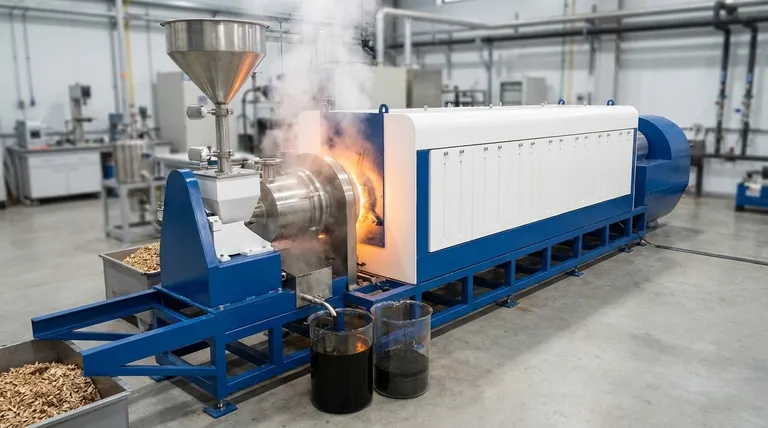
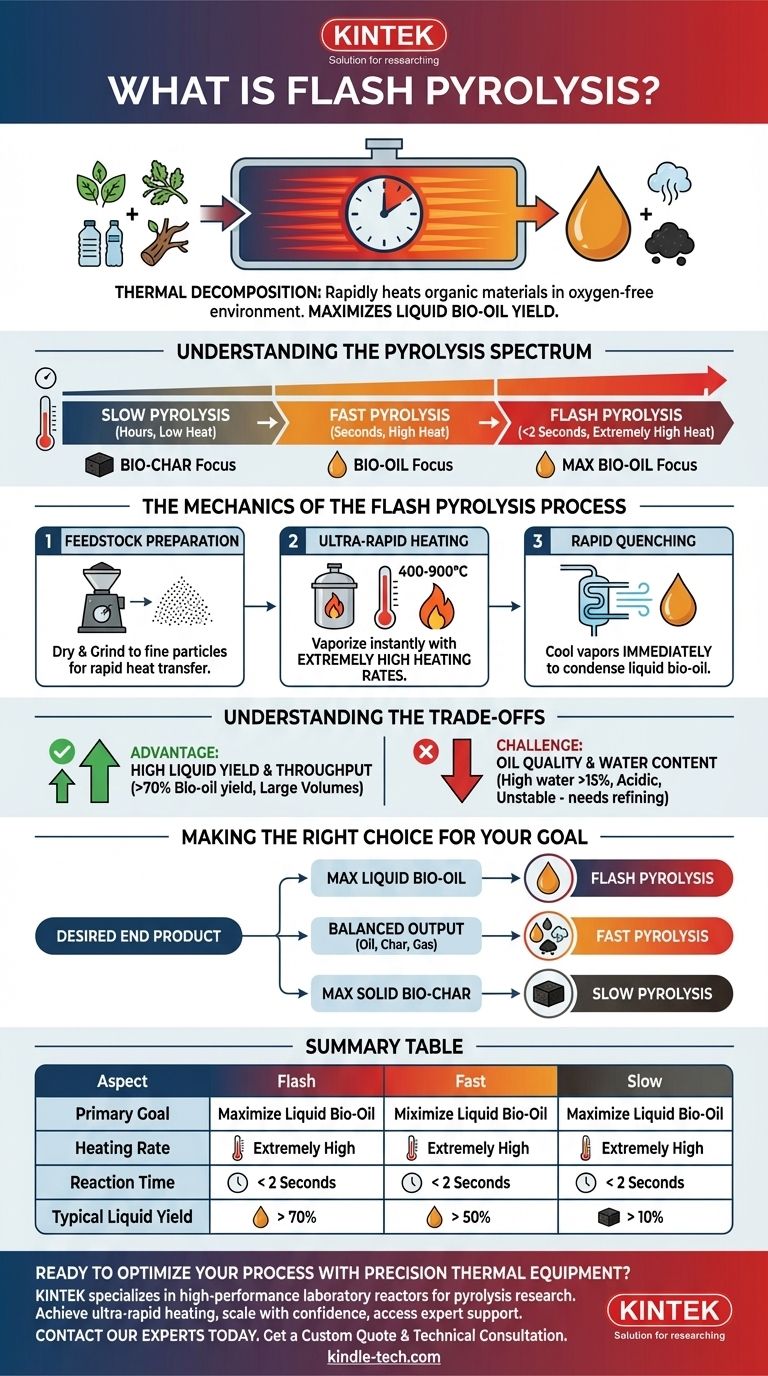
At its core, flash pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process that rapidly heats organic materials like biomass or plastic in an oxygen-free environment. Unlike slower methods, it uses extremely high heating rates and very short reaction times, specifically to maximize the production of liquid bio-oil.
The defining characteristic of flash pyrolysis is its focus on speed. By heating feedstock in seconds, it cracks long-chain molecules into valuable liquids before they can break down further into less desirable gases and solid char.

Understanding the Pyrolysis Spectrum
Pyrolysis is not a single process but a range of techniques defined by temperature, heating rate, and duration. The goal of the process dictates which method is used.
The Traditional Method: Slow Pyrolysis
Slow pyrolysis uses low heating rates over a long period (hours). This process is intentionally designed to break down material gently, maximizing the yield of the solid carbon-rich product known as bio-char. It produces the least amount of liquid oil.
A Faster Approach: Fast Pyrolysis
Fast pyrolysis increases the heating rate significantly, completing the process in seconds. This shifts the primary output from bio-char to bio-oil, creating a more balanced mix of liquid, solid, and gas products.
The Peak of Speed: Flash Pyrolysis
Flash pyrolysis represents the extreme end of the speed spectrum. It involves even higher heating rates and vapor residence times of less than two seconds. This ultra-rapid process is engineered almost exclusively to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil.
The Mechanics of the Flash Pyrolysis Process
Achieving the speed necessary for flash pyrolysis requires precise control over several stages.
Step 1: Feedstock Preparation
The raw material, such as plastic or biomass, must be pre-treated. This involves drying the material and grinding it into very fine particles. Small particle size is essential for the rapid heat transfer needed for the "flash" effect.
Step 2: Ultra-Rapid Heating
The prepared feedstock is fed into a reactor and heated to temperatures between 400-900°C. The key, however, is not just the temperature but the extremely high heating rate. The goal is to vaporize the material almost instantly.
Step 3: Rapid Quenching
As soon as the hot vapors are formed, they must be cooled (quenched) immediately. This rapid cooling condenses the vapors into a liquid—the bio-oil—before they have a chance to undergo secondary reactions and break down into gas. This step is critical for maximizing liquid yield.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Flash pyrolysis offers significant advantages in throughput and liquid yield, but it also comes with specific challenges and product characteristics.
Advantage: High Liquid Yield and Throughput
The primary benefit is a high yield of bio-oil, often exceeding 70% by weight depending on the feedstock. Its rapid nature also allows for processing significantly larger volumes of material compared to slower methods.
Product Characteristic: High Water Content
Flash pyrolysis bio-oil is fundamentally different from conventional crude oil. As noted in research, it has a high water content, often over 15%. This water comes from the initial moisture in the feedstock and from the chemical decomposition reactions themselves.
The Challenge: Oil Quality
This bio-oil, sometimes called "pyrolytic tar," is also acidic, unstable, and viscous. It cannot be used directly in conventional engines or refineries and typically requires further upgrading or refining to become a usable fuel or chemical feedstock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal process depends entirely on your desired end product.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid fuel (bio-oil) production: Flash pyrolysis is the superior method due to its extremely high liquid yields.
- If your primary focus is creating bio-char for agriculture or carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the most effective and efficient process.
- If your primary focus is a balanced output of oil, char, and gas: Standard fast pyrolysis provides a versatile middle ground.
Ultimately, mastering thermal decomposition means choosing the right tool for the job based on a clear understanding of the final product you wish to create.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Flash Pyrolysis | Fast Pyrolysis | Slow Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximize Liquid Bio-Oil | Balanced Output (Oil, Char, Gas) | Maximize Solid Bio-Char |
| Heating Rate | Extremely High | High | Low |
| Reaction Time | < 2 Seconds | Seconds | Hours |
| Typical Liquid Yield | > 70% | Balanced | Lowest |
Ready to optimize your biomass or plastic conversion process with precision thermal equipment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance laboratory reactors and systems designed for advanced pyrolysis research and development. Whether you are developing next-generation biofuels or optimizing waste-to-energy processes, our equipment provides the precise control and reliability you need.
We help you:
- Achieve ultra-rapid heating rates for maximum bio-oil yield.
- Scale your process from lab to pilot with confidence.
- Access expert support for your specific feedstock and application.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss how our solutions can accelerate your R&D and bring your projects to life.
Get a Custom Quote & Technical Consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















