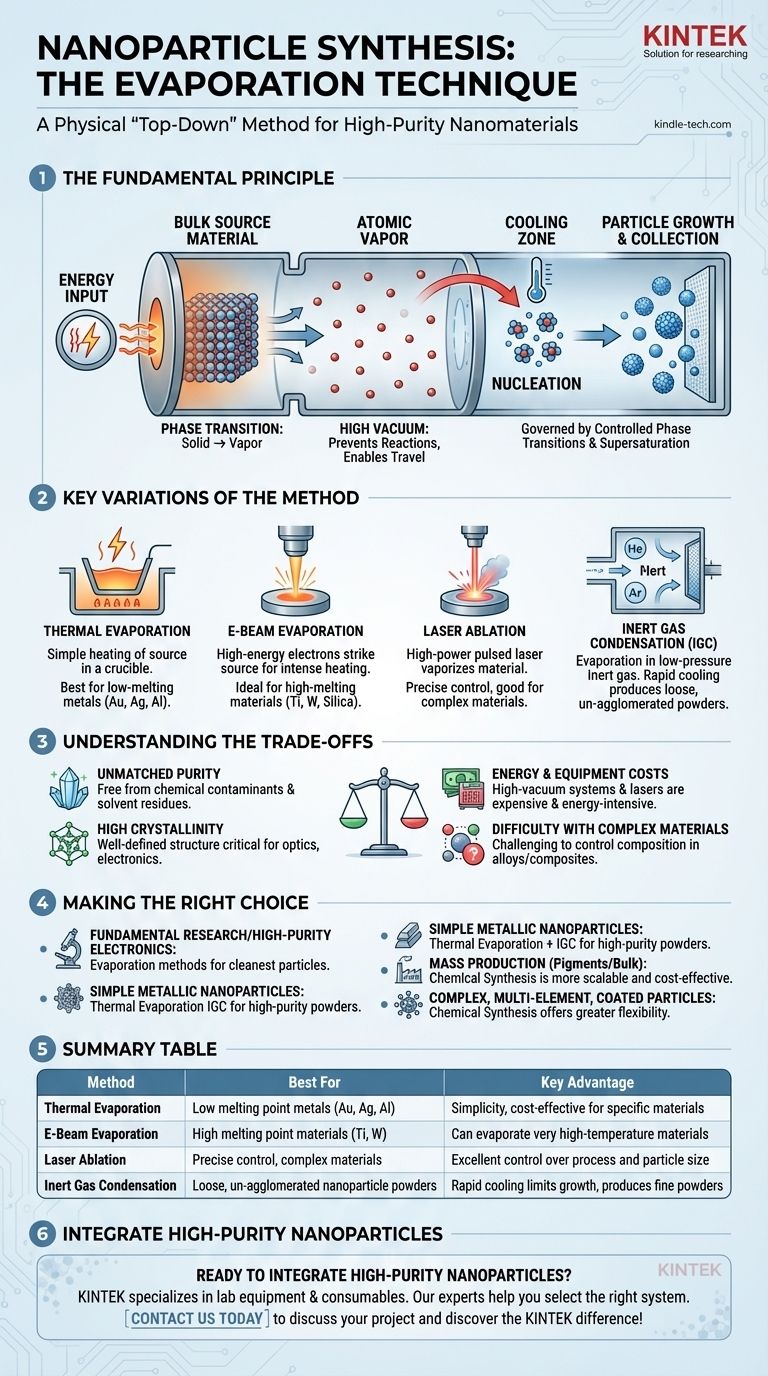
The evaporation technique for nanoparticles is a physical, "top-down" synthesis method where a bulk source material is heated in a controlled environment, typically a vacuum, until its atoms vaporize. This atomic vapor then travels, cools, and condenses to form nanometer-sized solid particles. It is a foundational technique for producing high-purity nanomaterials directly from a solid source without chemical precursors.
Choosing a synthesis method is a critical decision that dictates the final properties of nanoparticles. The evaporation technique is a powerful tool for achieving exceptional purity, but it's essential to understand its trade-offs against the scalability and compositional flexibility offered by chemical methods.
The Fundamental Principle: Phase Transition at the Nanoscale
The entire process is governed by controlled phase transitions from solid to gas and back to solid. The key is manipulating temperature and pressure to dictate particle size and structure.
From Solid to Vapor: The Energy Input
The process begins by placing a high-purity source material (like a piece of gold or silicon) inside a high-vacuum chamber. Energy is applied to heat this source material above its boiling point, causing atoms to break free and form a vapor.
The vacuum is critical. It prevents the hot vapor atoms from reacting with air (like oxygen) and allows them to travel freely without colliding with other gas molecules.
The Nucleation Process: Vapor to Solid
As the hot atomic vapor expands away from the source, it cools. This cooling causes the vapor to become supersaturated—a state where there are more atoms in the gas phase than the local temperature and pressure can sustain.
In this state, atoms that collide have a high probability of sticking together. This initial formation of tiny, stable clusters is called nucleation. These nuclei are the seeds for the future nanoparticles.
Particle Growth and Collection
Once nuclei have formed, they continue to grow as more atoms from the vapor phase condense onto their surface. The final size of the nanoparticles is determined by factors like the evaporation rate, the background pressure, and the distance the atoms travel before they are collected.
These newly formed nanoparticles are then collected, either on a cold surface placed in the path of the vapor or as a loose powder using techniques like inert gas condensation.
Key Variations of the Evaporation Method
While the principle is the same, different methods are used to supply the energy needed for evaporation. Each has specific advantages.
Thermal Evaporation
This is the simplest form, where the source material is placed in a small "boat" or crucible made of a refractory metal like tungsten. A high electrical current is passed through the boat, heating it and causing the source material to evaporate. It is best suited for materials with relatively low melting points, such as gold, silver, and aluminum.
Electron-Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
For materials with very high melting points (like titanium, tungsten, or silica), thermal evaporation is inefficient. E-beam evaporation uses a magnetically focused beam of high-energy electrons to strike the source material, causing intense, localized heating and vaporization.
Laser Ablation
In this technique, a high-power, pulsed laser is focused on the source material inside the vacuum chamber. Each laser pulse vaporizes a minuscule amount of material, creating an energetic plasma plume that expands and cools to form nanoparticles. This method offers very precise control over the evaporation process.
Inert Gas Condensation (IGC)
IGC is a key variation for producing loose, un-agglomerated nanoparticle powders. Evaporation occurs not in a high vacuum but in a low-pressure inert gas (like helium or argon). The hot vapor atoms quickly lose energy by colliding with the cool inert gas atoms, promoting rapid nucleation and limiting particle growth. The resulting nanoparticles are then carried by the gas flow to a collection filter.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No synthesis method is perfect. The evaporation technique's primary strength is also tied to its main limitations.
Advantage: Unmatched Purity
Because the process starts with a high-purity solid and occurs in a clean vacuum environment, the resulting nanoparticles are exceptionally pure. They are free from the solvent residues, surfactants, or precursor contaminants often present in particles made via chemical synthesis.
Advantage: High Crystallinity
The controlled condensation from a vapor phase often results in nanoparticles with a well-defined, highly crystalline structure. This is critical for applications in optics, catalysis, and electronics where atomic arrangement dictates performance.
Limitation: Energy and Equipment Costs
High-vacuum systems, electron guns, and high-power lasers are expensive to acquire and operate. The process is energy-intensive, making it less cost-effective for the bulk production of low-cost materials compared to large-scale chemical batch processes.
Limitation: Difficulty with Complex Materials
Creating alloy or composite nanoparticles with precise stoichiometry is challenging. Different elements have different vapor pressures and evaporation rates, making it difficult to control the final composition. Methods like co-evaporation from multiple sources are possible but add significant complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a synthesis method requires aligning the technique's strengths with your application's non-negotiable requirements.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or high-purity electronics: Evaporation methods provide the cleanest nanoparticles, ideal for studying intrinsic material properties without chemical interference.
- If your primary focus is producing simple metallic nanoparticles (e.g., silver, gold): Thermal evaporation combined with inert gas condensation is an excellent, well-established choice for creating high-purity powders.
- If your primary focus is mass production for applications like pigments or bulk composites: Wet-chemical synthesis methods (like precipitation) are almost always more scalable and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, multi-element, or coated nanoparticles: Chemical synthesis (like sol-gel or seed-mediated growth) offers far greater flexibility and control over composition and structure.
Ultimately, understanding the physics of evaporation empowers you to select a synthesis path that prioritizes the nanoparticle properties most critical to your success.

Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Evaporation | Low melting point metals (Au, Ag, Al) | Simplicity, cost-effective for specific materials |
| E-Beam Evaporation | High melting point materials (Ti, W) | Can evaporate very high-temperature materials |
| Laser Ablation | Precise control, complex materials | Excellent control over process and particle size |
| Inert Gas Condensation | Loose, un-agglomerated nanoparticle powders | Rapid cooling limits growth, produces fine powders |
Ready to integrate high-purity nanoparticles into your research? The evaporation technique is ideal for applications demanding exceptional material purity and crystallinity, from electronics to catalysis. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced material synthesis. Our experts can help you select the right evaporation system for your specific laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover the KINTEK difference!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
People Also Ask
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method



















