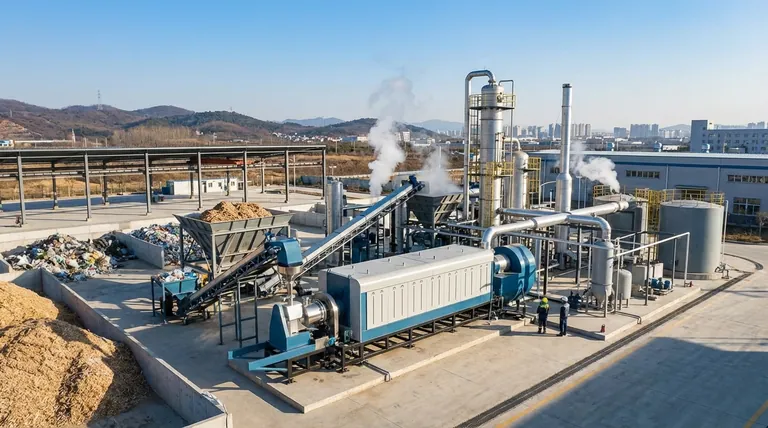
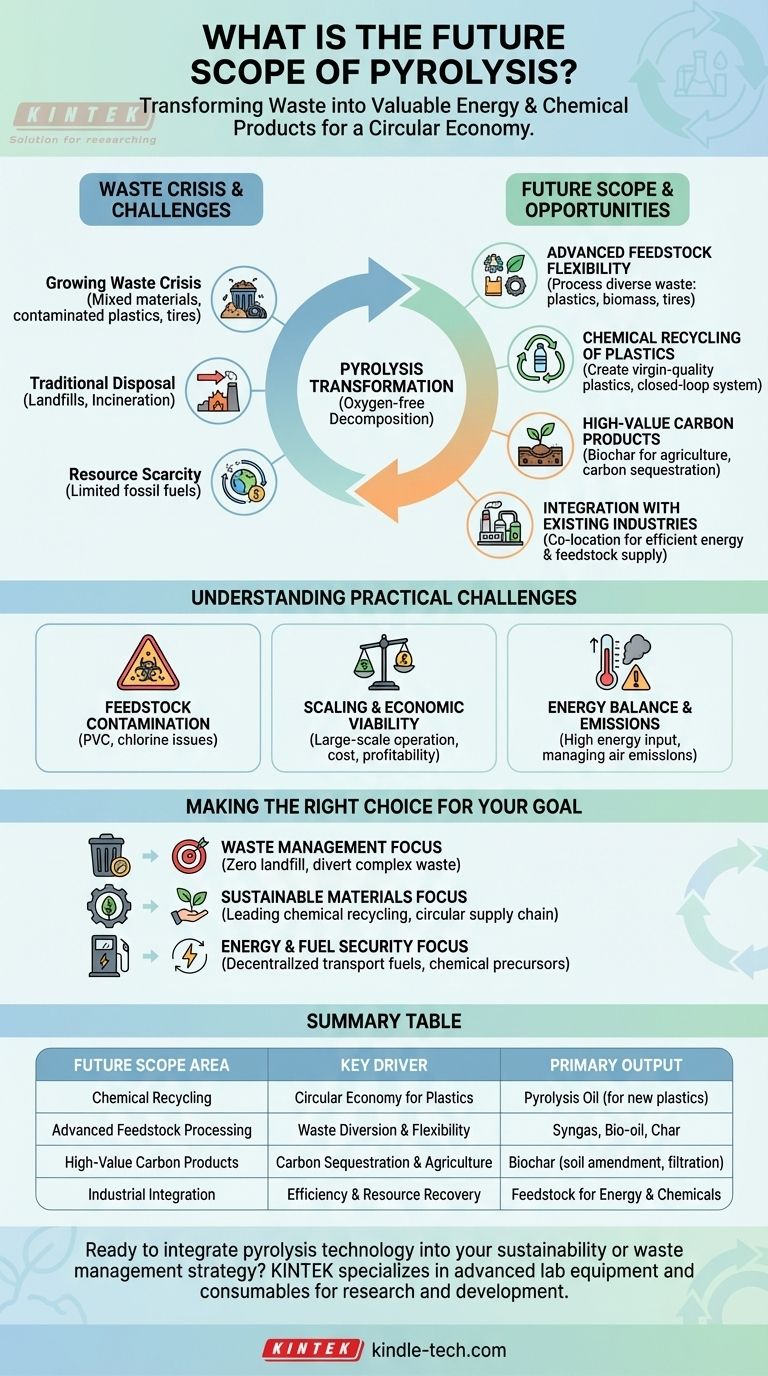
The future scope of pyrolysis is exceptionally broad, centered on its unique ability to transform diverse waste streams into valuable energy and chemical products. It is rapidly evolving from a simple waste-to-energy technology into a cornerstone of the circular economy, primarily due to its remarkable feedstock flexibility which allows it to process materials that are otherwise difficult or impossible to recycle.
Pyrolysis is transitioning from a niche disposal method into a core industrial technology for resource recovery. Its future lies not just in managing waste, but in its capacity to create high-value circular feedstocks for the chemical and energy industries.

Why Pyrolysis is a Critical Future Technology
The momentum behind pyrolysis is driven by converging global pressures related to waste, resource scarcity, and sustainability goals. It offers a direct technological solution to several major industrial and environmental challenges.
The Growing Waste Crisis
Traditional recycling methods struggle with mixed materials, contaminated plastics, and end-of-life products like tires. Pyrolysis offers a robust solution by chemically decomposing these materials in the absence of oxygen, preventing them from ending up in landfills or incinerators.
The Shift to a Circular Economy
A circular economy requires that we stop treating waste as refuse and start seeing it as a resource. Pyrolysis is a key enabler of this vision, effectively "upcycling" low-value waste into high-value raw materials like oils, gases, and char.
Demand for Sustainable Feedstocks
Industries are actively seeking non-fossil fuel sources for energy and chemical production. Pyrolysis oil, derived from waste plastics or biomass, can serve as a sustainable feedstock for producing new plastics, chemicals, and transportation fuels.
Key Growth Areas for Pyrolysis
The future development of pyrolysis is not uniform. Several key application areas are poised for significant expansion, driven by both technological innovation and market demand.
Advanced Feedstock Flexibility
The ability of a pyrolysis unit to process a wide variety_of materials—from mixed plastics and tires to agricultural biomass—is its greatest strength. As mentioned in the reference, this feedstock flexibility de-risks the supply chain and allows operators to adapt to available local waste streams, making it a highly versatile solution.
Chemical Recycling of Plastics
This is arguably the most significant future application. Pyrolysis can break down polymers into their basic hydrocarbon building blocks. This resulting pyrolysis oil can be refined and used to create new, virgin-quality plastics, creating a true closed-loop system for plastic waste.
High-Value Carbon Product Generation
When processing biomass, pyrolysis produces a stable, carbon-rich solid known as biochar. The future scope for biochar is enormous, with applications in soil amendment for agriculture, water filtration, and long-term carbon sequestration to combat climate change.
Integration with Existing Industries
Future pyrolysis plants will likely be co-located with existing infrastructure. A pyrolysis unit could feed its synthetic gas directly into a factory's power plant and its pyrolysis oil into a nearby petrochemical refinery, creating highly efficient industrial ecosystems.
Understanding the Practical Challenges
To fully appreciate the future scope of pyrolysis, we must also be objective about the hurdles that need to be overcome for widespread, commercial adoption.
Feedstock Contamination and Consistency
While flexible, pyrolysis processes are sensitive to contaminants. Materials like PVC in a plastic stream can release chlorine, creating corrosive acids that damage equipment and require costly purification steps for the final products.
Scaling and Economic Viability
Moving from pilot projects to large-scale, continuously operating industrial plants is a significant engineering and financial challenge. Achieving profitability depends on a stable supply of low-cost feedstock, efficient operation, and high-value offtake agreements for the products.
Energy Balance and Emissions
The pyrolysis process itself requires a significant energy input to reach high temperatures. A successful plant must be designed to use its own product gas to power the process, creating a positive net energy balance. Additionally, managing air emissions remains a critical regulatory and environmental consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The strategic application of pyrolysis depends entirely on the primary objective you aim to solve.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Pyrolysis is a powerful tool for achieving "zero landfill" goals by diverting complex, non-recyclable waste streams and converting them into useful products.
- If your primary focus is sustainable materials: View pyrolysis as the leading technology for chemical recycling, capable of creating a circular supply chain for plastics that reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
- If your primary focus is energy and fuel security: Consider pyrolysis a decentralized method for producing transport-grade fuels and valuable chemical precursors from locally sourced biomass and waste.
Ultimately, the future of pyrolysis is its transformation from a brute-force waste disposal method into a sophisticated resource recovery technology central to a sustainable industrial economy.
Summary Table:
| Future Scope Area | Key Driver | Primary Output |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Recycling | Circular Economy for Plastics | Pyrolysis Oil (for new plastics) |
| Advanced Feedstock Processing | Waste Diversion & Flexibility | Syngas, Bio-oil, Char |
| High-Value Carbon Products | Carbon Sequestration & Agriculture | Biochar (soil amendment, filtration) |
| Industrial Integration | Efficiency & Resource Recovery | Feedstock for Energy & Chemicals |
Ready to integrate pyrolysis technology into your sustainability or waste management strategy? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're exploring feedstock flexibility, optimizing biochar production, or scaling chemical recycling processes, our solutions provide the precision and reliability you need. Contact our experts today to discover how KINTEK can support your journey toward a circular economy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output

















