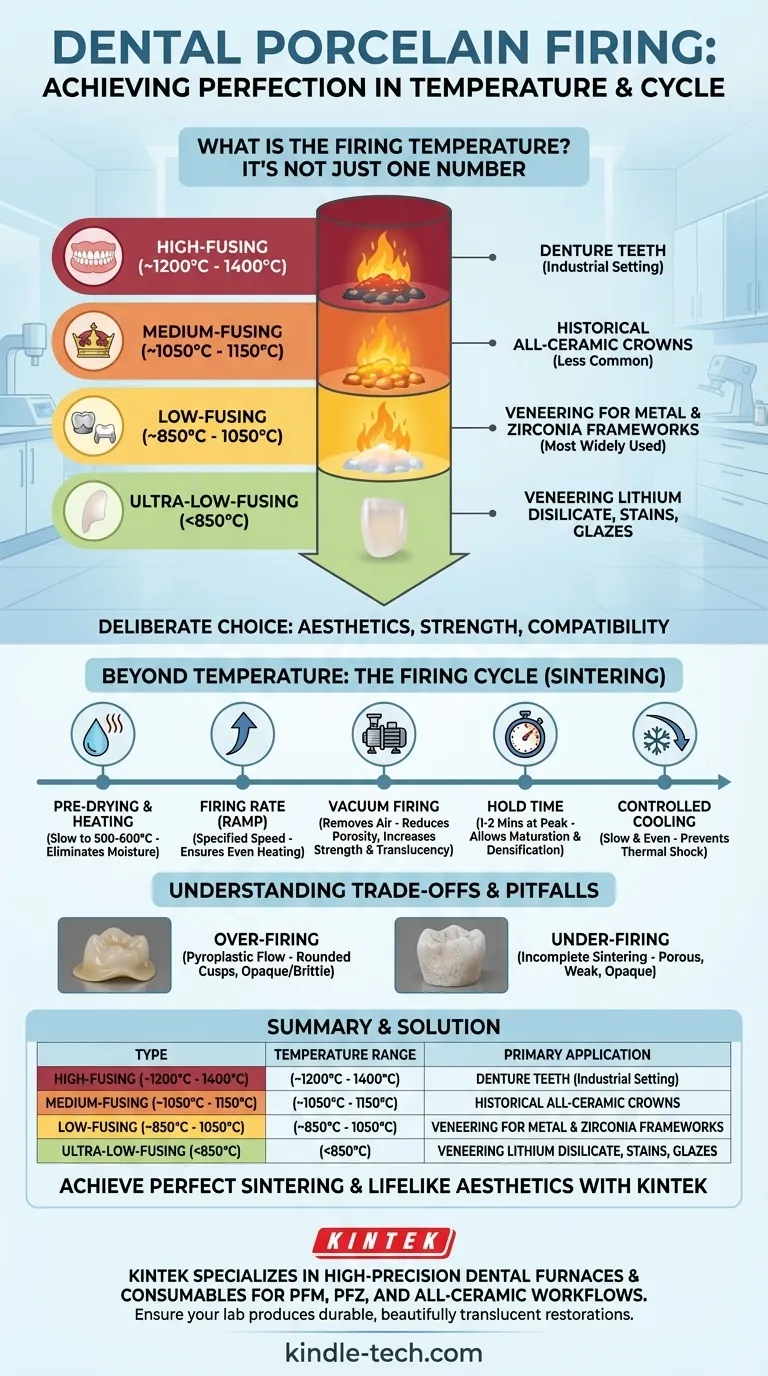
The firing temperature of dental porcelain is not one specific value, but rather falls into distinct categories ranging from over 1200°C for high-fusing types down to below 850°C for ultra-low-fusing materials. The correct temperature is dictated by the porcelain's specific composition, its manufacturer, and its intended clinical application, such as for denture teeth, crowns, or veneers over a metal or zirconia framework.
The selection of a dental porcelain and its corresponding firing temperature is a deliberate choice driven by the need to balance aesthetics, strength, and compatibility with underlying structures. Understanding the material's "fusing range" and the entire firing cycle is more critical than knowing a single number, as it directly controls the final density, translucency, and integrity of the restoration.

The Classification of Dental Porcelains by Firing Temperature
The most important concept to grasp is that "dental porcelain" is a broad term. Materials are grouped by the temperature at which they sinter and mature, which directly influences where and how they can be used.
High-Fusing Porcelain (~1200°C to 1400°C)
This type is primarily composed of feldspar and is the strongest and most wear-resistant of the porcelains.
Due to its extremely high firing temperature, it is almost exclusively used for manufacturing artificial denture teeth. This process is done in an industrial setting, not a typical dental laboratory.
Medium-Fusing Porcelain (~1050°C to 1150°C)
This category serves as a bridge between high and low-fusing types. It was historically used for constructing some all-ceramic crowns (jacket crowns) and pre-fabricated pontics.
Its use has become less common with the advent of modern high-strength ceramics and more versatile low-fusing systems.
Low-Fusing Porcelain (~850°C to 1050°C)
This is the most widely used category in modern dental labs. Its lower firing temperature is crucial for its primary application: veneering porcelain for metal and zirconia frameworks.
These porcelains contain more glass-forming fluxes (like sodium or potassium oxides) to lower the softening point. This allows them to be fused onto a framework without distorting or melting the underlying structure.
Ultra-Low-Fusing Porcelain (<850°C)
This modern class of porcelain is designed for maximum compatibility with newer materials and for delicate adjustments.
It is ideal for veneering high-strength ceramics like lithium disilicate, which may have lower thermal stability. It is also used for final characterization with stains, glazes, or for making minor additions and repairs without risking the integrity of the full restoration.
Beyond Temperature: Understanding the Firing Cycle
Achieving the correct final properties is about more than just hitting a peak temperature. The entire firing cycle is a precisely controlled process of sintering, where individual porcelain particles fuse together into a solid, dense mass without fully melting.
Key Stages of a Firing Cycle
A typical firing program for a crown or bridge involves several distinct phases:
- Pre-Drying and Heating: The restoration is slowly heated to around 500-600°C to completely eliminate any moisture. Rushing this step can cause steam to form within the porcelain, leading to cracking or voids.
- Firing Rate (Ramp): This is the speed at which the furnace temperature increases to its peak. The rate is specified by the manufacturer to ensure even heating throughout the porcelain mass.
- Vacuum Firing: For most of the heating ramp, firing is done under a strong vacuum. This removes air trapped between porcelain particles, dramatically reducing porosity and resulting in a stronger, more translucent final restoration. The vacuum is released just before or at the peak temperature.
- Hold Time: Once the peak temperature is reached, it is held for a specific duration (often 1-2 minutes). This "heat soaking" allows the porcelain to fully mature and densify, achieving its desired translucency and shrinkage.
- Controlled Cooling: The restoration must be cooled slowly and evenly to prevent thermal shock, which can cause catastrophic fractures. Modern furnaces control this cooling rate automatically.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Strict adherence to the manufacturer's recommended firing protocol is non-negotiable. Minor deviations can have major consequences for the final restoration.
The Problem of Over-Firing
If the temperature is too high or held for too long, the porcelain will begin to flow like a thick liquid (pyroplastic flow).
This leads to rounded cusps, loss of surface texture, and a slumped appearance. Paradoxically, severe over-firing can also cause devitrification, where the glass crystallizes and becomes opaque and brittle.
The Risk of Under-Firing
If the porcelain does not reach its proper maturation temperature, the sintering process will be incomplete.
The resulting restoration will be porous, weak, and appear chalky or opaque. It will be highly susceptible to fracture and staining in the patient's mouth.
Framework Compatibility is Paramount
For any Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) or Porcelain-Fused-to-Zirconia (PFZ) restoration, the veneering porcelain's firing temperature must be lower than the distortion or melting temperature of the underlying framework. This is the fundamental reason low-fusing porcelains dominate crown and bridge work.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of material and firing protocol is dictated entirely by the clinical or laboratory objective.
- If your primary focus is a Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) crown: You must use a low-fusing porcelain whose maturation temperature is safely below the sag temperature of your chosen metal alloy.
- If your primary focus is veneering a zirconia framework: Select a low or ultra-low fusing porcelain specifically formulated for zirconia to manage thermal expansion differences and prevent cracking.
- If your primary focus is creating denture teeth: High-fusing porcelain is the traditional choice due to its superior durability and wear resistance, though it requires specialized industrial-level equipment.
- If your primary focus is a monolithic ceramic (e.g., lithium disilicate): Your firing cycle is for crystallization and glazing, a different process than layering porcelain, and you must adhere strictly to the manufacturer's specific time-temperature program.
Mastering the firing cycle is about precisely controlling heat to transform powdered glass and minerals into a durable, lifelike restoration.
Summary Table:
| Porcelain Type | Typical Firing Range | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| High-Fusing | ~1200°C to 1400°C | Denture Teeth |
| Medium-Fusing | ~1050°C to 1150°C | Historical All-Ceramic Crowns |
| Low-Fusing | ~850°C to 1050°C | Veneering for Metal/Zirconia Frameworks |
| Ultra-Low-Fusing | <850°C | Veneering Lithium Disilicate, Stains/Glazes |
Achieve perfect sintering and lifelike aesthetics with every restoration. Mastering the dental porcelain firing cycle is critical for strength and aesthetics. KINTEK specializes in high-precision dental furnaces and consumables that deliver consistent, reliable results for PFM, PFZ, and all-ceramic workflows. Ensure your lab produces durable, beautifully translucent restorations – contact our experts today to find the ideal firing solution for your specific materials and applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What methods are used to control the temperature for sintering dental zirconia? Achieve Precise Results with KINTEK
- How are Dental Press Furnaces used with modern dental technologies? Optimize Your CAD/CAM Digital Workflow
- What properties of dental zirconia parts are affected by the sintering temperature? Master Thermal Precision
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is the sintering time for zirconia crowns? Master the Trade-Off Between Speed and Strength



















