In short, FTIR is used to measure how a sample absorbs infrared light. This measurement is not just a simple reading; it provides a detailed "fingerprint" of the sample's molecular structure by identifying the specific chemical bonds present. This technique is a cornerstone of chemical analysis, used to characterize new materials and to identify or verify known substances.
The core purpose of FTIR is not just to measure light absorption, but to translate that absorption data into a detailed map of a molecule's functional groups, effectively revealing its chemical identity.

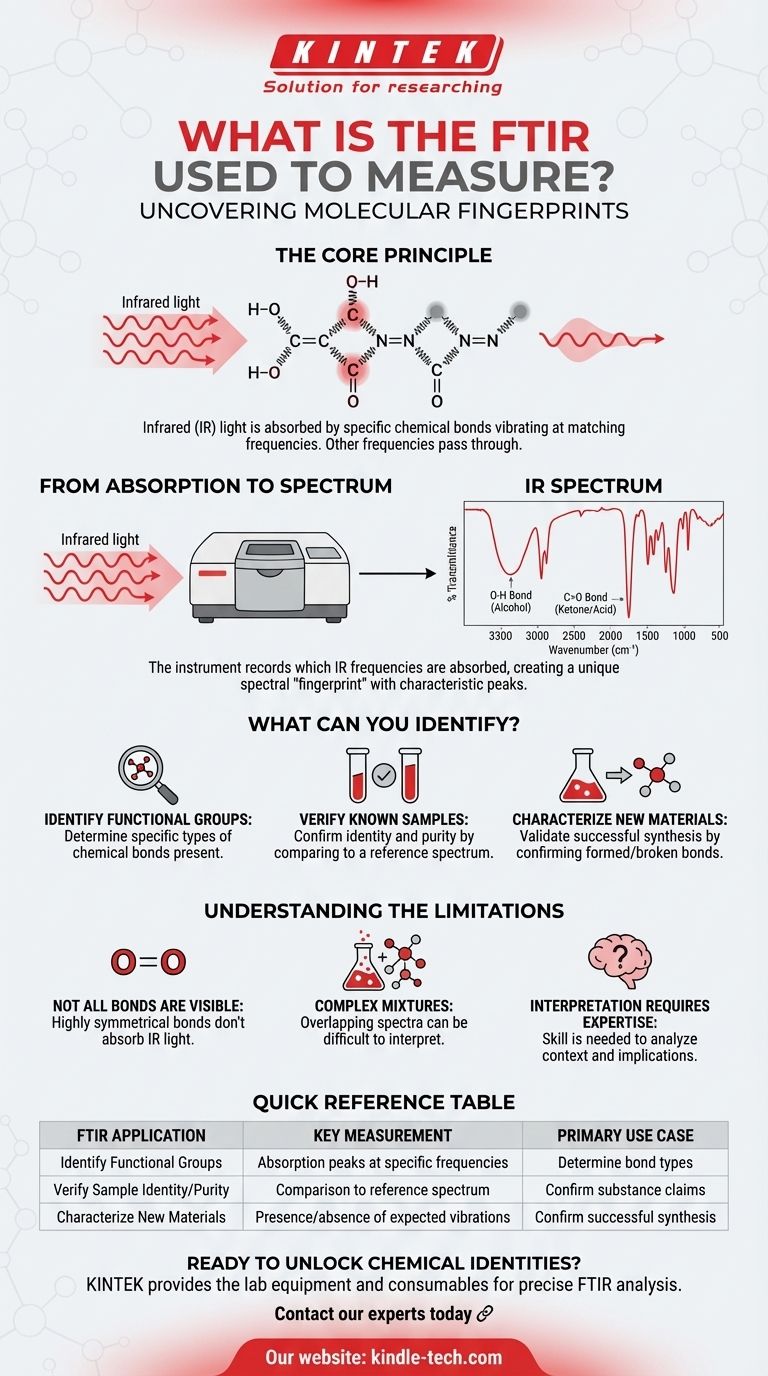
How FTIR Reveals a Molecule's Identity
To understand what FTIR measures, you must first understand how molecules interact with light. The process is a powerful way to probe the very structure of matter.
The Core Principle: Molecular Vibrations
Chemical bonds within a molecule are not rigid; they are constantly in motion, vibrating by stretching and bending. Each type of bond (like a carbon-hydrogen bond, C-H, or a carbon-oxygen double bond, C=O) vibrates at a unique, characteristic frequency.
Infrared Light as a Probe
Infrared (IR) light is a form of energy. When a beam of IR light passes through a sample, the bonds that vibrate at the same frequency as the light will absorb that energy. Bonds that vibrate at different frequencies will let the light pass through unaffected.
From Light Absorption to a Spectrum
The FTIR instrument measures precisely which frequencies of IR light are absorbed by the sample and to what extent. It then plots this information on a graph called an infrared spectrum. This spectrum shows sharp peaks at the frequencies where absorption occurred.
Decoding the "Fingerprint"
Because different chemical bonds absorb at different, predictable frequencies, this spectrum acts as a unique molecular fingerprint. By analyzing the position and intensity of the peaks, a chemist can determine which functional groups are present in the molecule.
What Can You Actually Identify?
The practical applications of FTIR are vast, stemming from its ability to provide a detailed structural snapshot of a sample.
Identifying Functional Groups
This is the primary output of an FTIR analysis. The spectrum clearly shows peaks corresponding to specific groups of atoms. For example, a broad peak around 3300 cm⁻¹ typically indicates an O-H bond (found in alcohols), while a sharp, strong peak near 1700 cm⁻¹ points to a C=O bond (found in ketones and acids).
Verifying Known Samples
If you have a substance that is supposed to be, for example, pure aspirin, you can run an FTIR scan and compare its spectrum to a reference spectrum of pure aspirin. If the spectra match perfectly, you can confirm the sample's identity and purity. Any extra peaks would indicate impurities.
Characterizing New Materials
In research and development, when scientists synthesize new molecules, they use FTIR to confirm that the reaction was successful. The spectrum can verify that the desired chemical bonds have formed and that bonds from the starting materials have disappeared.
Understanding the Limitations
While incredibly powerful, FTIR is not a universal solution and has important constraints that every analyst must understand.
Not All Bonds are Visible
For a bond to absorb infrared light, its vibration must cause a change in the molecule's dipole moment. Highly symmetrical bonds, such as the nitrogen-nitrogen bond in N₂ or the oxygen-oxygen bond in O₂, do not meet this requirement and are therefore "invisible" to FTIR.
Complexity of Mixtures
Analyzing a complex mixture of several different compounds can be challenging. The spectra of all the components will overlap, creating a complicated graph that can be very difficult to interpret accurately without advanced analytical techniques.
Interpretation Requires Expertise
While the instrument generates the data, interpreting an FTIR spectrum correctly requires knowledge and experience. Identifying peaks is one step, but understanding their context and what they imply about the overall molecular structure is a skill.
How to Apply FTIR to Your Goal
The way you use the data from an FTIR analysis depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is identifying an unknown substance: You should compare your sample's full spectrum to a spectral database, paying close attention to the unique pattern in the "fingerprint region" (typically below 1500 cm⁻¹).
- If your primary focus is verifying the purity of a sample: You should look for the presence of small, unexpected peaks in the spectrum that do not match the reference material, as these signify contaminants.
- If your primary focus is characterizing a new material: You should analyze the spectrum to confirm the presence of peaks for the expected functional groups and, just as importantly, the absence of peaks from your starting materials.
Ultimately, FTIR provides a direct and reliable method for translating a molecule's invisible vibrations into clear, actionable chemical insights.
Summary Table:
| FTIR Application | Key Measurement | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Identify Functional Groups | Absorption peaks at specific frequencies (e.g., C=O, O-H) | Determine the types of chemical bonds present |
| Verify Sample Identity/Purity | Comparison to a reference spectrum | Confirm a substance is what it claims to be |
| Characterize New Materials | Presence/absence of expected bond vibrations | Confirm successful synthesis in R&D |
Ready to unlock the chemical identity of your materials?
FTIR analysis provides the critical data you need for R&D, quality control, and material verification. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables that support precise FTIR and other analytical techniques.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and deliver the actionable chemical insights you require.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification



















