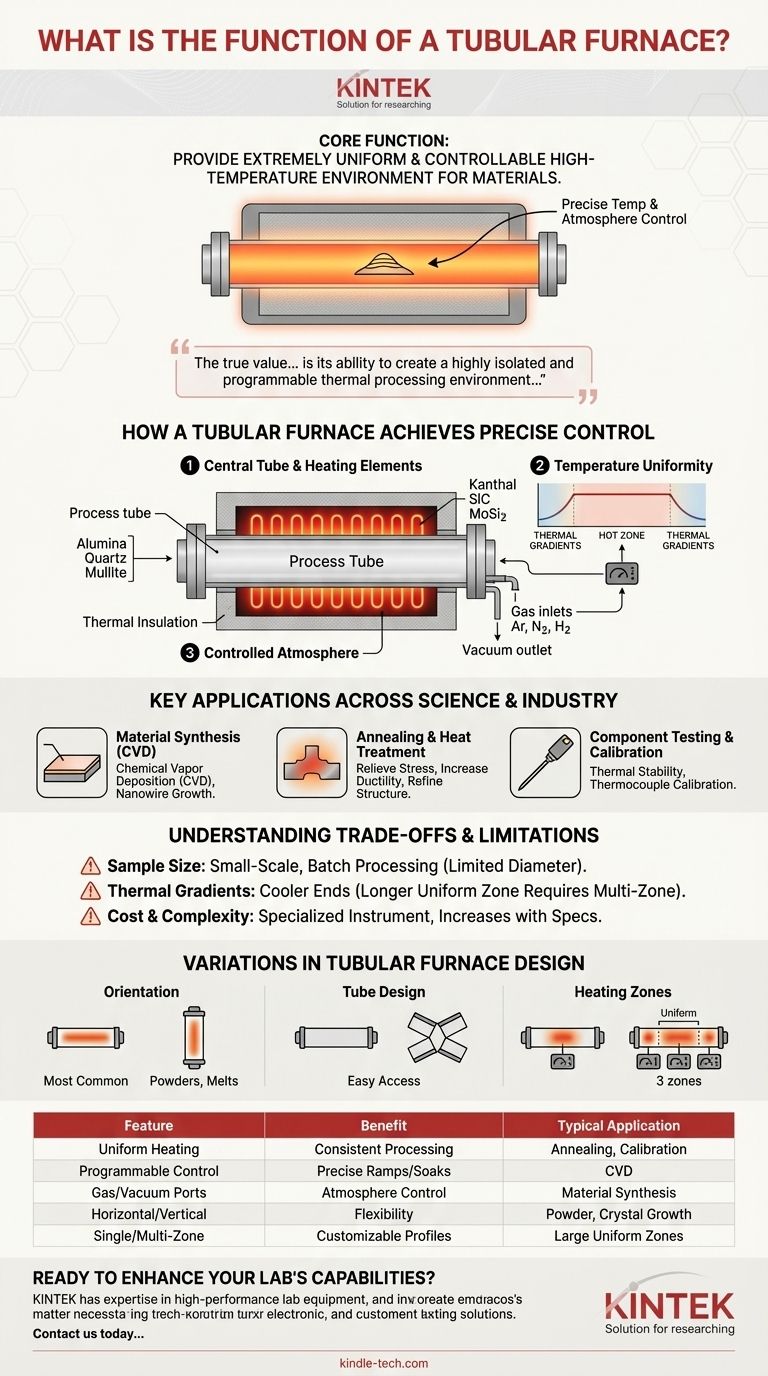
At its core, the function of a tubular furnace is to provide an extremely uniform and controllable high-temperature environment for processing materials. It is a specialized electric furnace designed around a central cylindrical chamber, or tube, which allows for precise control over not just temperature, but also the atmospheric conditions surrounding the sample.
The true value of a tubular furnace lies in its ability to create a highly isolated and programmable thermal processing environment, making it an indispensable tool for material synthesis, heat treatment, and advanced research in a laboratory setting.

How a Tubular Furnace Achieves Precise Control
A tubular furnace's function is best understood by looking at its core components and how they work together to create a controlled environment.
The Central Tube and Heating Elements
The heart of the furnace is the process tube, typically made from high-purity alumina, quartz, or mullite. This tube contains the sample and isolates it from the heating elements.
Heating elements, such as Kanthal (up to 1200°C), Silicon Carbide (SiC, up to 1500°C), or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2, up to 1800°C), are positioned around the exterior of the tube. High-grade thermal insulation surrounds these elements to maximize efficiency and ensure a stable hot zone.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
The cylindrical geometry of the furnace naturally promotes a uniform hot zone in the center of the tube. A programmable controller precisely manages the power sent to the heating elements, allowing for accurate temperature ramps, soaks, and controlled cooling cycles.
Creating a Controlled Atmosphere
The ends of the process tube are sealed with flanges that have ports for gas flow and vacuum. This is a critical feature that allows users to introduce inert gases (like argon or nitrogen), reactive gases (like hydrogen), or pull a vacuum, preventing oxidation and enabling specific chemical reactions.
Key Applications Across Science and Industry
The combination of temperature and atmospheric control makes tubular furnaces vital for a wide range of applications.
Material Synthesis and Purification
Tubular furnaces are essential for processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where reactive gases flow over a heated substrate to deposit a thin film. They are also used for purifying materials and growing novel structures like carbon nanotubes or nanowires.
Annealing and Heat Treatment
Annealing involves heating a material to a specific temperature and holding it there to relieve internal stresses, increase ductility, or refine its crystal structure. The precise control of a tube furnace is ideal for these sensitive metallurgical processes.
Component Testing and Calibration
Engineers use tubular furnaces to test the thermal stability of components and materials. They are also widely used to calibrate thermocouples and other temperature sensors against a known, stable temperature reference.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, tubular furnaces are not the solution for every heating application. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Sample Size and Throughput
By design, tubular furnaces are intended for small-scale, batch processing. The diameter of the tube inherently limits the size of the sample, making them unsuitable for high-volume industrial production.
Thermal Gradients at the Ends
The temperature is only perfectly uniform in the central hot zone. The ends of the tube will always be cooler, creating a thermal gradient. For applications needing a longer uniform zone, a longer furnace or a multi-zone configuration is required.
Cost and Complexity
These are specialized, high-precision instruments. The cost increases significantly with higher maximum temperatures, larger tube diameters, and more sophisticated controls like multi-zone heating.
Variations in Tubular Furnace Design
Different research needs have led to several common design variations.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Orientation
Horizontal furnaces are the most common configuration, offering easy loading and observation of samples. Vertical furnaces are better suited for processing powders, melting materials where gravity is a factor, or specific crystal growth techniques.
Split-Tube vs. Solid-Tube Designs
Split-tube furnaces are hinged and can be opened along their length. This allows for easy placement of the process tube or observation of the sample, especially if the tube has a complex setup with multiple inlets.
Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone Control
A single-zone furnace has one set of heating elements and one controller, creating a single hot zone. A multi-zone furnace (typically three zones) has independent controllers for the center and end zones, allowing a user to enlarge the uniform hot zone or even create a specific temperature gradient along the tube's length.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your specific processing goal.
- If your primary focus is uniform annealing or calibration: A single-zone horizontal furnace is often the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is material deposition (CVD) or growing crystals: A multi-zone furnace provides the superior control needed to create a large, stable hot zone.
- If your primary focus is working with powders or melts: A vertical furnace will prevent sample spillage and use gravity to your advantage.
- If your primary focus is rapid sample exchange or in-situ observation: A split-tube furnace offers the accessibility you need.
Ultimately, the function of a tubular furnace is to give you precise command over the thermal and atmospheric environment, empowering innovation at the material level.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Uniform Heating Zone | Consistent sample processing | Material Annealing, Calibration |
| Programmable Temperature Control | Precise ramps, soaks, and cooling | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
| Gas/Vacuum Ports | Controlled atmosphere processing | Material Synthesis under inert gas |
| Horizontal/Vertical Orientation | Flexibility for different sample types | Powder processing, Crystal Growth |
| Single or Multi-Zone Heating | Customizable temperature profiles | Creating large uniform hot zones |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a tubular furnace? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including tubular furnaces tailored for material synthesis, heat treatment, and advanced research. Our experts can help you select the perfect configuration—horizontal or vertical, single or multi-zone—to meet your specific processing needs. Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK tubular furnace can bring precision, control, and reliability to your laboratory workflows.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace with argon necessary for NaCrO2? Master Battery Material Synthesis
- What is the use of graphite tube? Essential for Extreme Heat & Corrosive Environments
- What is the main problem with vacuum tubes? Inefficiency, Heat, and Fragility Explained
- What is the maximum temperature for pyrolysis? Control Heat to Optimize Your End Product
- What is the purpose of refilling a quartz sealing tube with 300 mbar of argon? Optimize Pressure for Heat Treatment
- What is the function of the thermal treatment step in a tube furnace for LLZO pellets? Optimize Surface Conductivity
- How does a horizontal high-temperature tube furnace evaluate oxidation? Quantifying Coating Durability at 1100°C
- What is the specific function of a pre-firing furnace in the sol-gel synthesis of LZP? Expert Thermal Purification



















