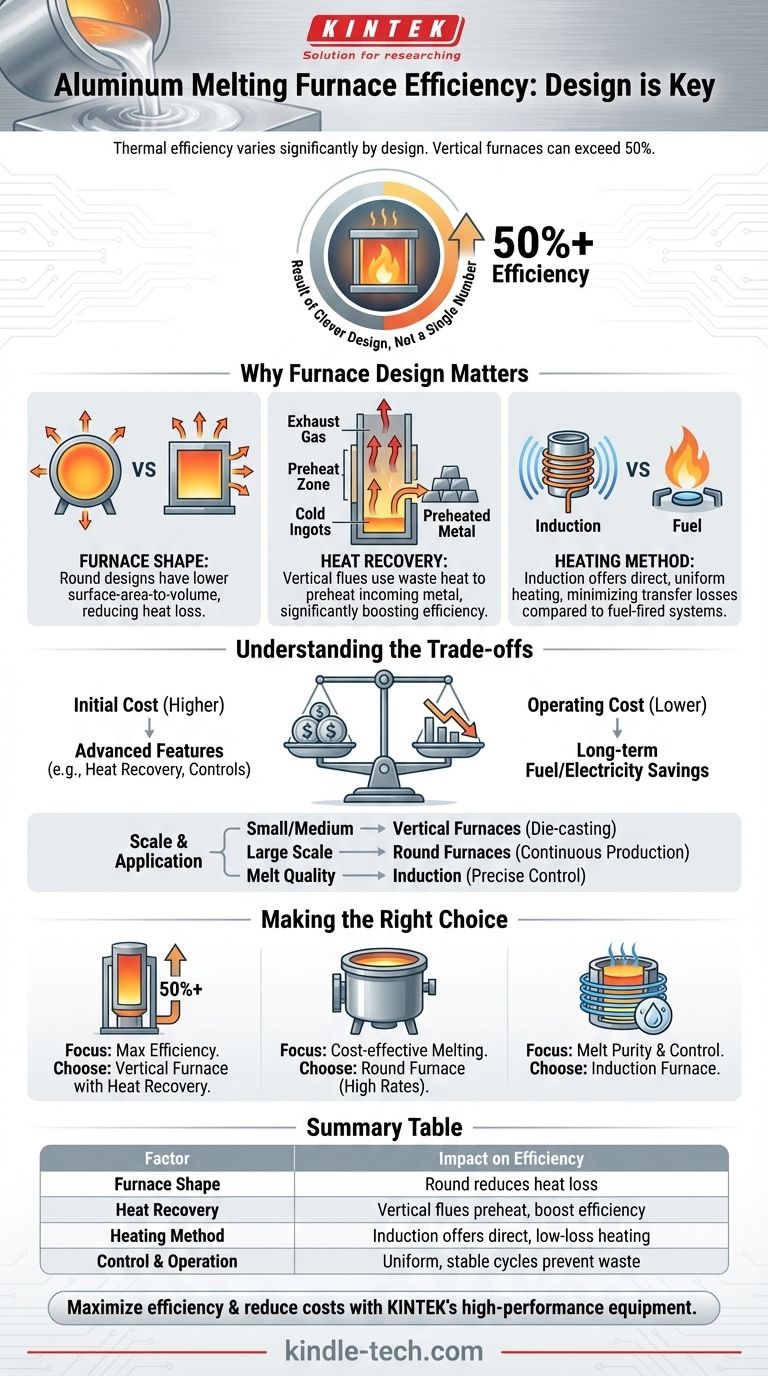
In short, the thermal efficiency of an aluminum melting furnace varies significantly by design, but certain types can achieve high performance. A vertical aluminum melting furnace, for example, often exceeds 50% thermal efficiency due to its ability to use hot exhaust gas to preheat the incoming metal. However, this figure is not universal, as efficiency is fundamentally determined by the furnace's shape, heating method, and heat recovery systems.
The central takeaway is that furnace efficiency is not a single number but a direct result of its design. The most efficient furnaces are those engineered to maximize heat transfer to the aluminum while minimizing energy loss to the surrounding environment, often through clever heat recovery and optimized shapes.

Why Furnace Design is the Key to Efficiency
Understanding what makes a furnace efficient requires looking beyond a single percentage. The core engineering principles focus on generating heat and ensuring as much of that heat as possible is absorbed by the aluminum charge.
The Impact of Furnace Shape
The physical geometry of the furnace is a primary factor in preventing heat loss. A round furnace generally offers superior efficiency compared to a rectangular one.
This is because a circular design has a lower surface-area-to-volume ratio, which reduces the area through which heat can escape. It also facilitates more uniform heat distribution and makes it easier to achieve a proper seal, further reducing energy waste.
The Power of Heat Recovery
The single biggest opportunity for improving efficiency is heat recovery. In many furnace designs, a significant amount of energy is lost through hot exhaust gases.
A vertical melting furnace is a prime example of efficient design. It uses a tall flue where hot gases from the burners at the bottom rise and preheat the cold aluminum ingots being added from the top. This process of recycling waste heat is why these furnaces can consistently achieve efficiencies exceeding 50%.
Heating Method and Control
The method of applying heat and the precision of temperature control also play a critical role. Furnaces that provide uniform heating and stable operation prevent energy waste from overheating or inefficient melting cycles.
Different technologies, such as induction furnaces, use electromagnetic fields to heat the metal directly. This method can be highly efficient as it generates heat within the aluminum itself, minimizing the heat transfer losses common in fuel-fired furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace is not just about choosing the highest possible efficiency rating. Practical considerations and operational needs create important trade-offs.
Initial Cost vs. Operating Cost
Furnaces with advanced features like flue gas heat recovery systems or sophisticated controls typically have a higher upfront investment.
However, their higher thermal efficiency translates directly into lower fuel or electricity consumption, leading to significant long-term operational savings that can offset the initial cost.
Scale of Operation and Application
The best furnace design is dependent on the production scale. Vertical furnaces are highly effective and common in the die-casting industry and for small to medium-sized enterprises.
For large-scale, continuous production, large round furnaces are often preferred due to their high melting rates and structural efficiency benefits. The choice must align with the required output.
Melt Quality vs. Throughput
While a high melting rate is desirable, it cannot come at the expense of metal quality. Precise temperature control is essential for producing specific alloys and preventing the formation of dross.
Some designs may prioritize raw melting speed, while others, like induction furnaces, offer superior control over the melt, which may be the more critical factor for a given application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal furnace is the one that best aligns with your specific operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing thermal efficiency: A vertical furnace with an integrated heat recovery system is a leading choice, capable of converting over 50% of its energy into useful heat.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, cost-effective melting: A well-designed round furnace offers significant efficiency advantages over older rectangular models due to superior heat retention and distribution.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature control and melt purity: An induction furnace should be a strong consideration, as its direct heating method provides excellent control and can be very energy efficient.
Ultimately, choosing the right aluminum melting technology is about matching the engineering of the furnace to the demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Furnace Shape | Round designs reduce heat loss vs. rectangular ones |
| Heat Recovery | Systems like vertical flues preheat metal, boosting efficiency |
| Heating Method | Induction furnaces offer direct heating with minimal loss |
| Control & Operation | Uniform heating and stable cycles prevent energy waste |
Ready to maximize your aluminum melting efficiency and reduce operational costs? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab and foundry equipment, including advanced aluminum melting furnaces designed for superior thermal efficiency and precise control. Whether you need a vertical furnace for optimal heat recovery or an induction system for melt purity, our experts can help you select the perfect solution for your production scale and quality requirements. Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your melting operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is temperature controlled in a furnace? Mastering Precise Thermal Management
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?



















