In Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (MPCVD), the process almost universally operates on one of two specific microwave frequencies: 2.45 GHz or 915 MHz. Both are designated ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) radio bands, which makes the required hardware, such as magnetrons and power supplies, readily available and cost-effective. The choice between them is not arbitrary but a critical decision that dictates the system's capabilities and ideal applications.
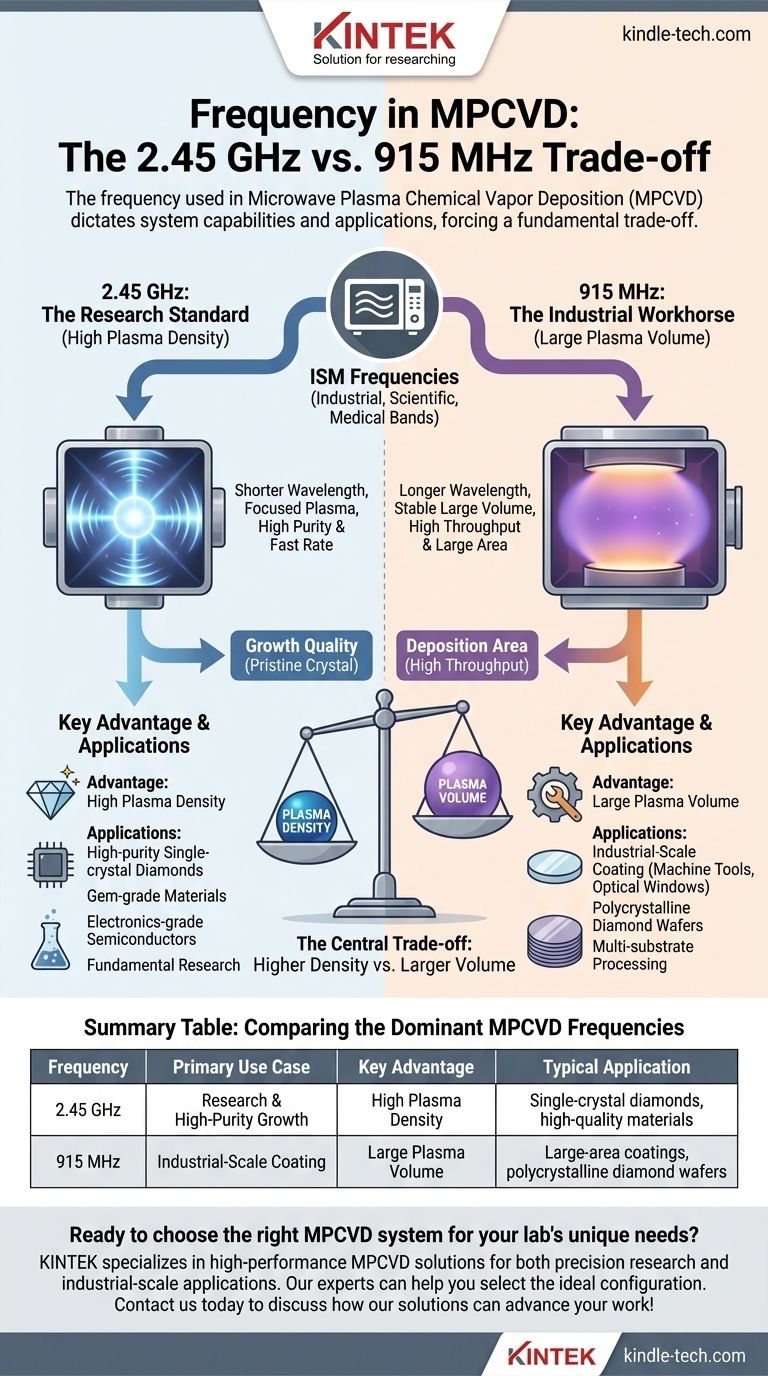
The frequency used in an MPCVD system is a fundamental design choice that forces a trade-off. Higher frequencies like 2.45 GHz create denser, more concentrated plasma ideal for high-purity growth, while lower frequencies like 915 MHz generate a larger plasma volume better suited for industrial-scale, large-area coating.

Why Microwaves Are Used in MPCVD
To understand the importance of frequency, you must first understand how microwaves are used to create the plasma essential for material deposition, particularly for growing high-quality lab-grown diamonds.
The Role of an Oscillating Electric Field
An MPCVD reactor is fundamentally a resonant cavity, much like a high-power, precision-tuned microwave oven. When microwaves are fed into this chamber, they establish a rapidly oscillating electromagnetic field.
This field primarily interacts with free electrons within the process gas (typically a mixture of a carbon source like methane and a large excess of hydrogen). The electric field accelerates these electrons, causing them to oscillate and gain significant kinetic energy.
From Energized Gas to Material Growth
These highly energetic electrons collide with the neutral gas molecules (H₂ and CH₄). These collisions are energetic enough to break the molecules apart, creating a reactive soup of hydrogen atoms, methyl radicals (CH₃), and other charged species. This energized, ionized gas is the plasma.
These reactive species are the building blocks for deposition. In diamond growth, for example, atomic hydrogen selectively etches away non-diamond carbon (graphite) while carbon-containing radicals find their place on the diamond seed crystal, growing the lattice layer by layer.
The Two Dominant MPCVD Frequencies
The choice of frequency directly impacts the characteristics of the plasma and, therefore, the entire deposition process.
The Standard for Research: 2.45 GHz
2.45 GHz is the most common frequency used in MPCVD, especially in research and for the production of high-purity single-crystal diamonds. Its shorter wavelength allows for the creation of a very dense and stable plasma in a relatively compact area.
This high plasma density is extremely efficient at dissociating the source gases, leading to high concentrations of the reactive species needed for high-quality, fast-rate growth. The widespread use of 2.45 GHz in consumer microwave ovens means that high-power components are affordable and widely available.
The Industrial Workhorse: 915 MHz
915 MHz systems are the choice for large-area deposition and industrial-scale production. The longer wavelength of the 915 MHz microwaves allows for the generation of a stable plasma that is significantly larger in volume compared to a 2.45 GHz system.
This enables the simultaneous coating of multiple large substrates or the growth of large-diameter polycrystalline diamond wafers. While the plasma is larger, its density is typically lower than that of a 2.45 GHz system at equivalent power, which can influence growth rates and crystal quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision between 2.45 GHz and 915 MHz is a classic engineering trade-off between quality, scale, and cost.
Plasma Density vs. Plasma Volume
This is the central trade-off. 2.45 GHz excels at producing high plasma density in a focused area. 915 MHz excels at producing a large plasma volume.
A higher density means more reactive species per unit volume, which is often crucial for achieving the highest material purity and crystal quality. A larger volume means you can process more or larger substrates at once.
Growth Quality vs. Deposition Area
As a direct consequence, 2.45 GHz systems are the go-to for applications demanding the utmost quality, such as gem-grade diamonds or electronics-grade semiconductor diamond. The deposition area, however, is limited.
Conversely, 915 MHz systems are optimized for throughput and large-area applications, like coating machine tools, optical windows, or producing large batches of polycrystalline diamond wafers where a massive deposition area is more important than achieving ultimate single-crystal perfection.
Equipment and Operational Costs
While components for both frequencies are from ISM bands, 915 MHz systems are generally larger, more complex, and more expensive to build and operate. They are true industrial machines, whereas 2.45 GHz systems range from small tabletop research units to mid-size production reactors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's primary goal will dictate the correct frequency choice.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or growing the highest-purity single-crystal diamond: A 2.45 GHz system provides the high plasma density required for pristine material quality.
- If your primary focus is industrial-scale production of polycrystalline diamond wafers or large-area coatings: A 915 MHz system offers the large plasma volume necessary for high throughput and covering large substrates.
- If you are balancing performance with accessibility and cost for a new project: A 2.45 GHz system is generally the more common and accessible starting point with a wider variety of available equipment.
Ultimately, the frequency is a foundational parameter that defines the capability and purpose of the MPCVD system from the outset.
Summary Table:
| Frequency | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.45 GHz | Research & High-Purity Growth | High Plasma Density | Single-crystal diamonds, high-quality materials |
| 915 MHz | Industrial-Scale Coating | Large Plasma Volume | Large-area coatings, polycrystalline diamond wafers |
Ready to choose the right MPCVD system for your lab's unique needs? The choice between 2.45 GHz and 915 MHz is critical for achieving your research or production goals. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including MPCVD systems tailored for both precision research and industrial-scale applications. Our experts can help you select the ideal configuration to optimize plasma density, deposition area, and material quality for your specific projects. Contact us today to discuss how our MPCVD solutions can advance your work in material science and diamond growth!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the primary advantages of the CVD method for growing diamonds? Engineering High-Purity Gems and Components
- How does a microwave plasma reactor facilitate the synthesis of diamond? Master MPCVD with Precision Technology
- What is the function of a Microwave PECVD system for Diamond Nanospikes? Precision 1-Step Nanostructure Synthesis
- What is the microwave plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition process? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Coatings
- How does Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapour Deposition (MPCVD) work? Your Guide to High-Purity Diamond Film Growth



















