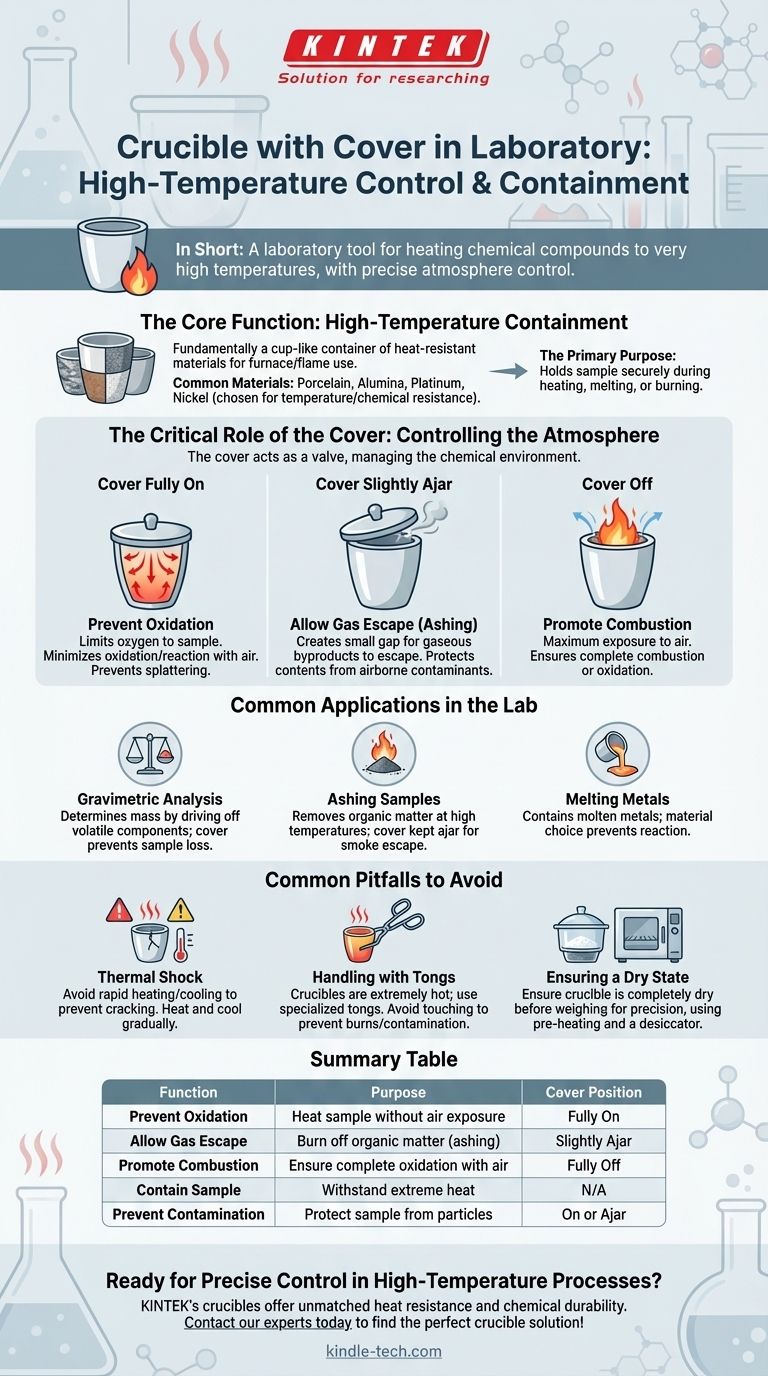
In short, a crucible with a cover is a laboratory tool used to heat chemical compounds to very high temperatures. The crucible itself acts as a container that can withstand extreme heat, while the cover provides precise control over the substance's exposure to the atmosphere during the heating process.
The true function of the crucible's cover is not just to "cover" the contents, but to act as a valve, allowing a scientist to precisely manage the chemical environment—either isolating the sample from the air, allowing gases to escape, or preventing contamination.

The Core Function: High-Temperature Containment
A crucible is fundamentally a cup-like container, but one made from highly heat-resistant materials. This allows it to be placed directly in a furnace or over a powerful Bunsen burner flame without melting or breaking.
Common Crucible Materials
The material is chosen based on the required temperature and the chemical nature of the substance being heated. Common choices include porcelain, alumina, and various metals like platinum or nickel, each offering different levels of heat and chemical resistance.
The Primary Purpose
The crucible's main job is to hold a sample securely while it is heated, melted, or burned. This is a foundational task in many analytical chemistry procedures.
The Critical Role of the Cover: Controlling the Atmosphere
The cover, or lid, is what transforms the crucible from a simple high-temperature dish into a tool for controlled chemical reactions. Its position dictates the entire process.
Scenario 1: Cover Fully On
Placing the cover securely on the crucible limits the amount of oxygen that can reach the sample. This is essential when you want to heat a substance without it oxidizing or reacting with the air. It also prevents any loss of the sample due to splattering.
Scenario 2: Cover Slightly Ajar
Setting the cover slightly off-center creates a small gap. This configuration is crucial for processes like ashing, where you are burning off organic matter. It allows the gaseous byproducts of the reaction to escape while still protecting the contents from airborne contaminants.
Scenario 3: Cover Off
Heating a crucible with the cover completely removed provides maximum exposure to the air. This is done when the goal is to achieve complete combustion or to fully oxidize a sample.
Common Applications in the Lab
The crucible and cover combination is a workhorse in quantitative analysis, where precise measurements are key.
Gravimetric Analysis
This is a technique used to determine the mass of a substance. A sample might be heated in a crucible to drive off water or other volatile components; the change in mass reveals the composition. The cover prevents loss of the sample during this process.
Ashing Samples
In food science or environmental analysis, a crucible is used to burn a sample at a high temperature to remove all organic matter. The remaining non-combustible material (ash) can then be weighed or analyzed. The cover is typically kept ajar to let smoke escape.
Melting Metals
In metallurgy or materials science, crucibles are used to contain metals while they are melted in a furnace. The choice of crucible material is critical to avoid reacting with the molten metal.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While robust, crucibles require proper handling to ensure accurate results and laboratory safety.
Thermal Shock
Heating or cooling a crucible (especially porcelain) too quickly can cause it to crack, a phenomenon known as thermal shock. Always heat and cool them gradually.
Handling with Tongs
Crucibles become extremely hot and must only be handled with specialized crucible tongs. Touching them can cause severe burns and contaminate the sample with oils from your skin, skewing mass measurements.
Ensuring a Dry State
Before weighing a crucible for precise analysis, it must be completely dry. This is often achieved by pre-heating it in an oven or furnace and then cooling it in a desiccator—a sealed container that absorbs moisture.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The way you use the crucible's cover should be directly determined by the objective of your experiment.
- If your primary focus is to heat a sample without oxidation: Keep the cover fully on to minimize exposure to air.
- If your primary focus is to drive off moisture or burn a sample: Place the cover slightly ajar to allow gases to escape while preventing contamination.
- If your primary focus is to ensure complete combustion with air: Remove the cover entirely.
Ultimately, mastering the use of a crucible and cover is about understanding that you are controlling a miniature, high-temperature environment.
Summary Table:
| Function | Purpose | Cover Position |
|---|---|---|
| Prevent Oxidation | Heat sample without air exposure | Fully On |
| Allow Gas Escape | Burn off organic matter (ashing) | Slightly Ajar |
| Promote Combustion | Ensure complete oxidation with air | Fully Off |
| Contain Sample | Withstand extreme heat without melting | N/A |
| Prevent Contamination | Protect sample from airborne particles | On or Ajar |
Ready to achieve precise control in your high-temperature processes? KINTEK's crucibles are crafted from premium materials like porcelain, alumina, and platinum to deliver unmatched heat resistance and chemical durability for your lab's most demanding applications. Whether you're performing gravimetric analysis, ashing, or metal melting, our equipment ensures accuracy and repeatability. Contact our experts today to find the perfect crucible solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data
- How does the use of corrosion-resistant ceramic crucibles ensure the chemical purity of materials? | KINTEK
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible preferred for high-temperature oxidation? Ensure Unmatched Data Integrity



















