in determining the output of biomass pyrolysis. Lower temperatures favor the production of solid biochar, intermediate temperatures maximize liquid bio-oil, and very high temperatures convert the biomass primarily into combustible gases. The choice of temperature directly controls whether you produce a solid, a liquid, or a gas.
Pyrolysis is not a single process but a tunable thermal conversion platform. By mastering temperature and heating rate, you can precisely control the breakdown of biomass to yield the specific product—solid, liquid, or gas—that meets your objective.
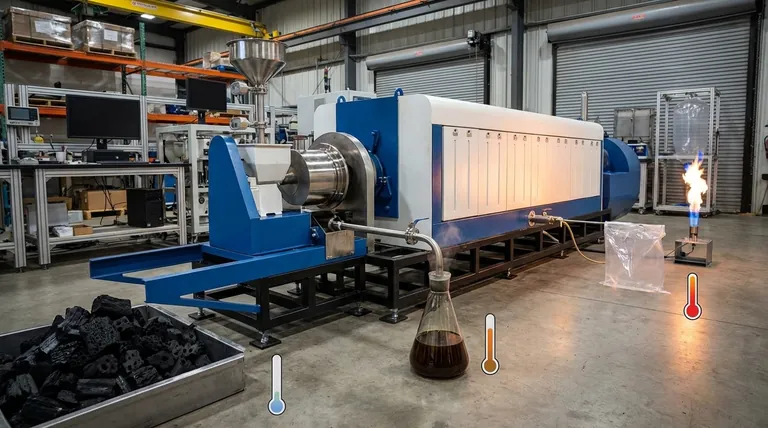

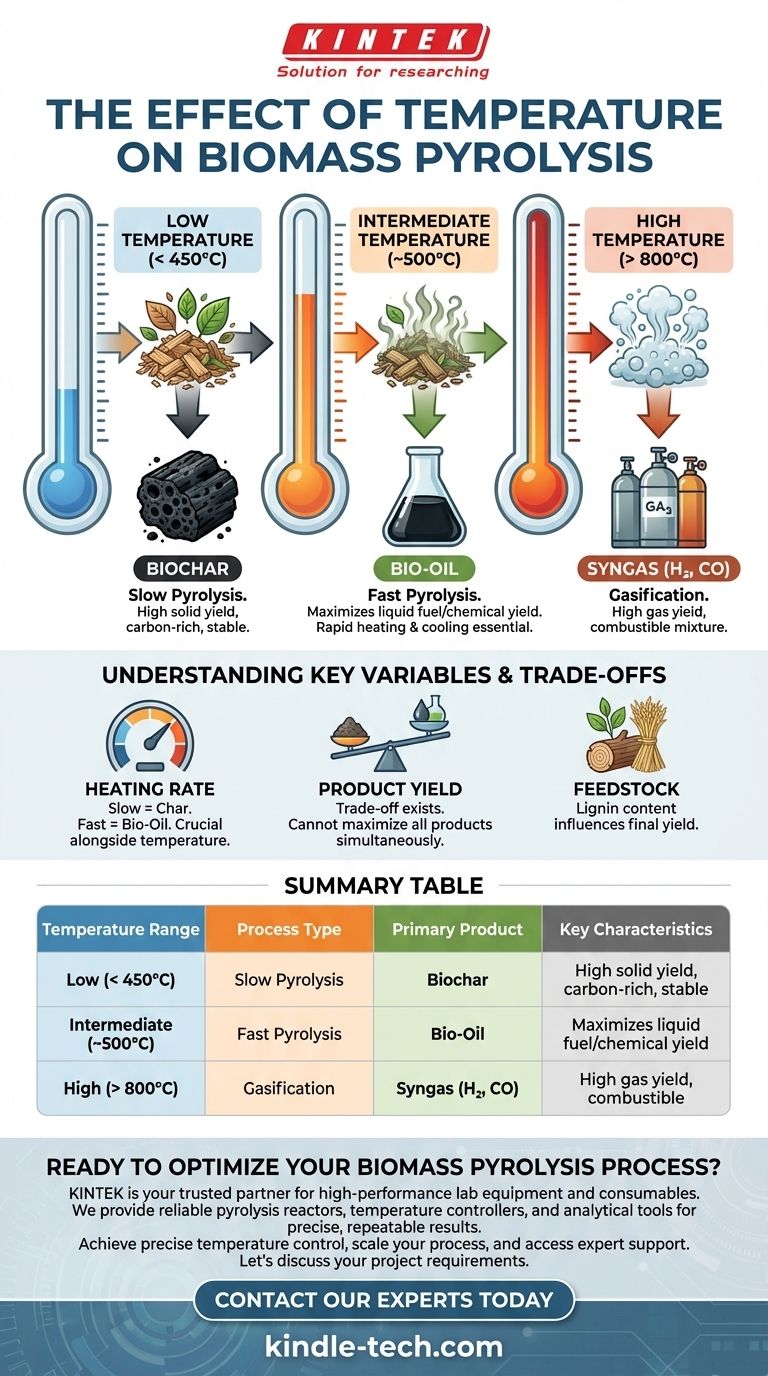
How Temperature Dictates Pyrolysis Outcomes
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an oxygen-deprived environment. Temperature acts as the primary lever, dictating which chemical bonds within the biomass break and how the resulting molecules re-form.
Low Temperature (< 450°C): Maximizing Biochar Production
At lower temperatures, typically below 450°C and with slow heating rates, the process is known as slow pyrolysis or carbonization.
The energy input is sufficient to drive off water and volatile compounds but not intense enough to break down the core carbon structure of the biomass. This preserves the solid carbon matrix, resulting in a high yield of biochar, a stable, carbon-rich charcoal-like substance.
Intermediate Temperature (~500°C): Optimizing for Bio-Oil
This regime, often called fast pyrolysis, is the sweet spot for producing liquid fuels. It occurs at moderate temperatures (around 500°C) but requires a very high heating rate.
The rapid heat transfer cracks the long polymer chains of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin into smaller, vaporized organic molecules. When these vapors are quickly cooled and condensed, they form a dark, dense liquid known as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil.
High Temperature (> 800°C): Driving Gas Production
At very high temperatures, the process shifts from pyrolysis to gasification. The intense thermal energy causes secondary cracking of all intermediate products, including any tars or oils that may have formed.
This breaks down nearly all organic matter into the simplest, most stable gaseous molecules. The primary output is syngas (synthesis gas), a mixture of hydrogen (H₂) and carbon monoxide (CO), along with other non-condensable gases like methane (CH₄) and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Understanding the Key Variables and Trade-offs
While temperature is the primary driver, other factors interact with it to influence the final product yield and quality. Understanding these is crucial for process control.
The Critical Role of Heating Rate
Heating rate is inseparable from temperature. Two processes run at 500°C can have vastly different outcomes.
A slow heating rate allows the biomass to slowly char, maximizing solid biochar yield even at intermediate temperatures. A fast heating rate is essential to bypass char formation and quickly vaporize the biomass, which is the key to maximizing bio-oil.
Product Yield vs. Process Goal
There is an inherent trade-off between product types. A process optimized for biochar will naturally produce very little bio-oil. Conversely, a high-yield fast pyrolysis process for bio-oil minimizes the production of char.
Your desired end-product dictates the entire operational setup. You cannot maximize the yield of all three products simultaneously.
Feedstock Composition
The type of biomass used also has a significant impact. For example, woody biomass with high lignin content tends to produce more biochar compared to agricultural residues like straw. While temperature sets the general outcome, the specific feedstock determines the precise yields and chemical properties of the final products.
Choosing the Right Temperature for Your Goal
Your operational temperature should be selected based on the product you want to create. There is no single "best" temperature; there is only the right temperature for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Use slow pyrolysis at low temperatures (<450°C) to maximize the yield of stable, high-quality biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing a liquid fuel or chemical feedstock: Use fast pyrolysis at intermediate temperatures (~500°C) with rapid heating rates to optimize for bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is generating power or producing synthesis gas: Use gasification at high temperatures (>800°C) to convert the entire biomass feedstock into a combustible syngas.
Ultimately, controlling temperature allows you to transform biomass from a raw material into a valuable, tailored product.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Process Type | Primary Product | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (< 450°C) | Slow Pyrolysis | Biochar | High solid yield, carbon-rich, stable |
| Intermediate (~500°C) | Fast Pyrolysis | Bio-Oil | Maximizes liquid fuel/chemical yield |
| High (> 800°C) | Gasification | Syngas (H₂, CO) | High gas yield, combustible |
Ready to optimize your biomass pyrolysis process?
KINTEK is your trusted partner for high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Whether you are researching biochar for soil amendment, developing bio-oil as a renewable fuel, or analyzing syngas composition, we provide the reliable pyrolysis reactors, temperature controllers, and analytical tools you need for precise, repeatable results.
We help you:
- Achieve precise temperature control for targeted product yields.
- Scale your process from lab research to pilot production.
- Access expert support to select the right equipment for your specific biomass and goals.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process

















