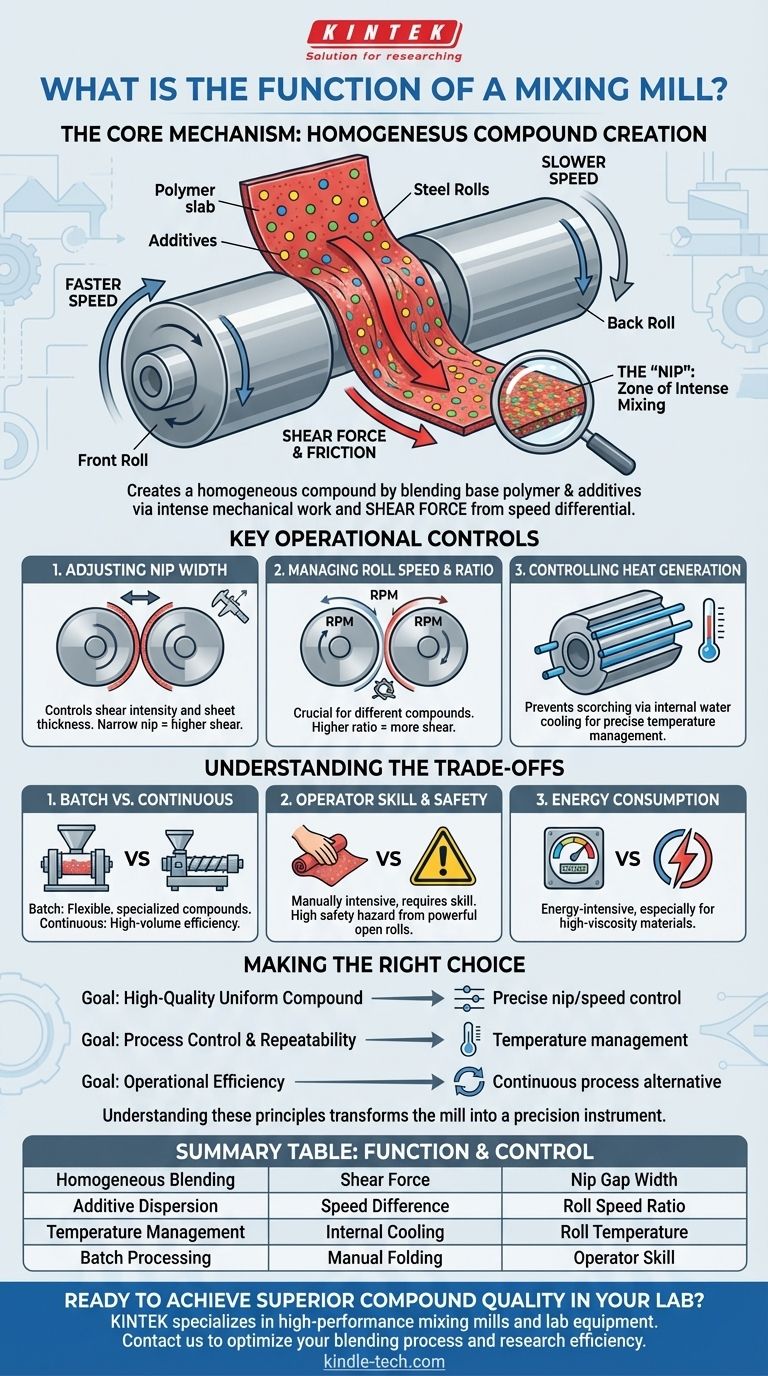
At its core, a mixing mill's primary function is to create a homogeneous compound by blending a base polymer, like rubber, with various additives. It accomplishes this by subjecting the material to intense mechanical work between two large, counter-rotating rolls, ensuring all ingredients are thoroughly and uniformly dispersed.
The crucial element of a mixing mill is not just the rolling action, but the shear force generated by a specific speed difference between the two rolls. This force is what tears, stretches, and folds the material, breaking down agglomerates and producing a consistent, high-quality mixture.

The Core Mechanism: How Rotation Creates a Compound
A mixing mill's design is simple in appearance but highly effective in its application. The process relies on a few key mechanical principles working in concert.
The Two-Roll Configuration
A mixing mill consists of two heavy, parallel steel rolls positioned horizontally. These rolls rotate towards each other, pulling material down into the gap between them.
The Critical Role of Shear Force
The key to the mixing action is that the two rolls rotate at slightly different speeds. This speed differential creates powerful friction and shear forces on the material caught between them. One surface of the material is pulled faster than the other, causing it to be stretched, torn, and folded continuously.
The "Nip": The Zone of Intense Mixing
The narrowest gap between the two rolls is called the nip. This is where the shearing action is most intense. As the material is forced through the nip, it is flattened into a sheet while being subjected to the powerful forces that ensure complete dispersion of all additives.
Key Operational Controls
An operator can precisely manipulate the mixing process by adjusting several key parameters to suit the specific requirements of the compound.
Adjusting the Nip Width
The distance between the two rolls—the nip gap—can be precisely adjusted. A smaller nip creates higher shear and results in a thinner sheet, while a wider nip reduces the intensity of the mixing action.
Managing Roll Speed and Ratio
The speed of the rolls and the friction ratio (the difference in speed between the front and rear roll) are critical variables. Different compounds require different levels of shear, which can be dialed in by changing this ratio.
Controlling Heat Generation
The intense friction and mechanical work generate a significant amount of heat. To prevent the rubber from scorching or degrading, the rolls are typically hollow and internally cooled with circulating water, allowing for precise temperature management.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the mixing mill is not the ideal solution for every scenario. Understanding its limitations is key to using it properly.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Mixing mills are fundamentally batch processing machines. An operator works with a finite amount of material at a time. This is excellent for flexibility and creating specialized compounds but can be less efficient for high-volume production compared to continuous mixers.
Operator Skill and Safety
The process is often manually intensive. An operator must repeatedly cut the sheet of rubber from one roll and feed it back into the nip to ensure a homogeneous mix. This requires significant skill and presents a major safety hazard due to the powerful open rolls.
Energy Consumption
The force required to shear and mix high-viscosity materials like rubber means that mixing mills are energy-intensive pieces of equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal determines how you should view the function of a mixing mill.
- If your primary focus is creating a high-quality, uniform compound: The key is to precisely control the nip gap and roll speed ratio to generate the exact amount of shear required for your specific formula.
- If your primary focus is process control and repeatability: Managing the roll temperature via the cooling system is just as important as managing shear, as temperature drastically affects material viscosity and curing characteristics.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Recognize that the mixing mill provides unparalleled quality for batch work, but for massive-scale production, a continuous mixing process might be a more suitable alternative.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles transforms the mixing mill from a simple set of rollers into a precision instrument for material engineering.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Mechanism | Key Control Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Homogeneous Blending | Shear force from counter-rotating rolls | Nip gap width |
| Additive Dispersion | Speed difference (friction ratio) | Roll speed ratio |
| Temperature Management | Internal water cooling | Roll temperature |
| Batch Processing | Manual cutting and folding | Operator skill |
Ready to achieve superior compound quality and process control in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance mixing mills and lab equipment designed for the precise needs of polymer and rubber development. Our experts can help you select the right mill to optimize your blending process, ensure repeatable results, and enhance your research and production efficiency. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory crushing and sieving system play in the shaping stage of CoCeBa catalysts? Precision Sizing
- What is the role of a laboratory crushing and sieving system? Optimize Copper-Based NH3-SCR Catalyst Preparation
- Why is grinding and sieving equipment used for waste tire hydrothermal liquefaction? Maximize Your Reaction Efficiency
- Why use grinding for SPS samples before XRD? Master Sample Prep for Pure Phase Analysis
- What technical issues are addressed by ball milling in sulfur/LPS cathode preparation? Optimize Battery Performance



















